Svalbard: A Remote Arctic Archipelago With Global Significance
Svalbard: A Remote Arctic Archipelago with Global Significance
Related Articles: Svalbard: A Remote Arctic Archipelago with Global Significance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Svalbard: A Remote Arctic Archipelago with Global Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Svalbard: A Remote Arctic Archipelago with Global Significance
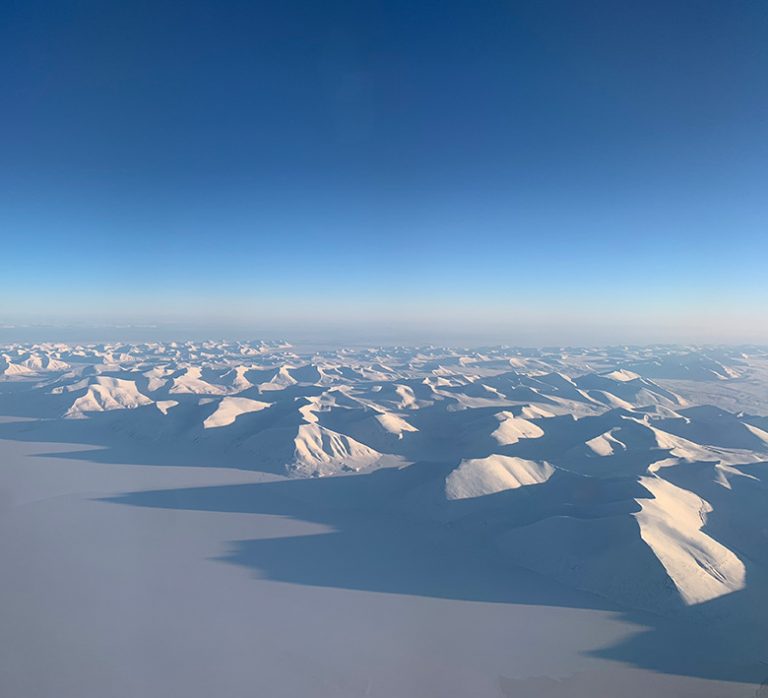

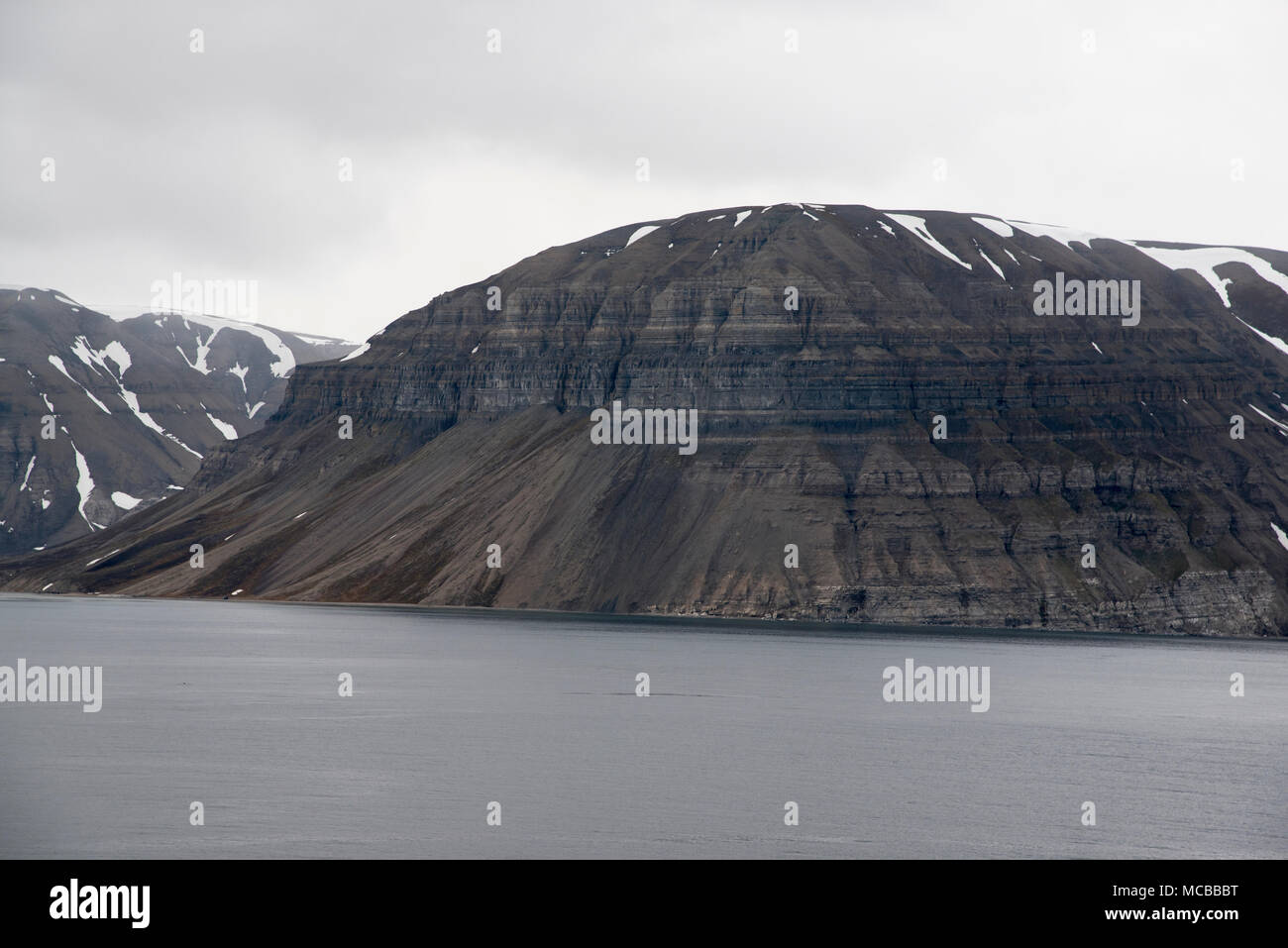
Svalbard, a Norwegian archipelago located in the Arctic Ocean, is a captivating blend of stark beauty and scientific importance. Situated between mainland Norway and the North Pole, this remote landmass offers a unique glimpse into the harsh yet captivating environment of the Arctic.
Geography and Climate:
Svalbard’s geography is characterized by rugged mountains, glaciers, and fjords. The archipelago comprises four main islands: Spitsbergen, Nordaustlandet, Edgeøya, and Barentsøya, along with numerous smaller islands. Its landscape is a tapestry of diverse ecosystems, from the icy expanses of glaciers to the tundra-covered plains and the dramatic cliffs overlooking the Arctic Ocean.
The climate of Svalbard is Arctic, with long, dark winters and short, cool summers. Temperatures can drop to -40°C (-40°F) in winter, while summer temperatures rarely exceed 10°C (50°F). Despite the harsh conditions, Svalbard is home to a surprising array of flora and fauna, including polar bears, reindeer, walruses, Arctic foxes, and various bird species.
History and Governance:
Svalbard’s history is intertwined with exploration and resource extraction. The archipelago was discovered in the 16th century by Dutch explorers and became a hub for whaling in the following centuries. Norway gained sovereignty over Svalbard in 1920 through the Svalbard Treaty, which established the archipelago as a demilitarized zone with open access for all signatory nations.
Today, Svalbard is governed by Norway, with a local administration based in Longyearbyen, the archipelago’s largest settlement. While Norway holds sovereignty, the Svalbard Treaty grants other signatory nations, including Russia, access to the archipelago’s resources and the right to conduct scientific research.
Scientific Importance:
Svalbard’s location in the Arctic makes it a crucial site for studying climate change and its impacts on the environment. The archipelago’s glaciers are melting at an alarming rate, providing valuable data on the effects of global warming. Furthermore, Svalbard’s unique ecosystem serves as a natural laboratory for understanding the adaptations of flora and fauna to extreme conditions.
The archipelago is home to several international research stations, including the Norwegian Polar Institute’s research station in Ny-Ålesund, which houses scientists from various countries working on projects related to climate change, geology, and biology.
Tourism and Recreation:
Despite its remote location and harsh climate, Svalbard has become a popular destination for adventure tourism. Visitors can experience the breathtaking beauty of the Arctic landscape, witness the diverse wildlife, and engage in activities such as hiking, skiing, and dog sledding.
Longyearbyen serves as the main gateway to Svalbard, offering accommodation, restaurants, and a variety of tourist services. The town’s unique Arctic atmosphere and cultural offerings provide a glimpse into life at the edge of the world.
Challenges and Sustainability:
Svalbard faces several challenges, primarily related to climate change and its impacts on the fragile Arctic ecosystem. Melting glaciers threaten coastal communities and ecosystems, while rising temperatures disrupt the delicate balance of the Arctic food web.
Svalbard’s limited infrastructure and remote location pose challenges for sustainable development. The archipelago relies heavily on fossil fuels for energy, and efforts are underway to transition towards renewable energy sources. Sustainable tourism practices are also crucial for minimizing the environmental impact of visitors.
FAQs about Svalbard:
1. Is Svalbard part of Norway?
While Svalbard is governed by Norway, it is not technically part of the Kingdom of Norway. The Svalbard Treaty grants Norway sovereignty over the archipelago, but also allows other signatory nations access to its resources and the right to conduct research.
2. What is the population of Svalbard?
The population of Svalbard is approximately 2,600, with most residents living in Longyearbyen.
3. Is it safe to travel to Svalbard?
Svalbard is generally safe for tourists, but it is important to be aware of the potential risks associated with the Arctic environment. Polar bears are a common sight in the area, and visitors must take precautions to avoid encounters. The weather can also be unpredictable, and it is essential to be prepared for extreme conditions.
4. What is the best time to visit Svalbard?
The best time to visit Svalbard depends on the type of experience you are seeking. Summer offers longer days and warmer temperatures, making it ideal for hiking and wildlife viewing. Winter, on the other hand, provides opportunities for seeing the Northern Lights and engaging in winter activities like dog sledding.
5. What are the main industries in Svalbard?
The main industries in Svalbard are tourism, research, and mining. Coal mining has historically been a significant industry, but its importance has declined in recent years.
Tips for Visiting Svalbard:
- Pack for extreme weather conditions: Temperatures can fluctuate significantly, so be prepared for both hot and cold weather.
- Respect the environment: Leave no trace and be mindful of the fragile Arctic ecosystem.
- Be aware of polar bears: Always travel with a guide and take precautions to avoid encounters with polar bears.
- Learn about the local culture: Svalbard has a unique culture that is influenced by its history and isolation.
- Consider visiting during the summer months: Summer offers longer days and warmer temperatures, making it ideal for outdoor activities.
Conclusion:
Svalbard is a unique and captivating archipelago with global significance. Its remote location, harsh climate, and rich history make it a destination for adventurers, scientists, and nature enthusiasts alike. As a vital site for studying climate change and its impacts on the environment, Svalbard plays a crucial role in understanding the future of the Arctic. By embracing sustainable practices and responsible tourism, we can ensure that this extraordinary place continues to be a source of wonder and scientific discovery for generations to come.
.jpg?auto=format,enhance,compressu0026fit=cropu0026crop=faces,edgesu0026w=0u0026h=288)
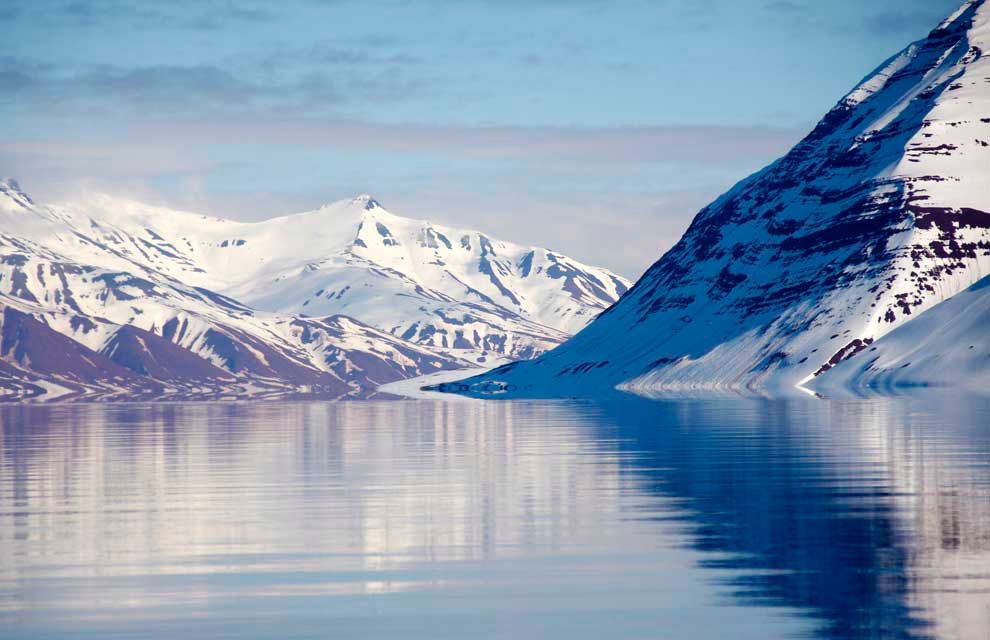
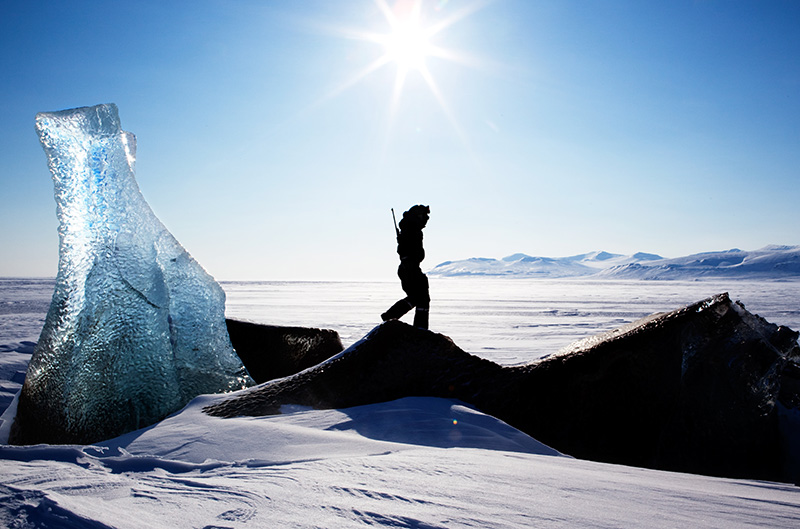






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Svalbard: A Remote Arctic Archipelago with Global Significance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!