Navigating The Path To Success: A Comprehensive Guide To Roadmaps
Navigating the Path to Success: A Comprehensive Guide to Roadmaps
Related Articles: Navigating the Path to Success: A Comprehensive Guide to Roadmaps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Path to Success: A Comprehensive Guide to Roadmaps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Path to Success: A Comprehensive Guide to Roadmaps

In the dynamic landscape of business and project management, a clear roadmap is essential for navigating the path to success. This strategic document serves as a visual representation of a project’s journey, outlining key milestones, timelines, and resources required to achieve desired outcomes.
Understanding the Essence of a Roadmap
A roadmap is not merely a checklist of tasks; it’s a living document that provides a holistic view of the project’s progress. It acts as a communication tool, fostering alignment among stakeholders and ensuring everyone is on the same page. By visualizing the project’s trajectory, roadmaps enable effective decision-making, resource allocation, and risk mitigation.
Key Components of a Roadmap
A well-structured roadmap typically encompasses the following elements:
- Project Objectives: Clearly defined goals and desired outcomes that the project aims to achieve.
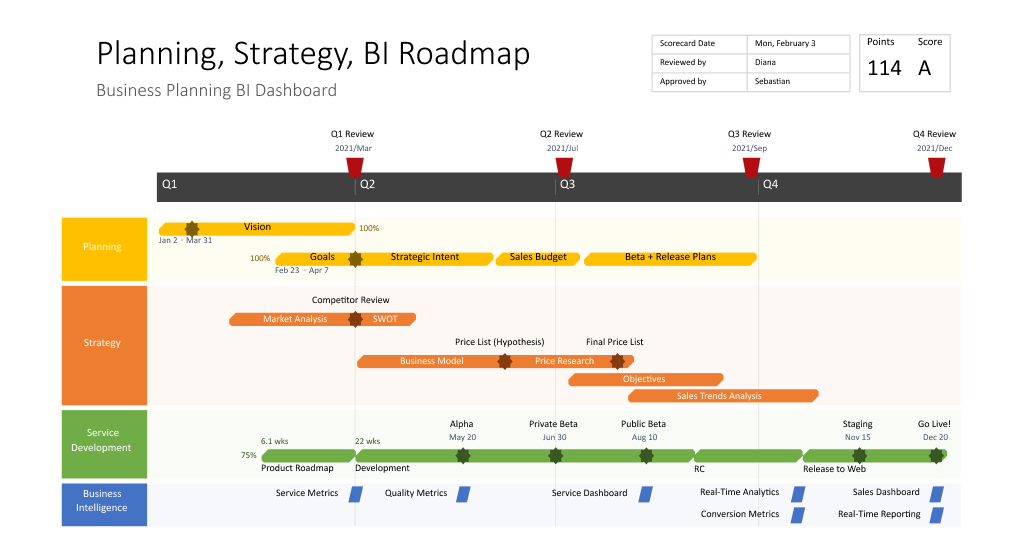
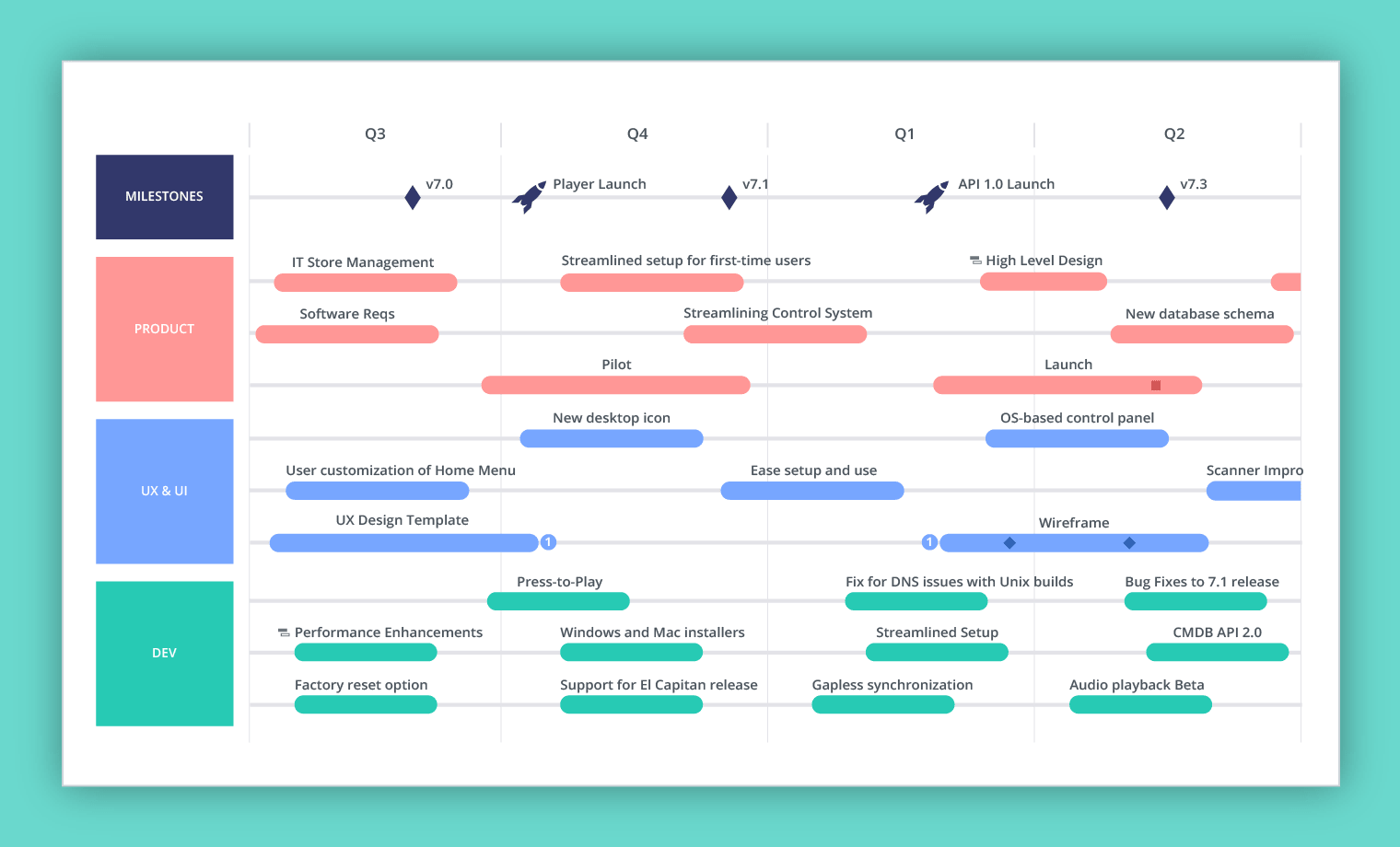
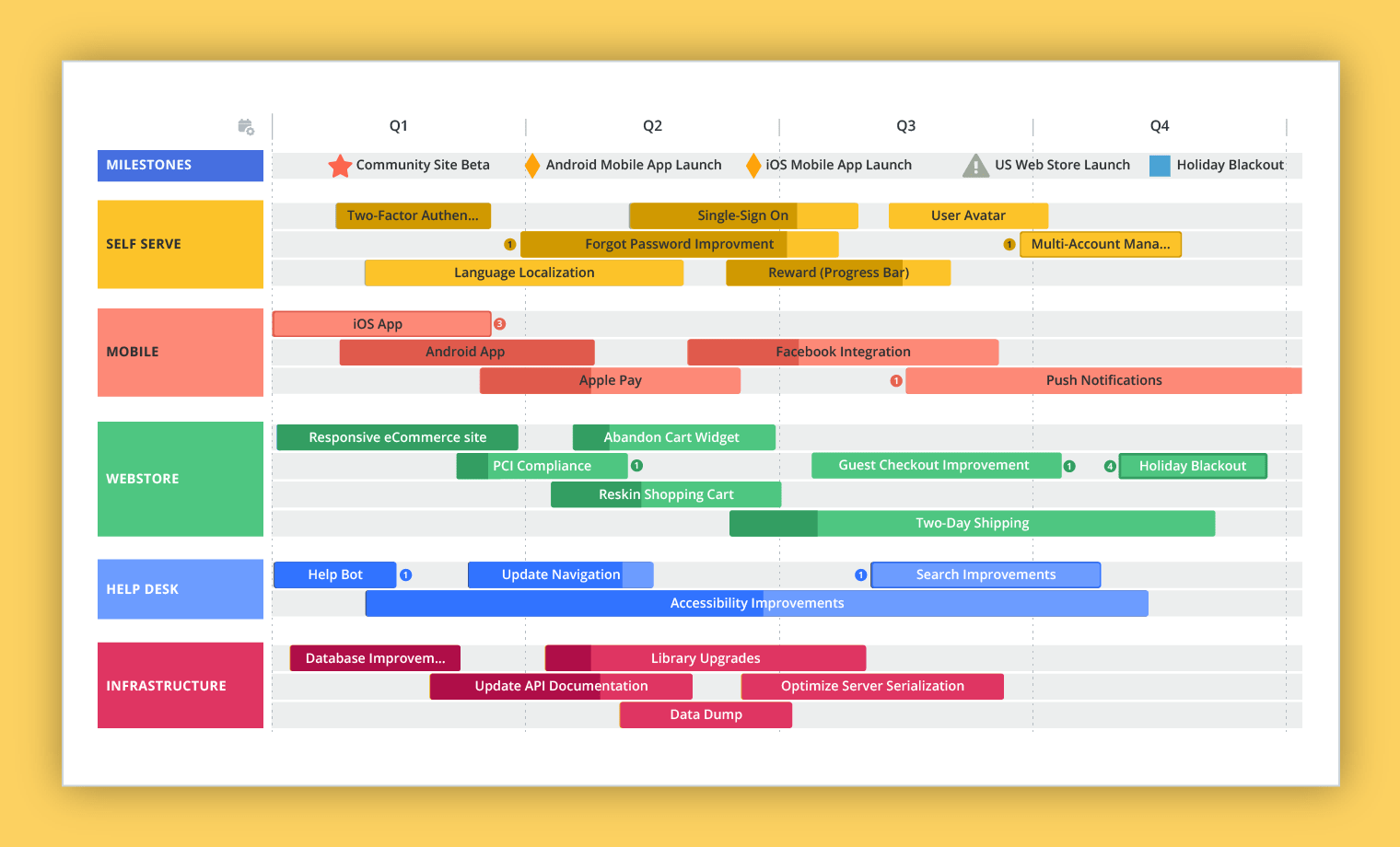
- Milestones: Significant events or achievements that mark progress towards project completion.
- Timeline: A visual representation of the project’s duration, showcasing key milestones and their corresponding dates.
- Resources: Allocation of personnel, budget, and other resources required for each milestone.
- Dependencies: Interrelationships between different tasks or milestones, highlighting potential bottlenecks or dependencies.
- Risks and Mitigation Strategies: Identification of potential challenges and proactive measures to address them.
Types of Roadmaps
Roadmaps can be tailored to various contexts and purposes. Some common types include:
- Product Roadmaps: Illustrate the development and launch of new products or features, outlining timelines and key milestones.
- Marketing Roadmaps: Outline marketing strategies and campaigns, focusing on target audiences, channels, and key performance indicators.
- Sales Roadmaps: Depict sales goals, target markets, and strategies for generating leads and converting customers.
- Technology Roadmaps: Showcase the evolution of technology within an organization, including infrastructure upgrades and software implementations.
- Strategic Roadmaps: Provide a high-level overview of an organization’s long-term goals and the steps required to achieve them.
Benefits of Utilizing Roadmaps
Embracing roadmaps offers numerous advantages for individuals, teams, and organizations:
- Enhanced Clarity and Focus: Roadmaps provide a clear vision of the project’s direction, ensuring everyone is aligned on goals and objectives.
- Improved Communication and Collaboration: By visualizing the project’s trajectory, roadmaps facilitate seamless communication among stakeholders, fostering collaboration and alignment.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: Roadmaps enable effective resource allocation by identifying key milestones and the resources required to achieve them.
- Proactive Risk Management: By identifying potential challenges, roadmaps allow for proactive risk mitigation strategies, minimizing disruptions and delays.
- Increased Accountability: Roadmaps establish clear responsibilities for each milestone, fostering accountability and promoting ownership among team members.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Roadmaps provide a comprehensive overview of the project’s progress, facilitating data-driven decision-making and course correction as needed.
- Improved Project Success Rate: By providing a structured framework for planning and execution, roadmaps significantly increase the likelihood of project success.
Creating a Winning Roadmap
Developing an effective roadmap requires careful consideration and a systematic approach:
- Define Clear Objectives: Begin by clearly defining the project’s goals and desired outcomes. Ensure these objectives are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Identify Key Milestones: Break down the project into manageable milestones, representing significant achievements towards the overall objective.
- Establish a Timeline: Determine the estimated duration for each milestone and create a visual representation of the project’s timeline.
- Allocate Resources: Identify the resources required for each milestone, including personnel, budget, and other essential elements.
- Assess Dependencies: Analyze the interrelationships between different tasks and milestones, highlighting potential bottlenecks or dependencies.
- Identify and Mitigate Risks: Conduct a risk assessment to identify potential challenges and develop proactive mitigation strategies.
- Communicate and Iterate: Regularly communicate the roadmap to stakeholders, ensuring transparency and alignment. Be prepared to adapt and iterate as needed based on feedback and changing circumstances.
Roadmaps in Action: Real-World Examples
Roadmaps are widely used across various industries and sectors, demonstrating their versatility and effectiveness:
- Product Development: Technology companies use roadmaps to plan the development and launch of new products or features, ensuring timely releases and meeting market demands.
- Marketing Campaigns: Marketing teams leverage roadmaps to outline their strategies and campaigns, aligning efforts to achieve specific marketing objectives.
- Sales and Business Development: Sales teams utilize roadmaps to track their progress towards sales targets, identifying key milestones and strategies for generating leads and closing deals.
- Project Management: Project managers rely on roadmaps to guide their teams through complex projects, ensuring timely delivery and achieving desired outcomes.
- Strategic Planning: Organizations use roadmaps to outline their long-term vision and strategic initiatives, ensuring alignment across departments and fostering a shared understanding of the company’s direction.
FAQs About Roadmaps
1. What are the key differences between a roadmap and a project plan?
While both roadmaps and project plans are valuable tools for project management, they serve distinct purposes. A roadmap provides a high-level overview of the project’s journey, focusing on key milestones and timelines. In contrast, a project plan delves into the specific details of each task, outlining dependencies, resources, and timelines.
2. How frequently should a roadmap be updated?
The frequency of roadmap updates depends on the project’s complexity and the pace of change in the environment. For agile projects with frequent iterations, updates may be required weekly or even daily. For more stable projects, updates may be sufficient quarterly or semi-annually.
3. Who should be involved in creating and reviewing a roadmap?
The roadmap creation process should involve all key stakeholders, including project managers, team members, executives, and relevant subject matter experts. This ensures everyone has a voice in shaping the project’s direction and fostering a shared understanding.
4. What are some common challenges associated with roadmaps?
Challenges with roadmaps can arise from a lack of clarity in objectives, unrealistic timelines, insufficient resources, or a failure to adapt to changing circumstances. Overcoming these challenges requires clear communication, effective collaboration, and a willingness to adapt as needed.
Tips for Creating a Winning Roadmap
- Keep it Simple and Visual: Roadmaps should be easy to understand and visually appealing, using clear language and concise descriptions.
- Focus on Key Milestones: Prioritize the most critical milestones, ensuring they are aligned with the project’s overall objectives.
- Embrace Flexibility: Be prepared to adjust the roadmap as needed based on changing circumstances, market trends, or feedback from stakeholders.
- Communicate Regularly: Regularly communicate the roadmap to stakeholders, ensuring transparency and alignment.
- Track Progress and Celebrate Achievements: Regularly track progress against milestones and celebrate successes to maintain momentum and motivation.
Conclusion
Roadmaps are essential tools for navigating the path to success in any project or endeavor. By providing a clear vision, fostering collaboration, and enabling proactive risk management, roadmaps empower individuals, teams, and organizations to achieve their goals. Embracing roadmaps as a strategic planning tool can significantly enhance project success rates and drive organizational growth. By adhering to best practices and leveraging the benefits of roadmaps, organizations can unlock their full potential and achieve lasting success.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Path to Success: A Comprehensive Guide to Roadmaps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!