Navigating The Seasons: A Comprehensive Guide To Wisconsin’s Growing Zones
Navigating the Seasons: A Comprehensive Guide to Wisconsin’s Growing Zones
Related Articles: Navigating the Seasons: A Comprehensive Guide to Wisconsin’s Growing Zones
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Seasons: A Comprehensive Guide to Wisconsin’s Growing Zones. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Seasons: A Comprehensive Guide to Wisconsin’s Growing Zones
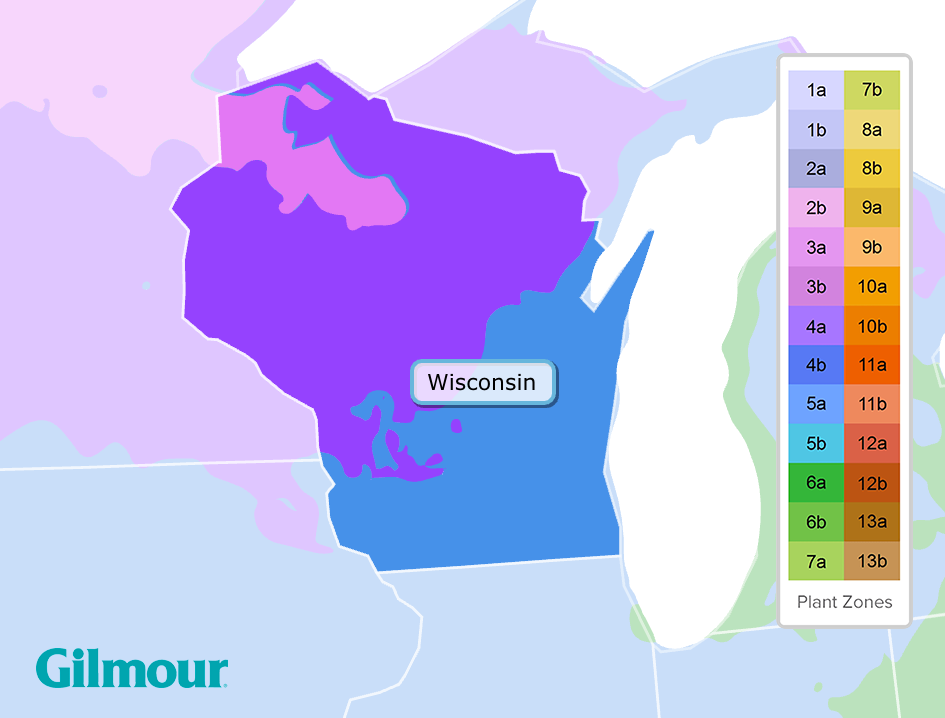
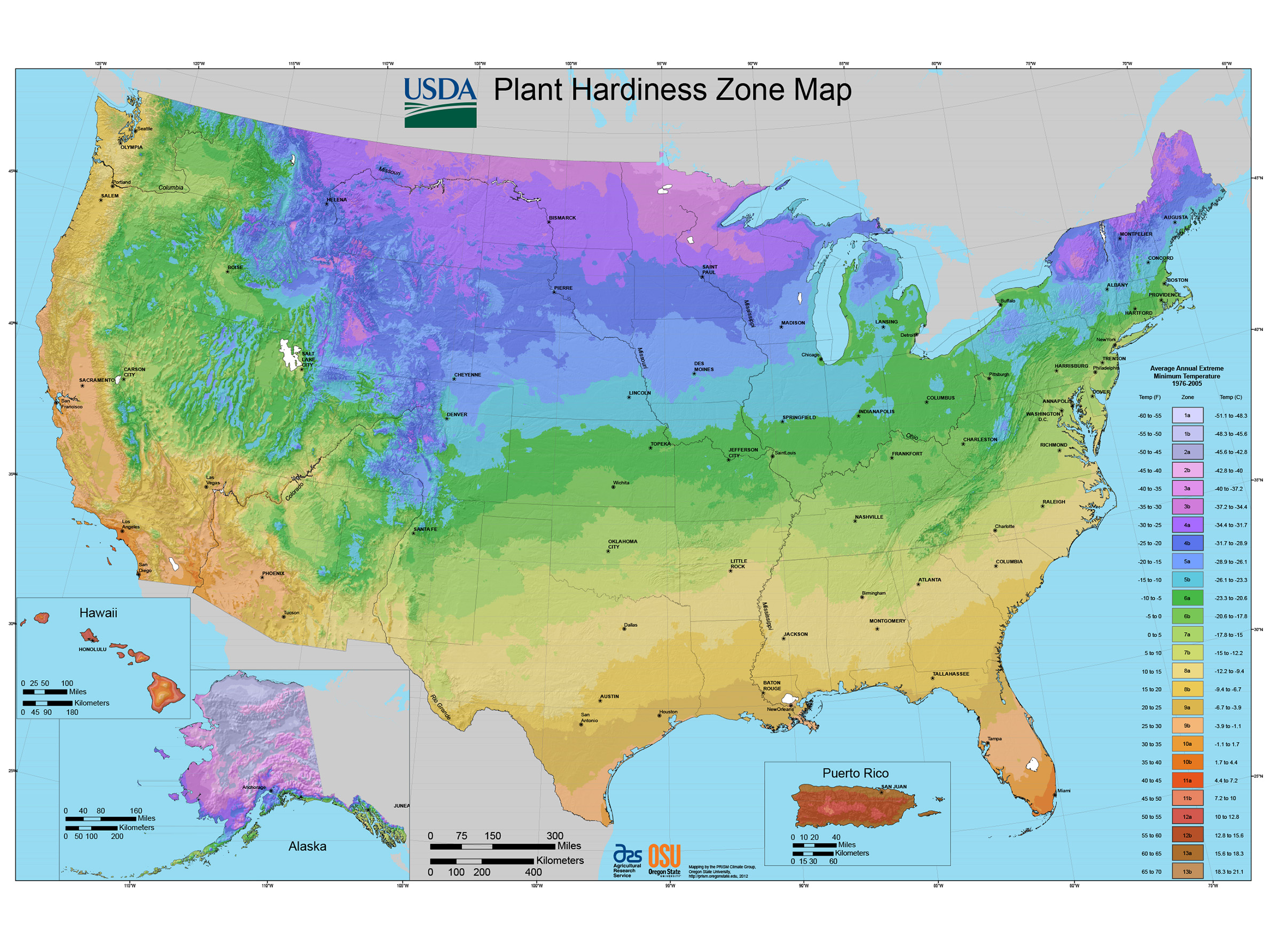
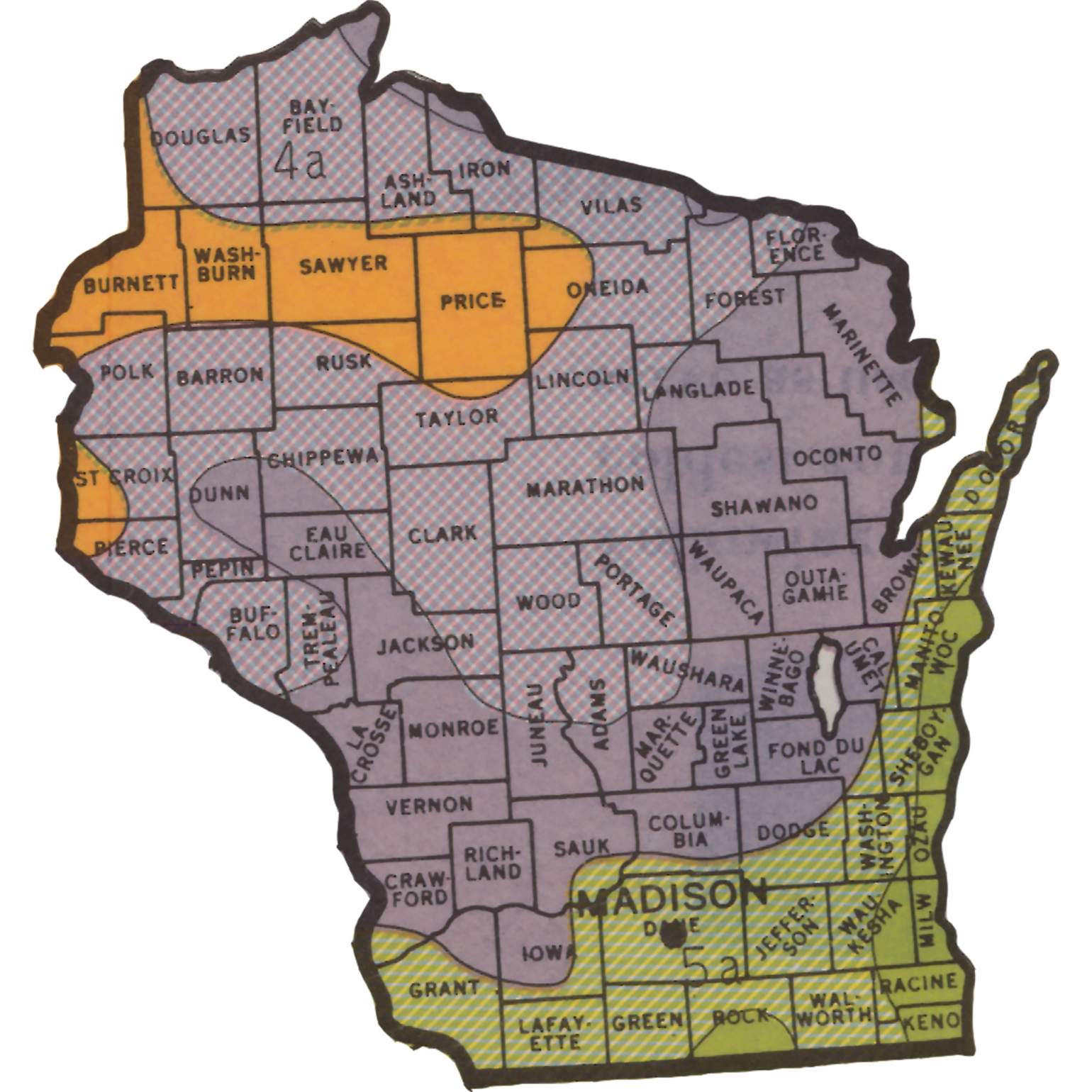
Wisconsin, known for its picturesque landscapes and diverse ecosystems, presents a unique challenge for gardeners and farmers alike: navigating the state’s varied climate. To help individuals understand the optimal planting times and suitable plant varieties for specific regions, the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map has been developed. This map, a valuable tool for horticultural success, divides the United States into zones based on average annual minimum winter temperatures.
Understanding the Zones: A Foundation for Success
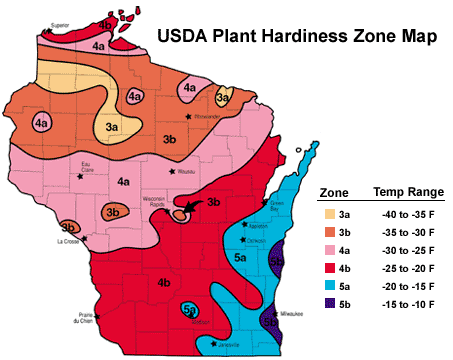
Wisconsin, with its distinct seasonal shifts, falls within USDA Plant Hardiness Zones 3 through 6. This means that different regions within the state experience varying levels of cold temperatures during the winter months.
- Zone 3: This zone, encompassing the northernmost parts of Wisconsin, experiences the coldest temperatures, with average annual minimum temperatures ranging from -40 to -30 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Zone 4: Located south of Zone 3, this zone experiences slightly milder winters, with average annual minimum temperatures ranging from -30 to -20 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Zone 5: This zone covers a significant portion of central and southern Wisconsin, with average annual minimum temperatures ranging from -20 to -10 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Zone 6: The southernmost region of Wisconsin, encompassing a small area along the border with Illinois, experiences the warmest winters, with average annual minimum temperatures ranging from -10 to 0 degrees Fahrenheit.
Decoding the Map: Unveiling the Secrets of Successful Gardening
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is a valuable resource for gardeners and farmers in Wisconsin. Understanding the specific zone for a given location allows individuals to:
- Select appropriate plant varieties: Each zone designates the plants that can thrive in that specific temperature range. Choosing plants that are well-suited to the local climate ensures optimal growth and survival.
- Determine the optimal planting time: Knowing the average last frost date and the first frost date for a particular zone helps individuals choose the appropriate time to plant their seeds or seedlings. This ensures that the plants have ample time to establish themselves before the onset of cold weather.
- Plan for winter protection: The map provides insights into the severity of winter conditions, allowing individuals to prepare for potential frost damage or harsh weather events. This might involve using protective measures such as mulching, winterizing plants, or providing shelter.
Beyond the Map: Factors Affecting Plant Growth
While the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map provides a valuable starting point, other factors can also influence plant growth and survival in Wisconsin:
- Microclimates: Variations in topography, elevation, and proximity to bodies of water can create localized microclimates that affect temperatures and growing conditions.
- Soil type: Different soil types possess varying water-holding capacities and drainage properties, influencing plant growth and survival.
- Sunlight exposure: The amount of sunlight a plant receives plays a crucial role in its growth and development.
- Wind patterns: Wind can exacerbate cold temperatures and increase the risk of frost damage.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: What is the difference between a hardiness zone and a growing zone?
A: A hardiness zone focuses on the minimum winter temperatures a plant can tolerate. A growing zone, on the other hand, considers the length of the growing season, the number of frost-free days, and the overall climate suitability for specific crops.
Q: Can I plant a plant that is rated for a warmer zone in Wisconsin?
A: While it is possible to try, it is not recommended. Plants that are not adapted to the colder temperatures of Wisconsin are more likely to experience frost damage or fail to thrive.
Q: How can I find the hardiness zone for my specific location?
A: You can use the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, which is available online and in print. You can also consult local nurseries or gardening experts for assistance.
Tips for Success: Cultivating a Thriving Garden
- Consult with local experts: Connect with local nurseries, garden centers, or agricultural extension offices for advice on plant selection, planting times, and winter protection strategies.
- Start with a small garden: Begin with a smaller garden and gradually expand as you gain experience and learn about the local growing conditions.
- Experiment with different plant varieties: Try different plant varieties within your hardiness zone to determine which ones perform best in your specific location.
- Observe your garden closely: Pay attention to the growth and development of your plants, noting any signs of stress or damage.
- Embrace the challenges: Gardening in Wisconsin can be rewarding, but it also requires patience, adaptability, and a willingness to learn from experience.
Conclusion: Embracing the Challenge of Wisconsin’s Climate
Wisconsin’s diverse climate presents both challenges and opportunities for gardeners and farmers. By understanding the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map and considering other factors that influence plant growth, individuals can cultivate thriving gardens and landscapes that reflect the beauty and resilience of the state. With careful planning, observation, and a touch of horticultural expertise, Wisconsin’s unique climate can be transformed into a canvas for vibrant and flourishing gardens.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/WisconsinZones-56a98bef3df78cf772a827b6.jpg)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Seasons: A Comprehensive Guide to Wisconsin’s Growing Zones. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!