Navigating The Web With Ease: Understanding Image Map Responsiveness
Navigating the Web with Ease: Understanding Image Map Responsiveness
Related Articles: Navigating the Web with Ease: Understanding Image Map Responsiveness
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Web with Ease: Understanding Image Map Responsiveness. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Web with Ease: Understanding Image Map Responsiveness
In the ever-evolving landscape of web design, user experience reigns supreme. Websites strive to provide seamless navigation, intuitive interactions, and captivating visual presentations. Image maps, a powerful tool for enhancing user engagement and interactivity, play a crucial role in achieving these goals. However, the effectiveness of image maps hinges on their ability to adapt seamlessly to different screen sizes and devices. This is where responsiveness comes into play.
Image maps, in essence, are clickable areas within an image that link to different web pages or sections. They provide a visually engaging way to navigate content, often replacing traditional text-based links. But in a world where users access websites on a multitude of devices, from desktops and laptops to smartphones and tablets, image maps must adapt to varying screen resolutions.
The Importance of Responsiveness in Image Maps
Responsiveness in image maps is paramount for several reasons:
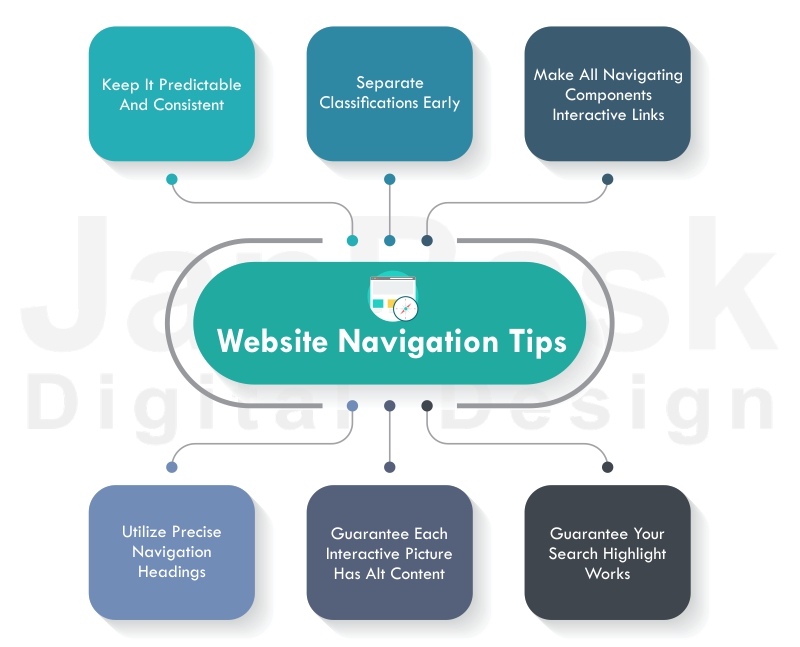
- Enhanced User Experience: Responsive image maps ensure that clickable areas remain easily accessible and clickable across all devices. This prevents frustration and promotes a smooth user journey, regardless of the screen size.
- Optimized Navigation: By adapting to different screen sizes, responsive image maps maintain their intended functionality and visual appeal. This prevents distortions, overlaps, or misaligned clickable areas, ensuring that users can navigate content effortlessly.
- Improved Accessibility: Responsive image maps are crucial for accessibility. They allow users with visual impairments or disabilities to navigate content effectively, ensuring inclusivity and equal access to information.
- Mobile-First Approach: In today’s mobile-centric world, optimizing for mobile devices is essential. Responsive image maps ensure that websites perform optimally on smartphones and tablets, providing a seamless experience for a vast audience.
Understanding the Mechanics of Responsiveness
Achieving responsiveness in image maps involves a combination of techniques and considerations:
- CSS Media Queries: This powerful tool allows developers to define different styles based on screen size, orientation, and other device-specific characteristics. By utilizing media queries, image map elements can be adjusted dynamically to fit the current viewport.
- Flexible Image Sizes: Images used for image maps should be responsive, meaning they adjust their size based on the screen dimensions. This can be achieved through techniques like using percentage-based widths or employing the "max-width" CSS property.
- Relative Positioning: Instead of using fixed pixel values for positioning clickable areas, developers can leverage relative positioning. This allows clickable areas to scale proportionally with the image, ensuring they remain clickable and accessible across all devices.
- JavaScript Libraries: Specialized JavaScript libraries can assist in creating responsive image maps. These libraries often provide pre-built functionalities for managing clickable areas and ensuring their responsiveness.
Implementing Responsive Image Maps: A Practical Guide
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to implement responsive image maps:
- Choose a Responsive Image: Select an image that scales well across different screen sizes. Avoid using large, pixelated images that can become blurry or distorted on smaller screens.
-
Define Clickable Areas: Use the
<map>and<area>tags in HTML to define the clickable areas within the image. Assign appropriatehrefattributes to each area to link to the desired web page or section. - Utilize CSS Media Queries: Apply CSS media queries to adjust the size and position of the clickable areas based on screen size. This ensures that the clickable areas remain accessible and visually appealing on all devices.
- Test Across Devices: Thoroughly test your image map across various devices and screen sizes. This helps identify any potential issues with responsiveness and ensures a seamless user experience.
FAQs about Image Map Responsiveness
1. What are the common challenges in creating responsive image maps?
- Maintaining Accuracy: Ensuring that clickable areas remain accurate and aligned across different screen sizes can be challenging, especially when dealing with complex image maps.
- Performance Optimization: Large images can impact page load times, particularly on mobile devices. Optimizing image sizes and utilizing efficient loading techniques is crucial for maintaining performance.
- Cross-Browser Compatibility: Ensuring that image maps function consistently across different web browsers can be a challenge due to variations in browser rendering engines.
2. How can I ensure that image maps are accessible to users with disabilities?
- Use Descriptive Alt Text: Provide meaningful alternative text for the image map, describing its purpose and the clickable areas within it. This allows screen readers to convey the information to users with visual impairments.
- Use ARIA Attributes: Utilize ARIA attributes to enhance accessibility, such as "aria-label" to provide additional context or "aria-disabled" to indicate disabled areas.
- Consider Keyboard Navigation: Ensure that image maps are navigable using the keyboard, allowing users with motor impairments to interact with the content.
3. What are some tips for creating effective responsive image maps?
- Keep It Simple: Avoid overly complex image maps with numerous clickable areas. This can lead to confusion and hinder navigation.
- Use Clear Visual Cues: Employ contrasting colors, shapes, or icons to clearly define clickable areas and make them easily recognizable.
- Provide Feedback: Offer visual feedback to users when they hover over or click on clickable areas. This helps confirm their interaction and enhances the user experience.
- Test and Iterate: Continuously test your image map across different devices and screen sizes. Identify any issues with responsiveness and make necessary adjustments to improve the user experience.
Conclusion
Responsive image maps are an essential element of modern web design, providing a seamless and engaging user experience across all devices. By embracing the principles of responsiveness, websites can ensure that image maps remain functional, accessible, and visually appealing, regardless of the screen size. This fosters a positive user experience, encourages interaction, and ultimately contributes to the success of any website.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Web with Ease: Understanding Image Map Responsiveness. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!