Navigating The Digital Landscape: Understanding And Utilizing Low-Latency Networks
Navigating the Digital Landscape: Understanding and Utilizing Low-Latency Networks
Related Articles: Navigating the Digital Landscape: Understanding and Utilizing Low-Latency Networks
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Digital Landscape: Understanding and Utilizing Low-Latency Networks. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Digital Landscape: Understanding and Utilizing Low-Latency Networks

In the realm of online gaming, digital communication, and real-time applications, network latency plays a crucial role. Latency, measured in milliseconds (ms), represents the time delay between sending a signal and receiving a response. This delay can significantly impact user experience, leading to lag, stuttering, and a compromised sense of immersion.
A "0 ping map" is a concept that alludes to a network environment with minimal latency, ideally approaching zero milliseconds. While achieving absolute zero ping is practically impossible due to the inherent limitations of physical infrastructure and data transmission, the pursuit of low-latency networks remains a paramount objective for gamers, developers, and businesses alike.
The Significance of Low Latency
Low latency is paramount for a seamless online experience across various domains. Here’s how it impacts different applications:
1. Online Gaming:
-
Competitive Advantage: In fast-paced games like first-person shooters and real-time strategy, even a few milliseconds of latency can mean the difference between victory and defeat. Players with low latency can react faster to in-game events, making precise shots, anticipating enemy movements, and gaining a competitive edge.
-
Immersive Gameplay: Low latency ensures smooth gameplay, reducing lag and stuttering. This allows players to experience the game world seamlessly, without interruptions that detract from the immersive experience.
-
Enhanced Communication: In team-based games, communication is vital. Low latency enables clearer voice chat and real-time text communication, facilitating coordinated strategies and effective teamwork.
2. Digital Communication:
-
Real-Time Collaboration: Video conferencing, online meetings, and collaborative work applications rely on low latency for smooth communication. It ensures seamless audio and video streaming, preventing delays and interruptions that hinder effective collaboration.
-
Live Streaming: Low latency is essential for live streaming platforms, enabling viewers to experience real-time events without noticeable delays. This is crucial for broadcasting sporting events, concerts, and other live content.
3. Financial Trading:
-
Speed is Key: In high-frequency trading, even fractions of a second can make a significant difference. Low latency networks enable traders to execute trades quickly, maximizing profits and minimizing losses.
-
Data Integrity: Low latency ensures that financial data is transmitted accurately and promptly, minimizing the risk of errors and delays that can impact trading decisions.
4. Remote Control and Automation:
-
Real-Time Control: Low latency is crucial for remote control applications, such as operating robots, drones, and other devices remotely. It ensures that commands are executed promptly, enabling precise control and real-time responses.
-
Industrial Automation: In industrial settings, low latency is essential for automated systems, ensuring that machines and processes respond promptly to changes in real-time data.
Factors Influencing Network Latency
Network latency is influenced by various factors, including:
- Physical Distance: The further the data has to travel, the longer the latency.
- Network Congestion: High network traffic can lead to delays as data packets compete for bandwidth.
- Server Location: The location of the server hosting the application or service also influences latency.
- Internet Service Provider (ISP): The quality of the internet connection provided by the ISP plays a significant role in latency.
- Network Infrastructure: The type and condition of network infrastructure, such as routers, switches, and cables, can affect latency.
- Device Hardware: The processing power and network capabilities of the device used to access the network can influence latency.
Strategies for Reducing Network Latency
While achieving zero ping is practically unattainable, several strategies can be employed to minimize latency and improve network performance:
- Choosing a Reliable ISP: Selecting an ISP with a robust network infrastructure and low latency is crucial.
- Optimizing Network Settings: Configuring network settings, such as MTU size and DNS servers, can improve latency.
- Using a Wired Connection: Wired connections generally offer lower latency compared to wireless connections.
- Minimizing Network Traffic: Reducing background applications and limiting unnecessary network activity can improve latency.
- Utilizing a VPN: A VPN can sometimes improve latency by routing traffic through a more efficient path.
- Employing a Gaming Router: Specialized gaming routers offer features designed to prioritize gaming traffic and reduce latency.
- Upgrading Hardware: Investing in faster hardware, such as a more powerful computer or a dedicated network card, can improve network performance and reduce latency.
- Choosing Server Locations: Selecting servers located geographically closer to the user can minimize latency.
FAQs about Low-Latency Networks
Q: What is the difference between ping and latency?
A: Ping and latency are often used interchangeably, but they represent slightly different concepts. Ping is a specific measurement tool used to test the round-trip time between a device and a server. Latency, on the other hand, refers to the overall delay experienced in a network connection. While ping provides a snapshot of latency at a particular moment, latency encompasses the overall delay throughout the connection.
Q: How can I measure my network latency?
A: Several online tools and software applications can measure network latency. Popular options include:
- Command Prompt (Windows): Using the "ping" command in the command prompt.
- Online Ping Testers: Websites like speedtest.net and fast.com provide latency measurements.
- Gaming Client Software: Many gaming platforms, such as Steam and Epic Games, offer built-in ping testing tools.
Q: Is low latency always better?
A: While low latency is generally desirable for most applications, there are situations where it might not be the primary concern. For example, in applications that prioritize data throughput, such as downloading large files, high bandwidth might be more important than low latency.
Q: Can I achieve zero ping?
A: Achieving absolute zero ping is practically impossible due to the inherent limitations of physical infrastructure and data transmission. However, striving for low latency, approaching zero milliseconds, remains a crucial objective for optimal network performance.
Tips for Optimizing Network Latency
- Prioritize Network Usage: Limit background applications and unnecessary network activity to minimize network congestion.
- Use a Wired Connection: Whenever possible, connect to the internet using a wired connection for lower latency.
- Update Drivers: Ensure that all network drivers are up-to-date for optimal performance.
- Check for Network Interference: Identify and resolve any potential sources of network interference, such as wireless devices or other electronic equipment.
- Monitor Network Performance: Regularly check network performance metrics, such as latency and bandwidth, to identify any issues.
Conclusion
In the digital age, low latency is no longer a luxury but a necessity for a seamless online experience. From competitive gaming to real-time communication and financial trading, the pursuit of low-latency networks is paramount. By understanding the factors that influence latency and employing strategies to minimize delays, individuals and businesses can unlock the full potential of the digital landscape, enjoying a responsive, immersive, and efficient online experience.
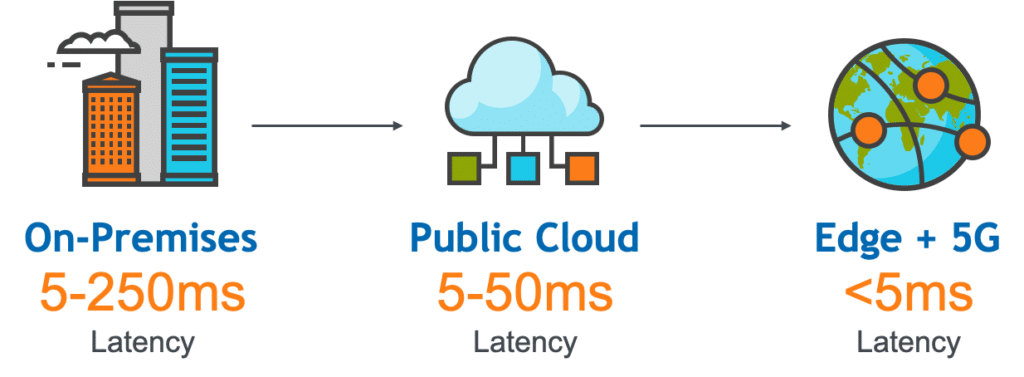

)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Digital Landscape: Understanding and Utilizing Low-Latency Networks. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!