The Wisconsin Gerrymandering Map: A Case Study In Political Manipulation
The Wisconsin Gerrymandering Map: A Case Study in Political Manipulation
Related Articles: The Wisconsin Gerrymandering Map: A Case Study in Political Manipulation
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Wisconsin Gerrymandering Map: A Case Study in Political Manipulation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Wisconsin Gerrymandering Map: A Case Study in Political Manipulation
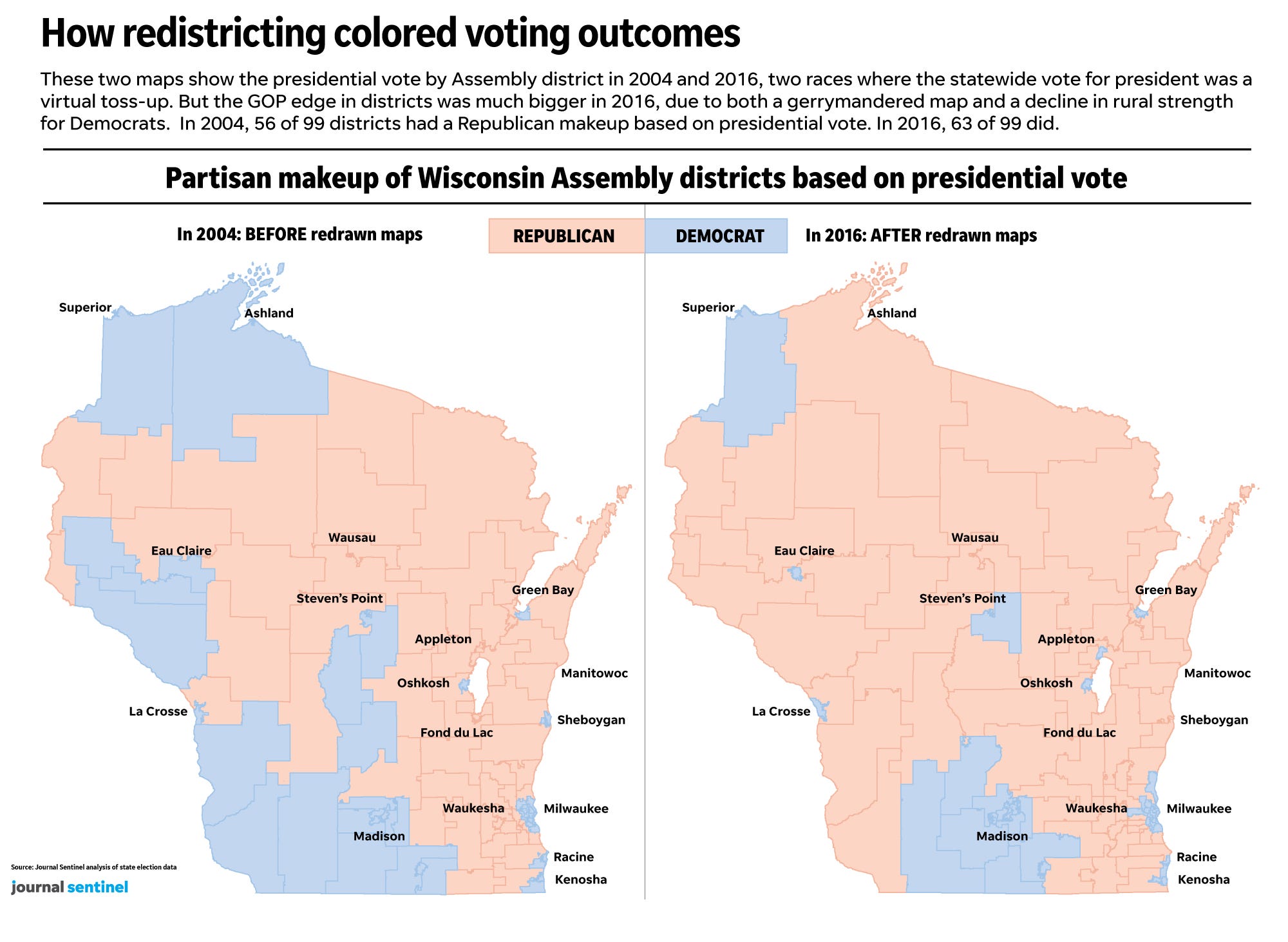
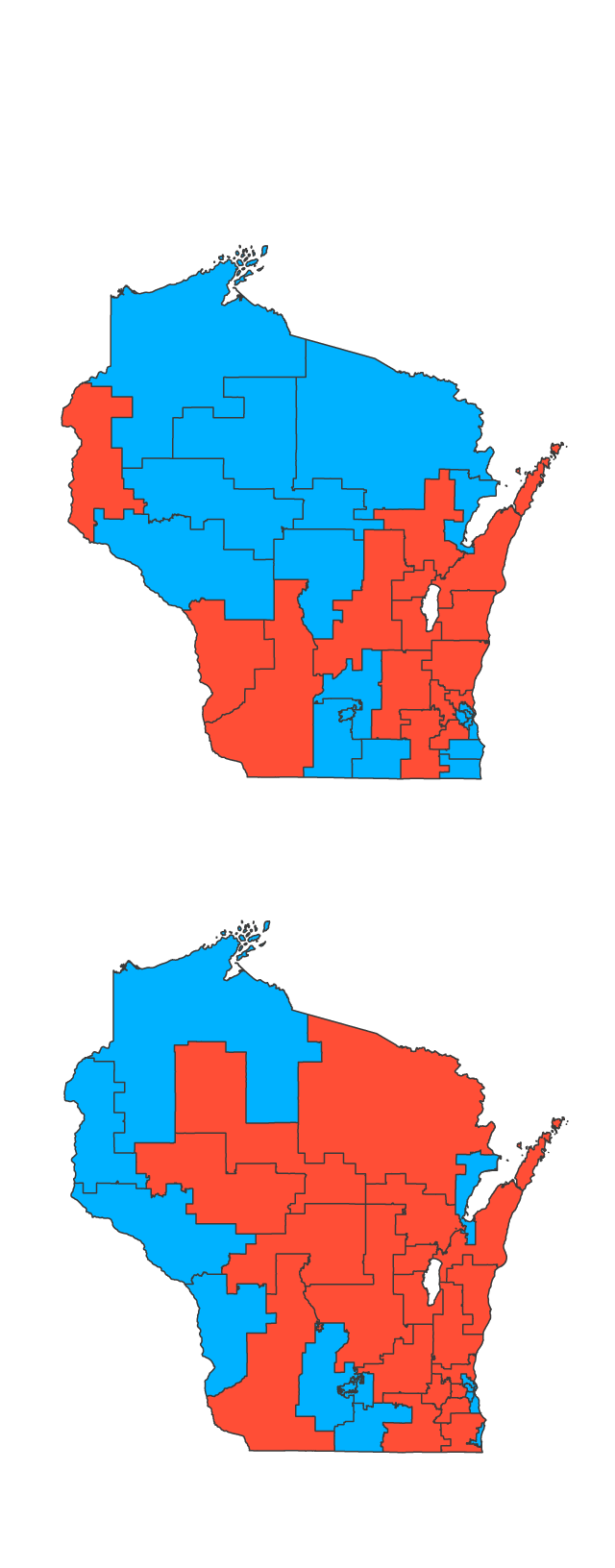
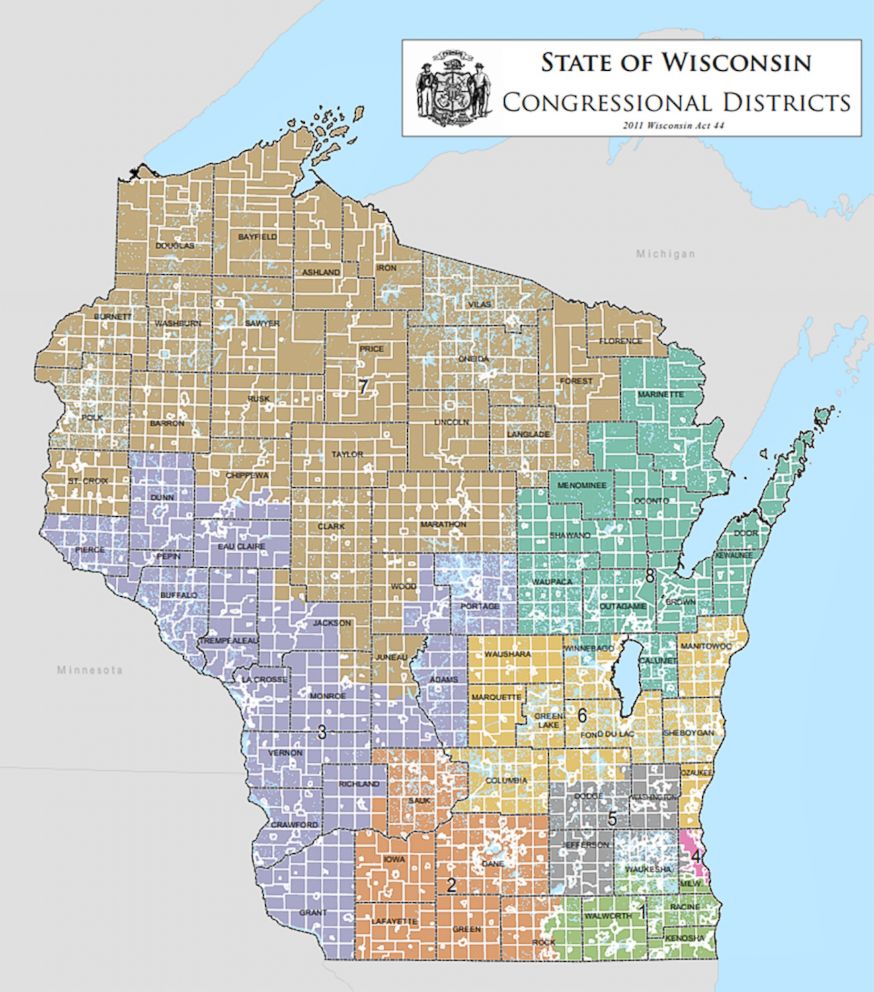
The Wisconsin gerrymandering map, a product of the 2011 redistricting process, stands as a prime example of how political boundaries can be manipulated to achieve partisan advantage. This map, with its convoluted lines and geographically disparate districts, has been the subject of intense scrutiny and legal challenges, highlighting the complex interplay between electoral processes and political power.
Understanding Gerrymandering: A Historical Perspective
Gerrymandering, the practice of manipulating electoral district boundaries to favor a particular political party or group, has a long and contentious history. Its origins can be traced back to the early 19th century, when Elbridge Gerry, the then-Governor of Massachusetts, signed a bill creating a district shaped like a salamander, designed to benefit his political party. This practice, named after Gerry, has persisted throughout American history, evolving in its techniques and impact.
The Wisconsin Case: A Tale of Partisan Advantage
The 2011 redistricting process in Wisconsin marked a turning point in the state’s political landscape. The Republican-controlled legislature, with the support of then-Governor Scott Walker, implemented a redistricting plan that resulted in a gerrymandered map heavily favoring the Republican party. This map, characterized by its unusually shaped districts, ensured Republican dominance in state legislative elections for years to come.
The Impact of Gerrymandering on Wisconsin’s Political Landscape
The consequences of the 2011 redistricting in Wisconsin have been profound. The map has created a situation where the electoral outcomes do not accurately reflect the underlying political preferences of the state’s population. This, in turn, has led to a number of negative consequences:
- Reduced Voter Choice: Gerrymandering can create districts where one party consistently wins by large margins, reducing the competitiveness of elections and limiting the choices available to voters.
- Increased Partisan Polarization: The creation of safe districts for one party can lead to increased partisan polarization, as elected officials are less likely to compromise or engage in bipartisan cooperation.
- Underrepresentation of Minority Groups: Gerrymandering can be used to dilute the voting power of minority groups, making it more difficult for them to elect representatives who reflect their interests.
- Erosion of Public Trust: The perception that elections are rigged or manipulated can erode public trust in the democratic process.
Legal Challenges and the Quest for Fair Representation
The Wisconsin gerrymandering map has been the subject of numerous legal challenges, with plaintiffs arguing that it violates the principles of "one person, one vote" and equal protection under the law. In 2018, the Wisconsin Supreme Court ruled that the map was unconstitutional, ordering the legislature to redraw the districts. However, the legislature’s subsequent attempt to create a new map was also challenged, leading to a protracted legal battle.
The Fight for Fair Representation: A Long and Winding Road
The Wisconsin gerrymandering case highlights the ongoing struggle for fair representation in American democracy. While the legal challenges have brought some progress, the issue of gerrymandering remains a persistent threat to the integrity of elections.
FAQs
Q: What are the main features of the Wisconsin gerrymandering map?
A: The Wisconsin gerrymandering map is characterized by its unusually shaped districts, with lines that often cut through communities and create geographically disparate areas. This allows for the manipulation of voting blocs to favor one party.
Q: Why is gerrymandering considered harmful?
A: Gerrymandering undermines fair representation by diluting the voting power of certain groups, reducing voter choice, increasing partisan polarization, and eroding public trust in the democratic process.
Q: What are the legal challenges to the Wisconsin gerrymandering map?
A: Plaintiffs have argued that the map violates the principles of "one person, one vote" and equal protection under the law, as it unfairly favors one party over another.
Q: What are the potential solutions to address gerrymandering?
A: Potential solutions include independent redistricting commissions, the use of nonpartisan criteria for drawing district lines, and the adoption of electoral systems that are less susceptible to manipulation.
Tips
- Stay informed: Keep abreast of the ongoing debate about gerrymandering and its impact on your state and national politics.
- Contact your elected officials: Express your concerns about gerrymandering and advocate for fair representation.
- Support organizations working to combat gerrymandering: Numerous organizations are dedicated to promoting fair elections and combating gerrymandering.
Conclusion
The Wisconsin gerrymandering map serves as a stark reminder of the potential for political manipulation in the electoral process. While legal challenges have brought some progress, the fight for fair representation is far from over. Addressing gerrymandering requires a concerted effort from citizens, policymakers, and the judiciary to ensure that elections accurately reflect the will of the people. Only by working together can we safeguard the integrity of our democratic system and ensure that every vote counts.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Wisconsin Gerrymandering Map: A Case Study in Political Manipulation. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!