Understanding The Ethiopian Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To The Map
Understanding the Ethiopian Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map
Related Articles: Understanding the Ethiopian Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Ethiopian Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding the Ethiopian Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding the Ethiopian Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map
- 3.1 A Historical Perspective: The Evolution of Ethiopia’s Political Map
- 3.2 Understanding the Ethiopian Political Map: Key Features
- 3.3 The Significance of the Ethiopian Political Map
- 3.4 FAQs about the Ethiopian Political Map
- 3.5 Tips for Understanding the Ethiopian Political Map
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding the Ethiopian Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map
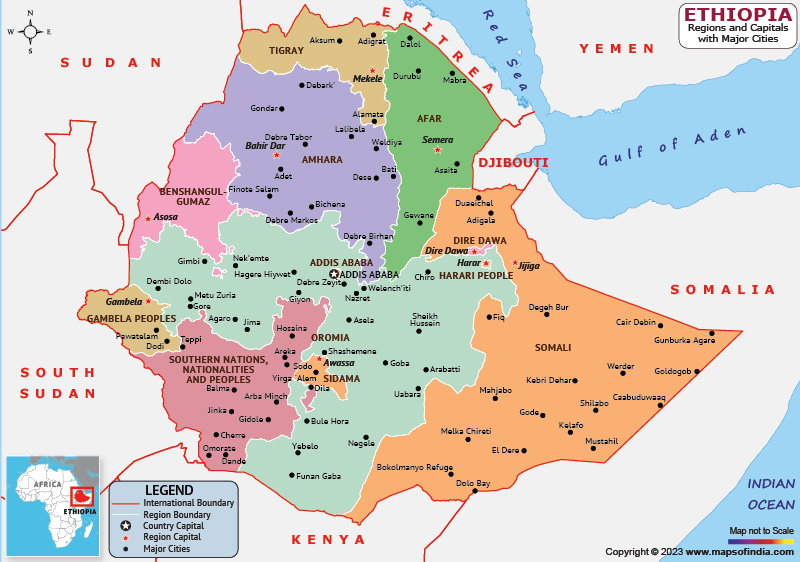
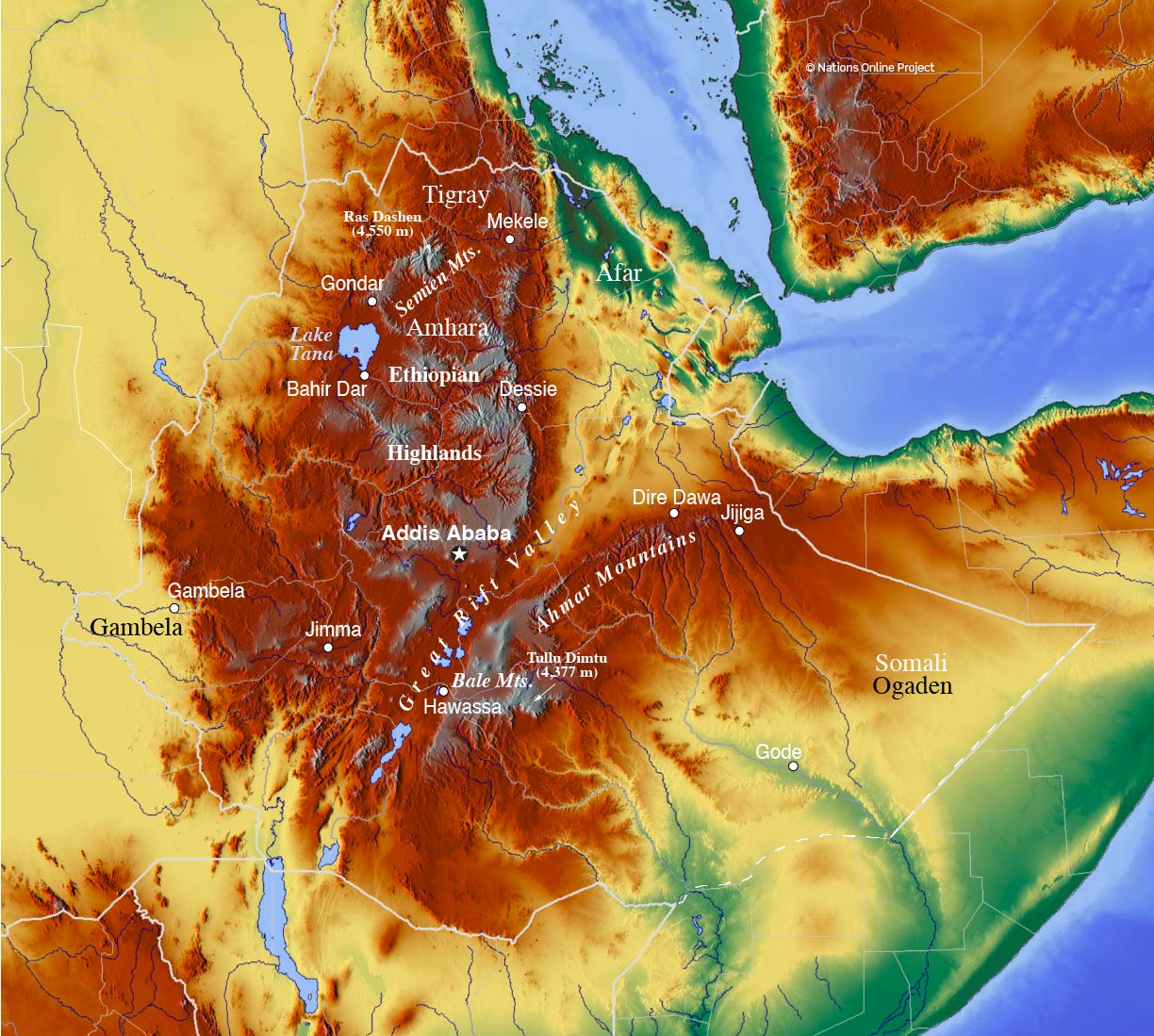
The Ethiopian political map is a complex and dynamic entity, reflecting the country’s rich history, diverse ethnicities, and ongoing political evolution. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the Ethiopian political landscape, exploring its key features, historical context, and the implications of its current configuration.
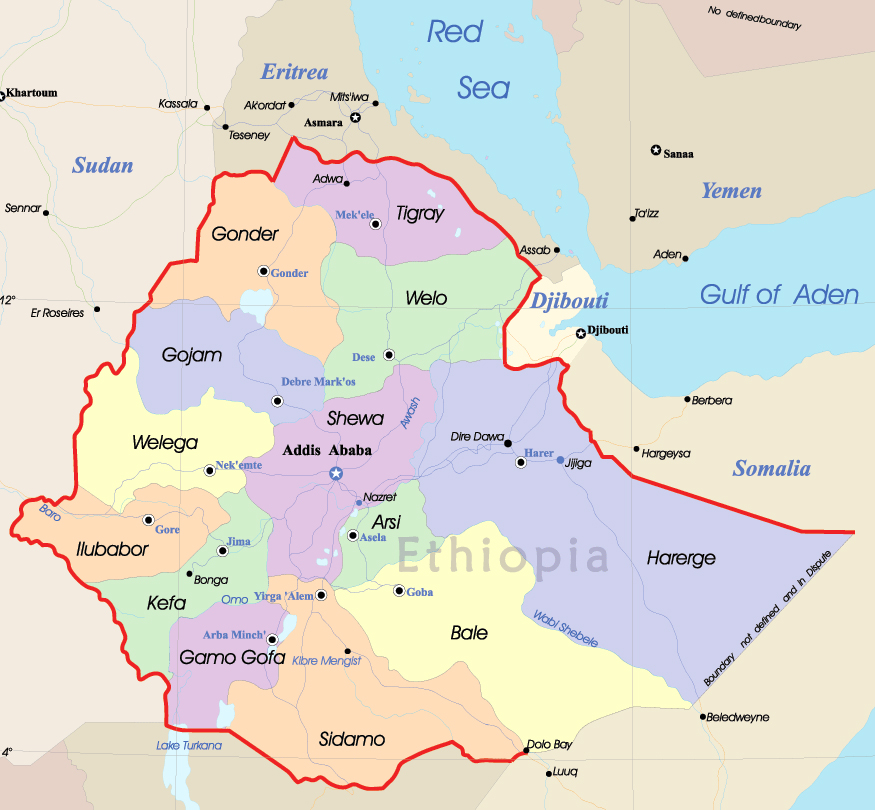
A Historical Perspective: The Evolution of Ethiopia’s Political Map
Ethiopia’s political map has undergone significant transformations throughout its history, shaped by internal dynamics, external influences, and shifting power structures.
Pre-Colonial Era:
- The Ethiopian Empire: For centuries, Ethiopia was ruled by a centralized empire, with the Emperor wielding significant authority. This period saw the establishment of distinct provinces and regions, often based on ethnic and linguistic lines.
- The Rise of Regional Kingdoms: Several regional kingdoms emerged, challenging the central authority of the Emperor. This period saw the fragmentation of the empire and the emergence of distinct political entities.
Colonial Era:
- Italian Occupation: During the early 20th century, Ethiopia was occupied by Italy, leading to the establishment of a colonial administration. This period saw the imposition of a new political map, with administrative divisions reflecting Italian interests.
- The Fight for Independence: Ethiopian resistance movements fought against Italian occupation, ultimately achieving independence in 1941. This period saw the re-establishment of the Ethiopian Empire, with a focus on consolidating national unity.
Post-Independence Era:
- The Derg Regime: The Ethiopian Empire was overthrown in 1974 by a military junta known as the Derg. This period saw the implementation of socialist policies and the establishment of a centralized, authoritarian state.
- The Transition to a Federal System: In 1991, the Derg regime was overthrown, paving the way for the establishment of a federal republic. This period saw the adoption of a new constitution, which recognized ethnic diversity and established a federal system of government.
Understanding the Ethiopian Political Map: Key Features
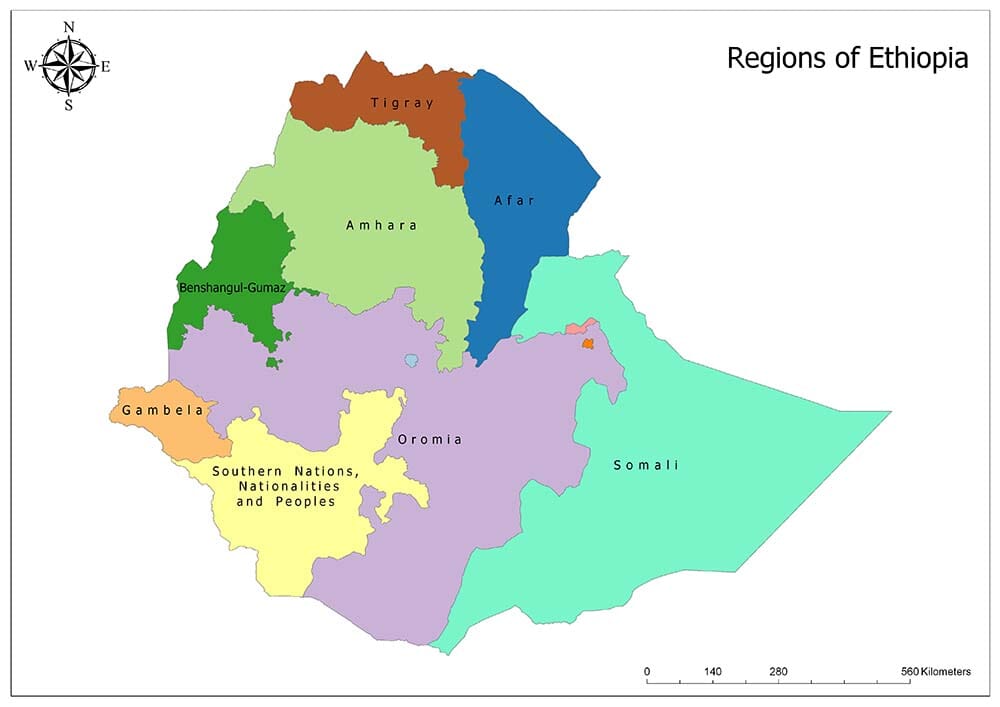
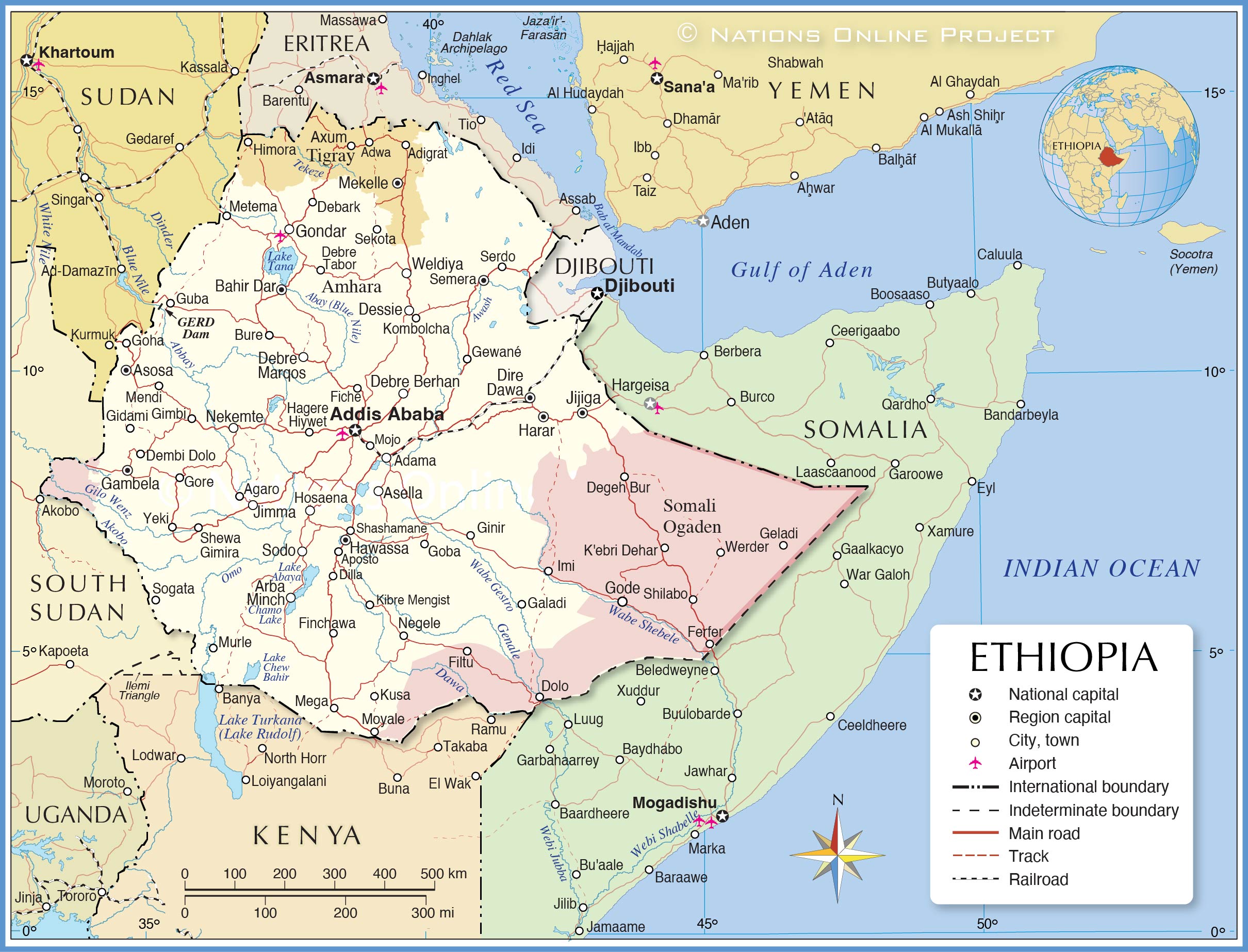
The current Ethiopian political map is structured around a federal system, with nine regional states and two chartered cities (Addis Ababa and Dire Dawa) enjoying significant autonomy.
Regional States:
- Regional Autonomy: Each regional state has its own government, legislature, and administrative structures. They have the authority to manage their own affairs, including language, education, and cultural heritage.
- Ethnic Representation: Regional states are generally based on ethnic lines, reflecting the country’s diverse population. This system aims to promote ethnic self-determination and ensure representation for all groups.
- Boundaries: Regional state boundaries are often contested, reflecting historical grievances and competing claims over land and resources.
Chartered Cities:
- Special Status: Addis Ababa and Dire Dawa are chartered cities, meaning they have a special status within the federal system. They are not part of any regional state and have their own administrations.
- National Significance: Addis Ababa serves as the capital of Ethiopia and is home to the federal government and major institutions. Dire Dawa is a major commercial and industrial center.
The Significance of the Ethiopian Political Map
The Ethiopian political map has significant implications for the country’s stability, development, and the future of its diverse ethnicities.
Promoting Ethnic Harmony:
- Representation and Participation: The federal system aims to ensure the representation of all ethnic groups in the political process. This is intended to promote inclusivity and prevent the marginalization of any particular group.
- Decentralization of Power: Decentralization of power to regional states allows for greater autonomy and decision-making at the local level. This is intended to address the concerns of different ethnic groups and promote a sense of ownership over their affairs.
Addressing Ethnic Tensions:
- Balancing Regional Interests: The federal system attempts to balance the interests of different ethnic groups, ensuring that no single group dominates the political process. This is crucial for maintaining stability and preventing conflicts.
- Addressing Historical Grievances: The federal system provides a framework for addressing historical grievances and resolving long-standing disputes between different ethnic groups.
Challenges and Concerns:
- Ethnic Fragmentation: The federal system has been criticized for exacerbating ethnic tensions and promoting fragmentation. Some argue that it has led to a weakening of national unity and a focus on narrow ethnic interests.
- Political Instability: The country has experienced periods of political instability, particularly in the context of ethnic conflicts and disputes over regional boundaries.
- Economic Disparities: Significant economic disparities exist between different regions, with some regions experiencing higher levels of poverty and underdevelopment.
FAQs about the Ethiopian Political Map
1. What are the main ethnic groups in Ethiopia?
Ethiopia is home to over 80 ethnic groups, with the largest being Oromo, Amhara, Tigray, Somali, and Sidama.
2. How many regional states are there in Ethiopia?
There are nine regional states in Ethiopia, each with its own government and legislature.
3. What is the role of the federal government in Ethiopia?
The federal government is responsible for national defense, foreign policy, and other matters of national importance. It also has the authority to resolve disputes between regional states.
4. What are the challenges facing the Ethiopian federal system?
The Ethiopian federal system faces challenges such as ethnic tensions, political instability, and economic disparities between different regions.
5. What is the future of the Ethiopian political map?
The future of the Ethiopian political map is uncertain. The country is undergoing a period of political transition and reform, and the future of the federal system is a subject of ongoing debate.
Tips for Understanding the Ethiopian Political Map
- Study the history of Ethiopia: Understanding the country’s historical context is essential for grasping the complexities of its political map.
- Explore the different ethnic groups: Learn about the various ethnic groups in Ethiopia, their cultures, and their historical experiences.
- Follow current events: Stay informed about current events in Ethiopia, including political developments and ethnic conflicts.
- Consult reliable sources: Use reputable sources of information, such as academic journals, government reports, and news organizations.
Conclusion
The Ethiopian political map is a dynamic and evolving entity, reflecting the country’s complex history, diverse ethnicities, and ongoing political transitions. Understanding the Ethiopian political map requires a nuanced understanding of the country’s historical context, the principles of the federal system, and the challenges it faces. By studying the map, we can gain insights into the country’s political landscape and its implications for stability, development, and the future of its diverse ethnicities.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Ethiopian Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!