Navigating The World With Precision: A Comprehensive Guide To NGS Maps
Navigating the World with Precision: A Comprehensive Guide to NGS Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the World with Precision: A Comprehensive Guide to NGS Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World with Precision: A Comprehensive Guide to NGS Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World with Precision: A Comprehensive Guide to NGS Maps
In the realm of geospatial technology, precise and reliable maps are crucial for a multitude of applications. From urban planning and infrastructure development to navigation and disaster management, accurate spatial information forms the bedrock of informed decision-making. Within this domain, the National Geodetic Survey (NGS) plays a pivotal role, providing a robust framework for mapping and geospatial data through its meticulously curated collection of geodetic control points, known as NGS maps.
Understanding the Foundation: What are NGS Maps?
NGS maps are not simply static representations of geographical features; they are meticulously constructed datasets encompassing a wealth of geodetic information. These maps serve as the foundational reference for establishing accurate positioning and measurements across vast geographical areas. The core components of NGS maps include:
- Geodetic Control Points: These are strategically placed physical markers on the Earth’s surface, serving as fixed reference points for precise positioning. These points are meticulously surveyed and documented, ensuring their accuracy and longevity.
- Horizontal and Vertical Datums: These provide a standardized framework for measuring and representing locations on the Earth’s surface. NGS utilizes the North American Datum of 1983 (NAD83) for horizontal positioning and the North American Vertical Datum of 1988 (NAVD88) for vertical positioning.
- Geospatial Data: NGS maps incorporate a wide range of geospatial data, including elevation data, gravity measurements, and other relevant information. This data is essential for a variety of applications, from mapping and navigation to surveying and engineering.
The Significance of NGS Maps: A Comprehensive Overview
NGS maps are not just static representations; they are dynamic tools that underpin a multitude of critical applications:
1. Infrastructure Development and Planning:
- Precise Land Surveying: NGS maps provide the foundation for accurate land surveying, enabling precise property boundary delineation, infrastructure construction, and development planning.
- Construction and Engineering Projects: Engineers rely on NGS data to ensure the stability and accuracy of structures, bridges, and other infrastructure projects.
2. Navigation and Positioning:
- Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS): NGS control points serve as reference points for GNSS systems like GPS, ensuring accurate positioning and navigation for vehicles, aircraft, and other mobile devices.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): NGS data is integrated into GIS systems, enabling the creation of detailed maps and spatial analyses for a wide range of applications.
3. Disaster Response and Management:
- Emergency Response: NGS maps facilitate rapid response to natural disasters by providing precise location data for emergency personnel, enabling efficient rescue efforts and resource allocation.
- Hazard Assessment: NGS data is crucial for assessing disaster risks, identifying vulnerable areas, and developing effective mitigation strategies.
4. Scientific Research and Monitoring:
- Geodetic Research: NGS data is essential for studying the Earth’s movements, including tectonic plate shifts, volcanic activity, and sea level rise.
- Environmental Monitoring: NGS maps support environmental monitoring by providing accurate data for tracking changes in land cover, water resources, and other environmental variables.
5. Legal and Regulatory Frameworks:
- Property Boundaries: NGS maps are used to define property boundaries, ensuring legal clarity and facilitating land transactions.
- Regulatory Compliance: NGS data is essential for complying with various regulations related to construction, environmental protection, and other areas.
NGS Maps: A Foundation for Innovation
The significance of NGS maps extends beyond their traditional applications. As technology advances, these maps continue to play a crucial role in shaping the future of geospatial technology:
- Autonomous Vehicles: NGS data is essential for developing and deploying autonomous vehicles, providing accurate positioning and navigation information.
- Precision Agriculture: NGS maps support precision agriculture by providing accurate location data for optimizing crop yields and resource management.
- Smart Cities: NGS data is crucial for developing smart cities by providing accurate spatial information for infrastructure management, traffic optimization, and other applications.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries about NGS Maps
1. How are NGS control points established?
NGS control points are established through a rigorous process involving precise surveying techniques, including:
- Global Positioning System (GPS) Observations: GPS receivers are used to measure the distances between control points and satellites, enabling precise positioning.
- Trigonometric Leveling: This method involves measuring vertical distances between control points using specialized equipment.
- Precise Geodetic Positioning: NGS employs advanced techniques like Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) and Satellite Laser Ranging (SLR) to establish control points with sub-millimeter accuracy.
2. How can I access NGS map data?
NGS provides a wealth of geospatial data through its online portal, the National Geodetic Survey Data Portal (NGS Data Portal). This portal offers a wide range of data products, including:
- Geodetic Control Point Data: This data includes the coordinates, elevations, and other attributes of NGS control points.
- Geospatial Data Products: NGS offers a variety of geospatial data products, such as elevation data, gravity measurements, and other relevant information.
- Mapping Tools and Applications: NGS provides tools and applications to visualize, analyze, and utilize its data for various purposes.
3. What are the benefits of using NGS maps?
Using NGS maps offers numerous benefits, including:
- Increased Accuracy: NGS maps provide a high level of accuracy, ensuring reliable and precise positioning for various applications.
- Standardized Framework: NGS maps utilize a standardized framework, ensuring consistency and compatibility across different datasets.
- Publicly Available Data: NGS data is publicly available, enabling access to valuable spatial information for a wide range of users.
- Continuous Improvement: NGS continuously updates and improves its data, ensuring the accuracy and relevance of its maps.
4. How do NGS maps contribute to sustainable development?
NGS maps play a vital role in sustainable development by enabling:
- Efficient Infrastructure Planning: NGS data allows for optimized infrastructure development, minimizing environmental impact and maximizing resource utilization.
- Environmental Monitoring: NGS maps support environmental monitoring, enabling the tracking of changes in land cover, water resources, and other environmental variables.
- Disaster Risk Reduction: NGS data helps assess disaster risks, identify vulnerable areas, and develop effective mitigation strategies, contributing to community resilience.
Tips for Utilizing NGS Maps Effectively
- Understanding the Data: Familiarize yourself with the specific data products and their limitations before using them.
- Data Accuracy and Precision: Be aware of the accuracy and precision of the data, as it can vary depending on the data source and collection methods.
- Data Transformation and Projection: Ensure that the data is transformed and projected correctly for your specific application.
- Integration with Other Data: Integrate NGS data with other relevant datasets to create comprehensive spatial analyses.
- Data Visualization and Interpretation: Use appropriate tools and techniques for visualizing and interpreting NGS data effectively.
Conclusion: NGS Maps – A Foundation for a Connected World
NGS maps are not just maps; they are the foundation of a robust geospatial infrastructure that enables informed decision-making, promotes sustainable development, and drives innovation across various sectors. By providing a precise and standardized framework for mapping and geospatial data, NGS maps empower individuals, organizations, and governments to navigate the world with confidence, ensuring a more accurate, connected, and sustainable future. As technology continues to evolve, NGS maps will remain an indispensable tool, shaping the future of geospatial technology and driving progress across a multitude of fields.


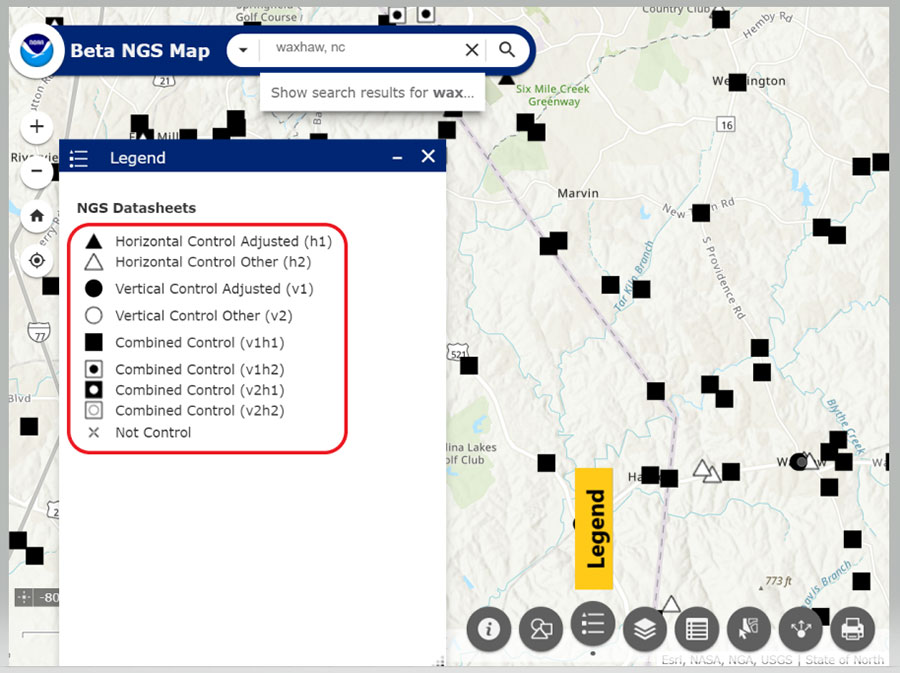



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World with Precision: A Comprehensive Guide to NGS Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!