Shiloh: A Crossroads Of History And Faith In Ancient Israel
Shiloh: A Crossroads of History and Faith in Ancient Israel
Related Articles: Shiloh: A Crossroads of History and Faith in Ancient Israel
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Shiloh: A Crossroads of History and Faith in Ancient Israel. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Shiloh: A Crossroads of History and Faith in Ancient Israel
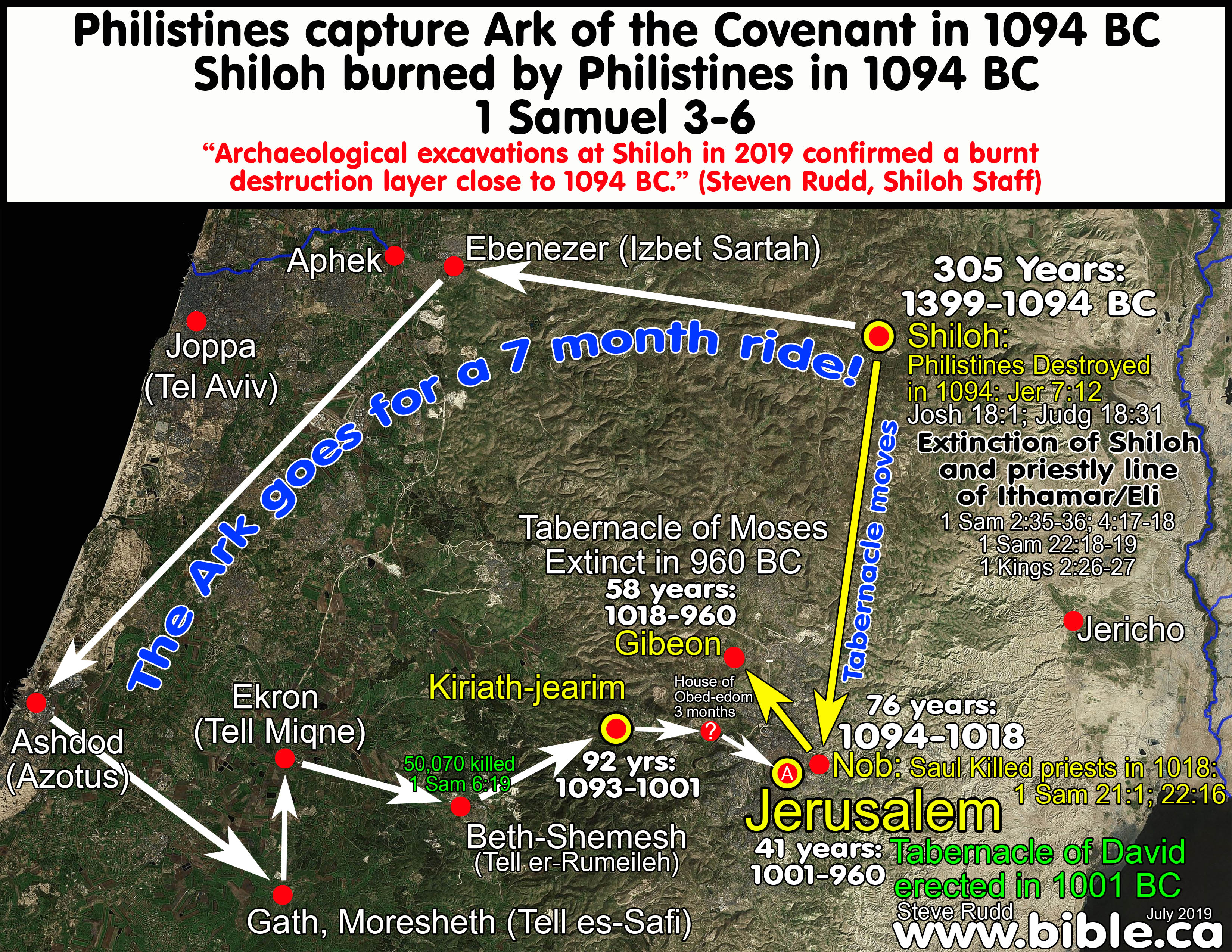
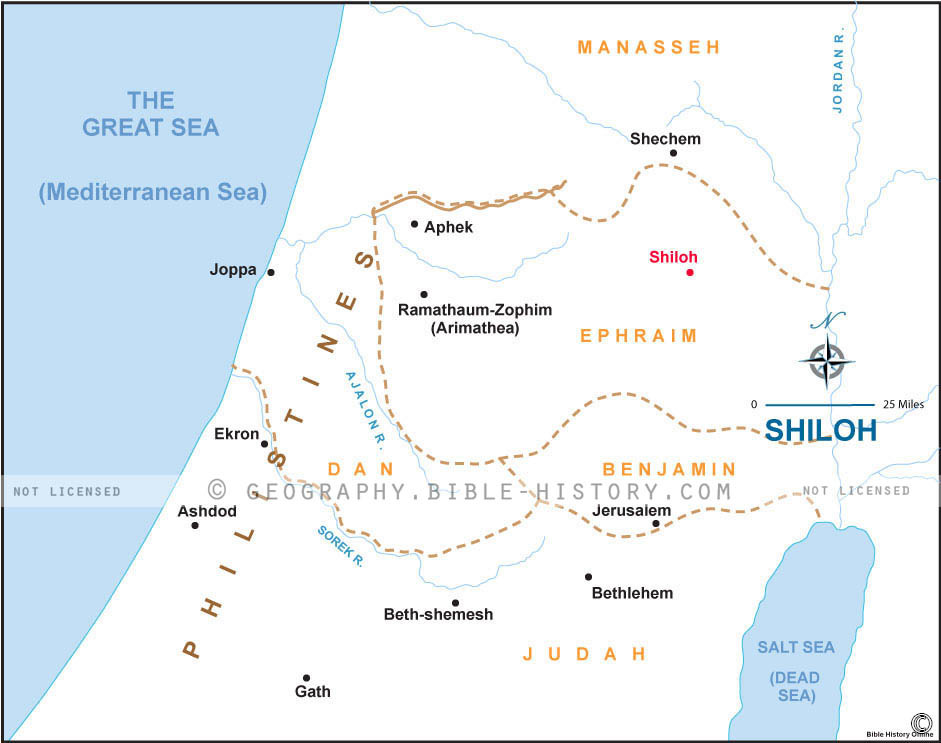
Shiloh, a site deeply intertwined with the narrative of ancient Israel, holds a prominent place in biblical history and archaeology. Located in the central highlands of Israel, approximately 30 kilometers north of Jerusalem, Shiloh served as the religious and political center of the Israelites for several centuries. This article explores the significance of Shiloh, tracing its historical evolution, archaeological discoveries, and enduring impact on Jewish faith and culture.
A Glimpse into Shiloh’s Past: Archaeological Evidence and Biblical Narratives
Shiloh’s prominence is evident in its archaeological remains, which reveal a complex and fascinating history. Excavations have unearthed evidence of a fortified city dating back to the Early Bronze Age, indicating early human settlement in the region. However, Shiloh’s true significance lies in its connection to the Israelite period.
The Book of Joshua recounts the conquest of Canaan by the Israelites, culminating in the establishment of Shiloh as the central sanctuary. The Ark of the Covenant, containing the tablets of the Ten Commandments, was housed in Shiloh, symbolizing divine presence and authority. The Tabernacle, a portable structure serving as a place of worship, was also located in Shiloh. This period witnessed the rise of Shiloh as a religious and political hub, a testament to its importance in the early stages of Israelite history.
The Role of Shiloh in Israelite Society
Shiloh served as the primary sanctuary for the Israelites for several centuries, playing a crucial role in their religious and social life. The Tabernacle housed the Ark of the Covenant, making Shiloh the center of worship and pilgrimage for the Israelites. Priests and Levites officiated religious ceremonies, offering sacrifices and upholding the rituals prescribed in the Torah.
Beyond its religious significance, Shiloh also held political importance. The site served as a gathering place for the tribes of Israel, where they convened for council and decision-making. The presence of the Ark of the Covenant, symbolizing God’s presence and authority, solidified Shiloh’s role as a central point of unity for the fledgling nation.
Shiloh’s Decline and Its Legacy
Despite its early prominence, Shiloh eventually lost its status as the primary sanctuary. The Bible recounts the capture of the Ark of the Covenant by the Philistines, marking a turning point in Shiloh’s fortunes. The loss of the Ark, a symbol of divine favor, signaled a decline in Shiloh’s influence and authority.
The reasons for Shiloh’s decline remain debated among historians and scholars. Some attribute it to internal divisions within the Israelite tribes, while others point to external pressures from neighboring nations. Regardless of the precise reasons, Shiloh’s decline marks a significant shift in Israelite history, ushering in a period of greater decentralization and the rise of other religious centers.
Archaeological Discoveries at Shiloh
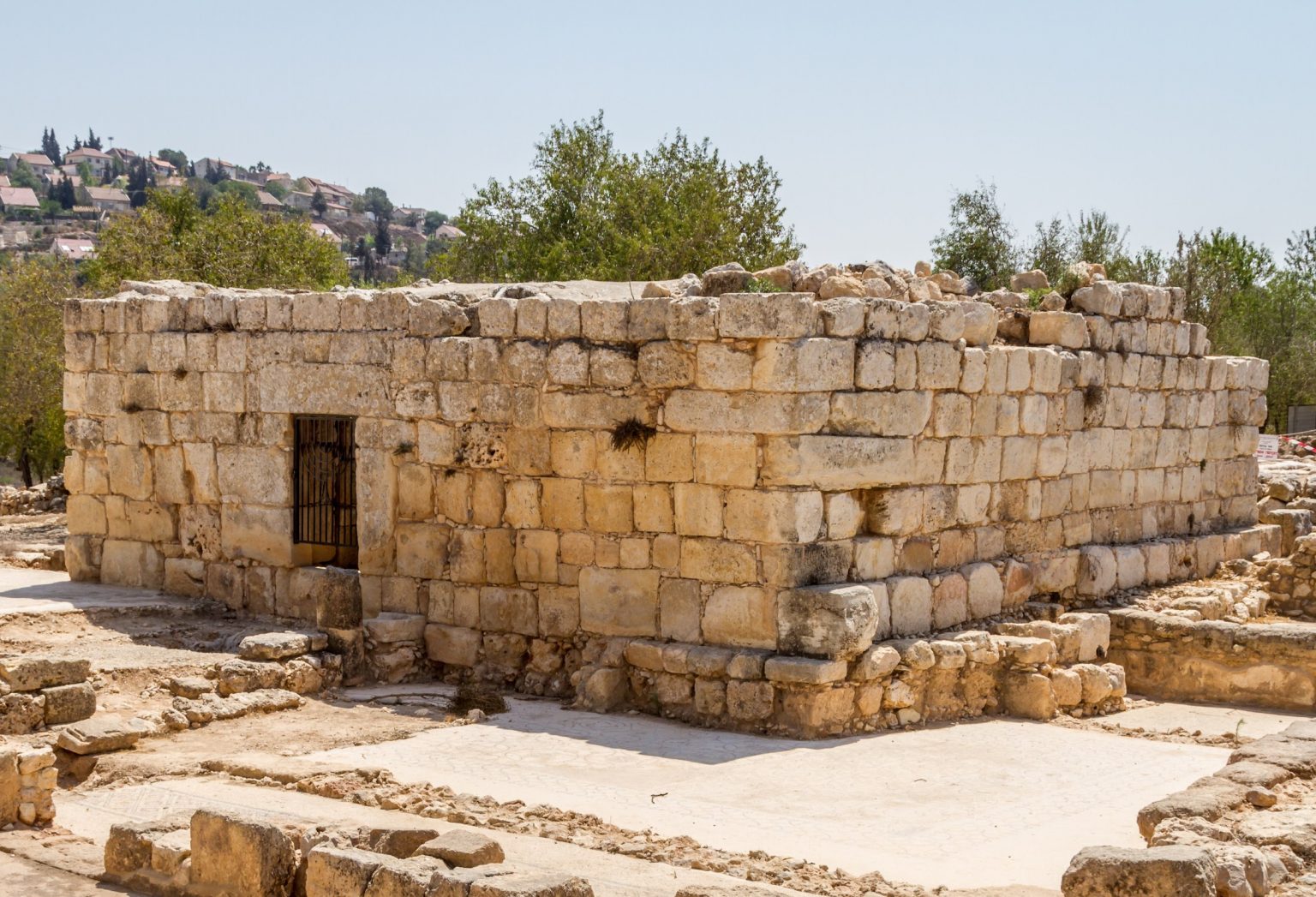
Archaeological excavations at Shiloh have provided invaluable insights into the site’s history and its significance within the broader context of ancient Israel. Excavations have revealed the remains of a fortified city with a complex layout, including a central courtyard, residential areas, and structures associated with religious activities.
Among the most notable discoveries are the remains of the Tabernacle, the portable structure that housed the Ark of the Covenant. While the Tabernacle itself was likely made of perishable materials and has not survived, its foundations have been unearthed, providing tangible evidence of its existence. Other significant findings include pottery shards, tools, and other artifacts dating back to the Israelite period, offering valuable insights into the daily life and culture of the people who lived in Shiloh.
Shiloh’s Enduring Significance
Despite its decline, Shiloh remains a significant site for Jewish history and faith. Its association with the Ark of the Covenant, the Tabernacle, and the early history of the Israelites makes it a place of pilgrimage and reflection for Jews worldwide. The site is a testament to the enduring power of faith and the importance of historical memory in shaping cultural identity.
FAQs about Shiloh
Q: What is the significance of Shiloh in the Bible?
A: Shiloh is described as the first central sanctuary of the Israelites after their conquest of Canaan, where the Ark of the Covenant was housed. It served as a religious and political center for several centuries, playing a pivotal role in the early stages of Israelite history.
Q: What archaeological evidence exists for Shiloh?
A: Excavations have uncovered remains of a fortified city dating back to the Early Bronze Age, as well as evidence of structures associated with religious activities during the Israelite period. The foundations of the Tabernacle have been unearthed, providing tangible evidence of its existence.
Q: What is the story of the Ark of the Covenant in Shiloh?
A: The Ark of the Covenant, containing the tablets of the Ten Commandments, was housed in Shiloh, symbolizing divine presence and authority. Its capture by the Philistines marked a turning point in Shiloh’s fortunes, signaling a decline in its influence and authority.
Q: Why did Shiloh decline?
A: The reasons for Shiloh’s decline remain debated, with theories ranging from internal divisions within the Israelite tribes to external pressures from neighboring nations. The loss of the Ark of the Covenant, a symbol of divine favor, likely contributed to its decline.
Q: Is Shiloh still a significant site today?
A: Yes, Shiloh remains a significant site for Jewish history and faith. Its association with the Ark of the Covenant, the Tabernacle, and the early history of the Israelites makes it a place of pilgrimage and reflection for Jews worldwide.
Tips for Visiting Shiloh
- Plan your visit: The site is open to visitors daily, with guided tours available. Check the official website for opening hours and other information.
- Explore the archaeological remains: Take your time to explore the excavated structures and artifacts, gaining a deeper understanding of Shiloh’s history.
- Visit the Shiloh Museum: The museum provides further insights into the site’s history and its significance in the broader context of ancient Israel.
- Engage with the local community: Shiloh is also home to a modern Israeli settlement. Interact with the residents and learn about their perspectives on the site.
- Reflect on the significance of Shiloh: The site offers a unique opportunity to connect with the history and faith of the Israelites, providing a powerful reflection on the enduring power of faith and the importance of historical memory.
Conclusion
Shiloh stands as a testament to the complex and multifaceted history of ancient Israel. Its archaeological remains and biblical narratives offer a window into a pivotal period in the development of Israelite society and faith. While Shiloh may have lost its status as the central sanctuary, its legacy endures, reminding us of the enduring power of faith, the importance of historical memory, and the ongoing dialogue between past and present. The site continues to inspire reflection and dialogue, offering a unique opportunity to connect with the rich tapestry of Jewish history and culture.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Shiloh: A Crossroads of History and Faith in Ancient Israel. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!