Charting The Waters: A Comprehensive Look At The Lake Michigan Shoreline
Charting the Waters: A Comprehensive Look at the Lake Michigan Shoreline
Related Articles: Charting the Waters: A Comprehensive Look at the Lake Michigan Shoreline
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Charting the Waters: A Comprehensive Look at the Lake Michigan Shoreline. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Waters: A Comprehensive Look at the Lake Michigan Shoreline
Lake Michigan, the second-largest of the Great Lakes, holds a unique place in the North American landscape. Its vast expanse, encompassing over 22,300 square miles, is defined by a shoreline that stretches over 1,600 miles, a dynamic frontier shaped by both natural forces and human activity. Understanding this shoreline, its intricate details, and its changing nature is crucial for navigating the lake’s resources, appreciating its ecological significance, and informing responsible development.
A Shoreline of Diverse Landscapes:
The Lake Michigan shoreline is a tapestry of diverse landscapes, each with its own character and history. From the towering bluffs of Door County, Wisconsin, to the sandy beaches of Indiana, the coastline reveals a spectrum of geological formations and ecological niches.
The Influence of Geology:
The shoreline’s form is a testament to the geological forces that have shaped the region for millennia. Glacial activity, the primary sculptor of the Great Lakes basin, left behind a legacy of sculpted landscapes. The Wisconsin glaciation, the most recent major glacial event, carved out the lake’s basin, deposited vast quantities of sediment, and shaped the dramatic features of the shoreline.
- Bluffs and Escarpments: The iconic bluffs of Door County, Wisconsin, and the Niagara Escarpment in Michigan are prime examples of glacial erosion. These towering cliffs, formed by the retreat of glaciers, offer breathtaking views of the lake and provide valuable habitat for a variety of flora and fauna.
- Sand Dunes: The vast sand dunes of Indiana and Michigan, sculpted by wind and wave action, are another testament to the dynamic nature of the shoreline. These shifting landscapes, constantly evolving under the influence of natural forces, provide a unique ecosystem for specialized plants and animals.
- River Deltas: The mouths of rivers flowing into Lake Michigan, like the St. Joseph River in Michigan and the Fox River in Wisconsin, create fertile deltas where sediment accumulates and forms wetlands. These areas are vital for migratory birds, fish spawning, and water quality regulation.
The Human Footprint:
Human activity has left its indelible mark on the Lake Michigan shoreline. From historic settlements to modern infrastructure, human interventions have shaped the landscape and impacted the environment.
- Urbanization and Development: Coastal cities like Milwaukee, Chicago, and Grand Rapids have grown along the shoreline, transforming the natural landscape and creating a complex urban environment. This development has brought economic prosperity but also raised concerns about pollution, habitat loss, and the impact on water quality.
- Ports and Shipping: The Great Lakes have served as vital transportation routes since the early days of European settlement. Major ports like Chicago, Milwaukee, and Green Bay handle vast amounts of cargo, contributing significantly to the region’s economy but also raising concerns about environmental impacts.
- Tourism and Recreation: The Lake Michigan shoreline is a popular destination for tourism and recreation, attracting millions of visitors each year. This economic engine provides jobs and revenue but also necessitates careful management to balance tourism with environmental protection.
Mapping the Shoreline: A Tool for Understanding and Management:
Maps of the Lake Michigan shoreline are essential tools for understanding and managing this dynamic environment. They provide a visual representation of the coastline’s physical characteristics, facilitating the study of its evolution, the identification of critical habitats, and the assessment of human impacts.
- Topographic Maps: These maps depict the elevation and terrain of the shoreline, revealing the location of bluffs, dunes, and other landforms. This information is crucial for planning development, managing coastal erosion, and identifying areas of ecological importance.
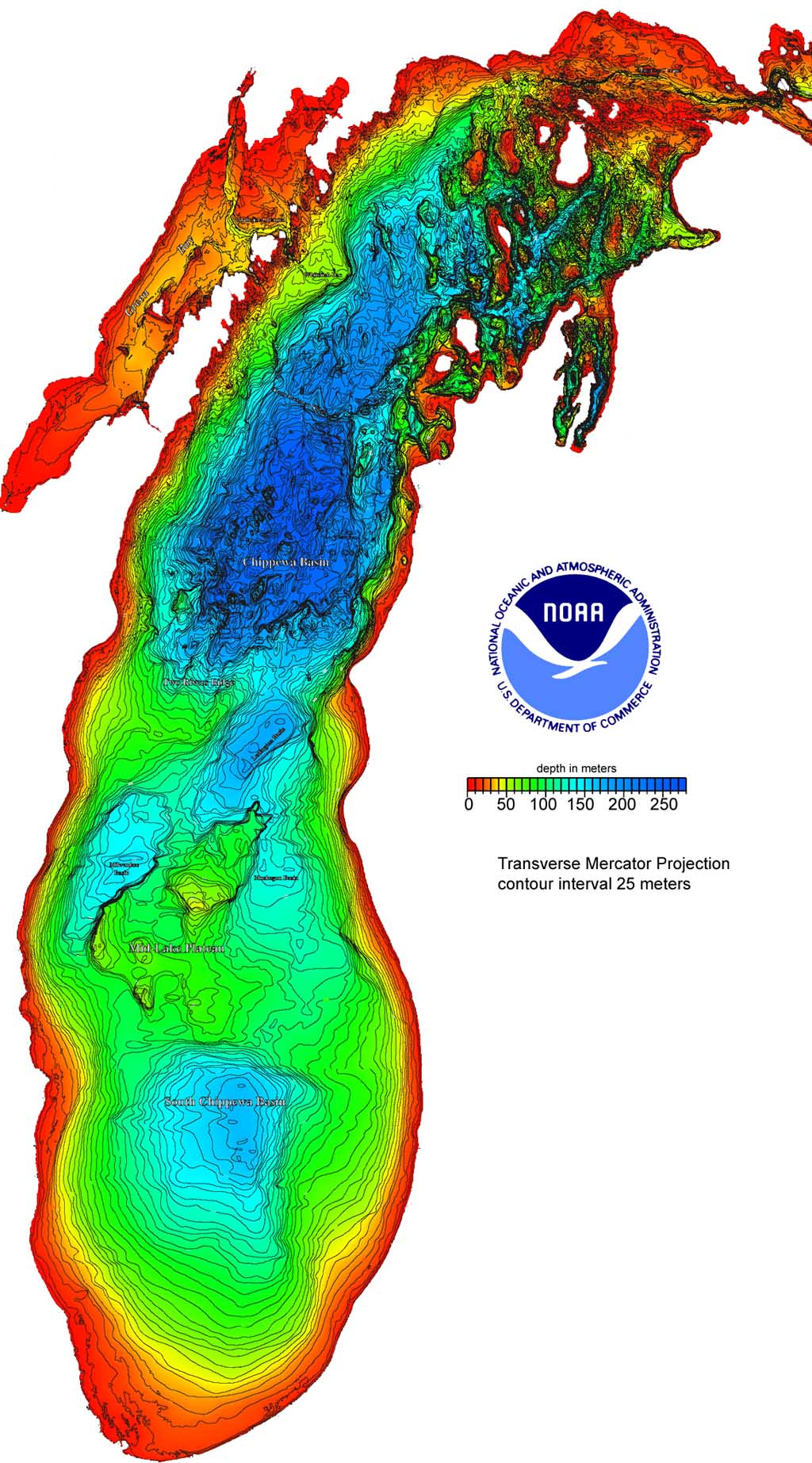
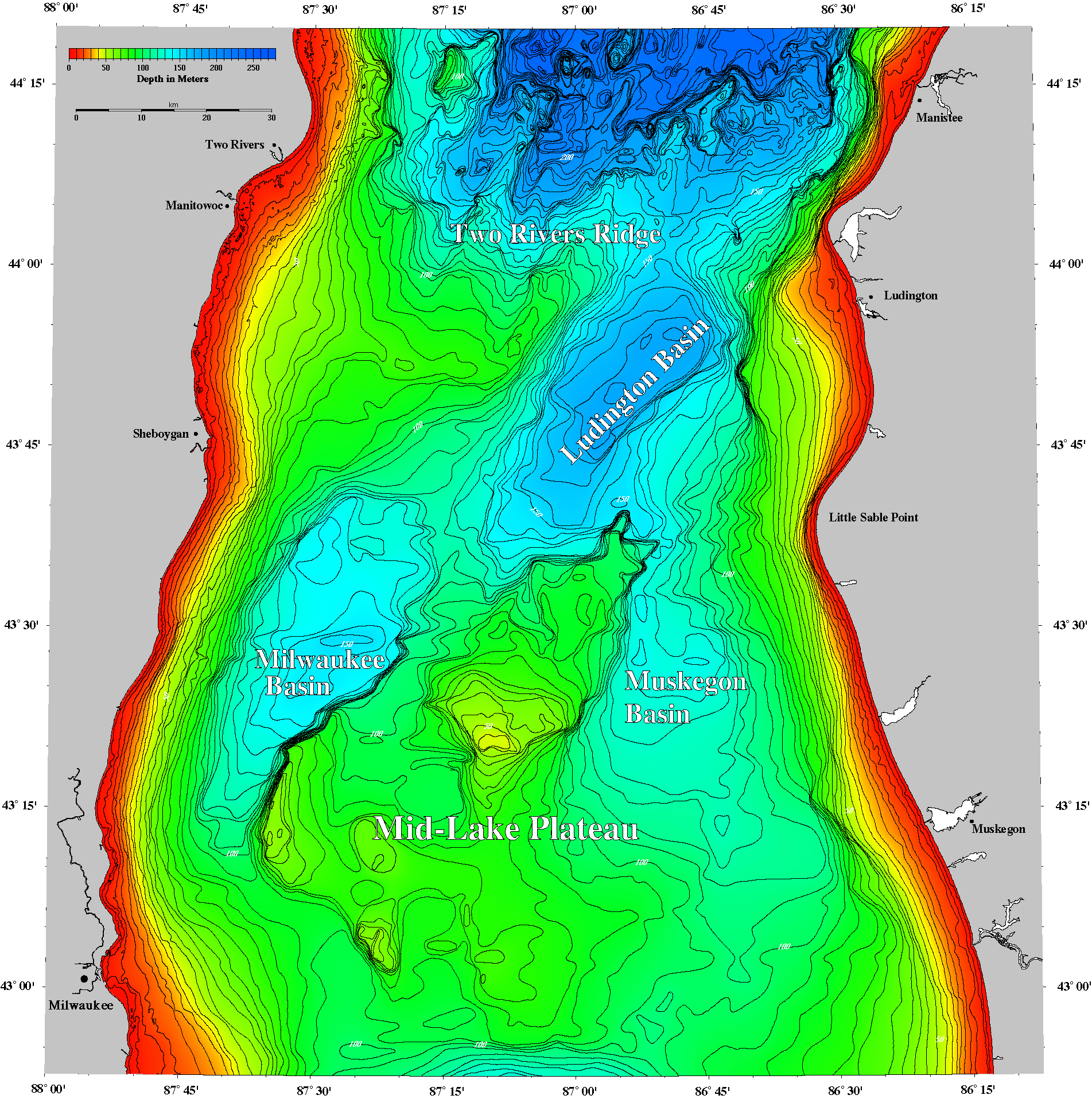
- Bathymetric Maps: These maps illustrate the underwater topography of the lake, showing the depth and shape of the lakebed. This information is crucial for navigation, fisheries management, and understanding the distribution of aquatic life.
- Ecological Maps: These maps highlight the distribution of different plant and animal communities along the shoreline, identifying areas of high biodiversity and critical habitats. This information is crucial for conservation efforts and sustainable resource management.
- Historical Maps: These maps provide a glimpse into the evolution of the shoreline over time, showing how human activity and natural forces have shaped the landscape. This historical perspective is valuable for understanding the present state of the shoreline and predicting future changes.
Navigating the Challenges:
The Lake Michigan shoreline faces a multitude of challenges, from climate change and invasive species to pollution and habitat loss. Effective management requires a comprehensive understanding of the shoreline’s dynamics and a commitment to sustainable practices.
- Climate Change: Rising lake levels, increased storm frequency, and changing weather patterns are all impacting the Lake Michigan shoreline. These changes can exacerbate erosion, threaten coastal infrastructure, and alter the distribution of aquatic life.
- Invasive Species: The introduction of non-native species, such as zebra mussels and quagga mussels, has significantly impacted the lake’s ecosystem. These invasive species can disrupt food webs, alter water quality, and threaten native populations.
- Pollution: Runoff from agricultural fields, industrial facilities, and urban areas can contribute to water pollution in Lake Michigan. These pollutants can harm aquatic life, affect human health, and degrade the quality of recreational waters.
- Habitat Loss: Development, agriculture, and other human activities can lead to habitat loss along the shoreline. This loss of critical habitat can threaten the survival of numerous plant and animal species.
The Importance of Conservation:
Protecting the Lake Michigan shoreline is essential for maintaining its ecological integrity, supporting its economic value, and ensuring its future sustainability. Conservation efforts require a multi-faceted approach, involving government agencies, businesses, communities, and individuals.
- Habitat Restoration: Restoring degraded habitats, such as wetlands and coastal forests, can help mitigate habitat loss and enhance biodiversity.
- Pollution Control: Implementing stricter regulations on industrial discharges and agricultural runoff can help reduce water pollution and protect aquatic life.
- Sustainable Development: Planning for development that minimizes environmental impacts, such as using green infrastructure and promoting sustainable tourism, is crucial for balancing economic growth with environmental protection.
- Public Awareness: Educating the public about the importance of the Lake Michigan shoreline and promoting responsible stewardship can foster a sense of ownership and encourage responsible actions.
FAQs about the Lake Michigan Shoreline:
1. What are the major cities located along the Lake Michigan shoreline?
The major cities located along the Lake Michigan shoreline include:
- Michigan: Grand Rapids, Muskegon, Holland, Traverse City, Sault Ste. Marie, Mackinaw City, Petoskey, and St. Joseph.
- Wisconsin: Milwaukee, Green Bay, Sheboygan, Manitowoc, Door County, and Kenosha.
- Illinois: Chicago.
- Indiana: Gary, Michigan City, and South Bend.
2. What are the most common types of beaches along the Lake Michigan shoreline?
The most common types of beaches along the Lake Michigan shoreline are:
- Sandy Beaches: These beaches are typically found in areas where the lake bottom is composed of sand. They are popular for swimming, sunbathing, and other recreational activities.
- Pebble Beaches: These beaches are found in areas where the lake bottom is composed of pebbles or cobbles. They can be more challenging to walk on but offer unique views and a different beach experience.
- Bluff Beaches: These beaches are located at the base of bluffs and often feature rocky outcroppings and dramatic views. They can be more challenging to access but offer a sense of adventure and a unique perspective on the shoreline.
3. What are the major threats to the Lake Michigan shoreline?
The major threats to the Lake Michigan shoreline include:
- Climate Change: Rising lake levels, increased storm frequency, and changing weather patterns can exacerbate erosion, threaten coastal infrastructure, and alter the distribution of aquatic life.
- Invasive Species: The introduction of non-native species, such as zebra mussels and quagga mussels, can disrupt food webs, alter water quality, and threaten native populations.
- Pollution: Runoff from agricultural fields, industrial facilities, and urban areas can contribute to water pollution in Lake Michigan. These pollutants can harm aquatic life, affect human health, and degrade the quality of recreational waters.
- Habitat Loss: Development, agriculture, and other human activities can lead to habitat loss along the shoreline. This loss of critical habitat can threaten the survival of numerous plant and animal species.
4. What are some ways to protect the Lake Michigan shoreline?
Protecting the Lake Michigan shoreline requires a multi-faceted approach, involving government agencies, businesses, communities, and individuals. Some key strategies include:
- Habitat Restoration: Restoring degraded habitats, such as wetlands and coastal forests, can help mitigate habitat loss and enhance biodiversity.
- Pollution Control: Implementing stricter regulations on industrial discharges and agricultural runoff can help reduce water pollution and protect aquatic life.
- Sustainable Development: Planning for development that minimizes environmental impacts, such as using green infrastructure and promoting sustainable tourism, is crucial for balancing economic growth with environmental protection.
- Public Awareness: Educating the public about the importance of the Lake Michigan shoreline and promoting responsible stewardship can foster a sense of ownership and encourage responsible actions.
Tips for Enjoying the Lake Michigan Shoreline:
- Respect the Environment: Always dispose of trash properly, avoid disturbing wildlife, and minimize your impact on the natural landscape.
- Be Aware of Safety Hazards: Pay attention to weather conditions, be aware of currents and waves, and always swim with a buddy.
- Learn About the Local Ecosystem: Take the time to learn about the plants and animals that inhabit the shoreline, and appreciate the unique biodiversity of this region.
- Support Conservation Efforts: Consider volunteering for a local conservation organization or donating to support shoreline protection efforts.
Conclusion:
The Lake Michigan shoreline is a dynamic and valuable resource, shaped by both natural forces and human activity. Understanding its intricate details, appreciating its ecological significance, and navigating its challenges is essential for ensuring its future sustainability. By promoting responsible stewardship, embracing sustainable practices, and fostering a deep connection with this remarkable landscape, we can ensure that the Lake Michigan shoreline continues to thrive for generations to come.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Waters: A Comprehensive Look at the Lake Michigan Shoreline. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!