Understanding The Power Of Weather In Motion Radar Maps
Understanding the Power of Weather in Motion Radar Maps
Related Articles: Understanding the Power of Weather in Motion Radar Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Power of Weather in Motion Radar Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Power of Weather in Motion Radar Maps

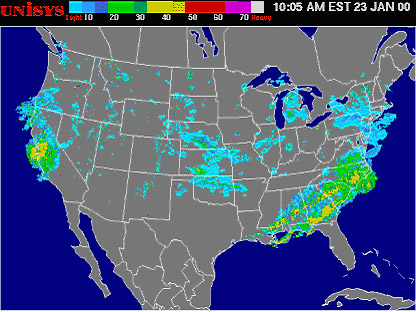
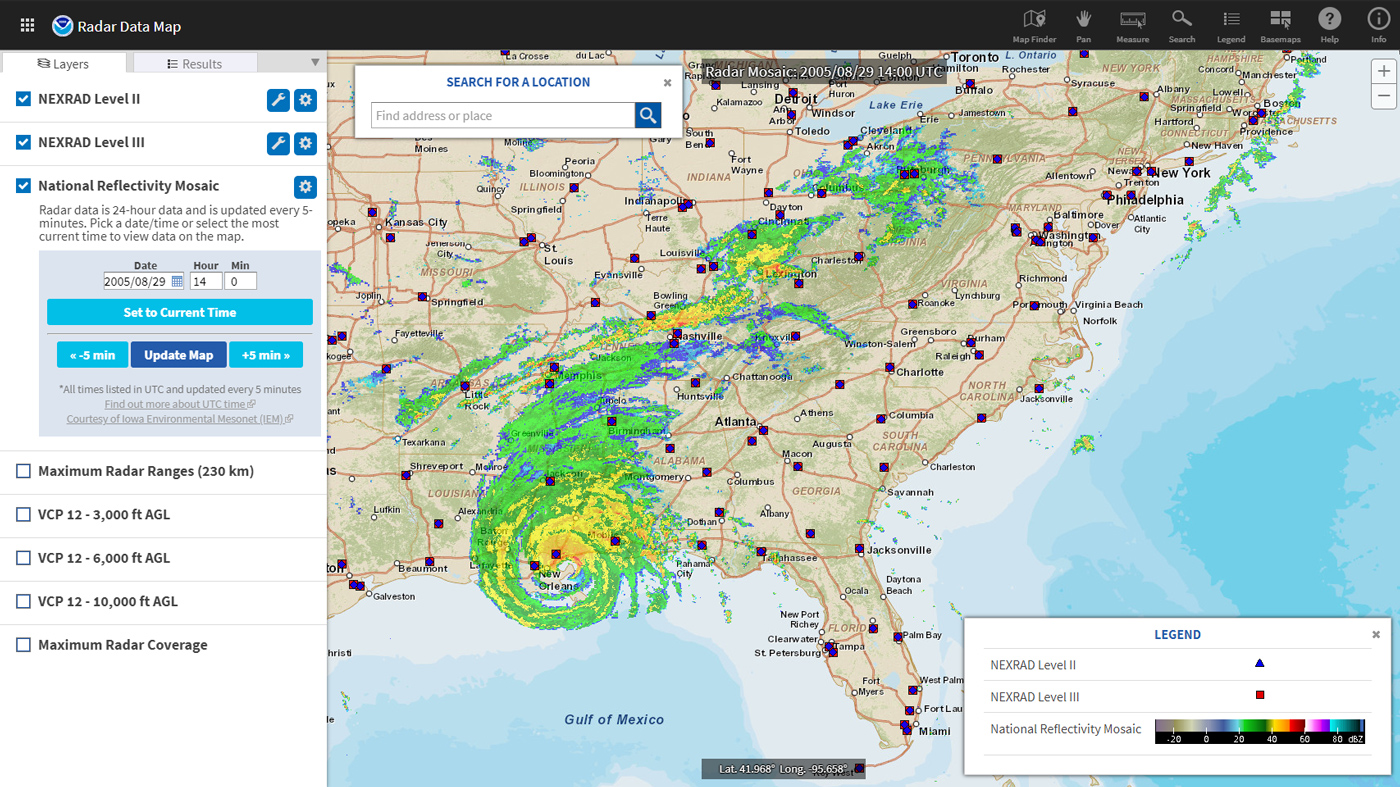
Weather in motion radar maps are a vital tool for meteorologists and the general public alike, providing real-time insights into the movement and intensity of precipitation. These maps utilize the principles of Doppler radar, offering a dynamic visual representation of weather patterns that aids in forecasting, preparedness, and safety.
The Science Behind the Images:
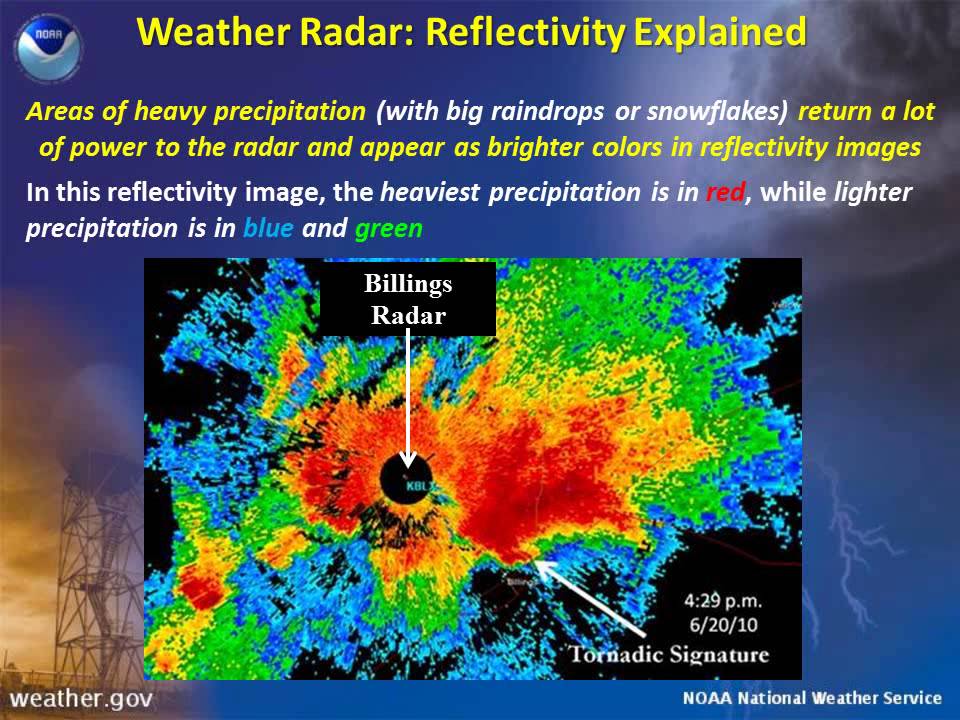
Doppler radar works by emitting radio waves that bounce off precipitation particles, such as rain, snow, or hail. The radar system measures the speed and direction of these reflected waves, allowing meteorologists to determine the movement and intensity of precipitation.
Key Features of Weather in Motion Radar Maps:
- Real-Time Data: Radar maps offer a continuous stream of data, capturing the evolution of weather systems as they develop and move.
- Visual Representation: Color-coded overlays on the map depict precipitation intensity, with shades of green indicating light rain, yellow for moderate rain, and red for heavy rain or thunderstorms.
- Motion Arrows: Arrows superimposed on the map indicate the direction and speed of precipitation movement, providing crucial information for forecasting the arrival and duration of storms.
- Time Lapses: Many radar maps offer time lapse features, allowing users to observe the progression of weather events over time. This helps in understanding the potential impact of storms and making informed decisions.
Benefits of Utilizing Weather in Motion Radar Maps:
- Accurate Forecasting: Radar maps provide valuable data for meteorologists, enabling them to issue accurate and timely weather forecasts, improving preparedness and safety.
- Public Awareness: Access to radar maps empowers individuals to stay informed about approaching storms, allowing them to take necessary precautions such as seeking shelter or delaying outdoor activities.
- Transportation Safety: Radar maps are crucial for aviation and maritime industries, providing real-time information about weather conditions that can impact flight paths and maritime navigation.
- Disaster Preparedness: By monitoring the development and movement of severe weather events, radar maps aid in emergency response and disaster preparedness efforts.
FAQs about Weather in Motion Radar Maps:
1. What types of precipitation can be detected by radar maps?
Weather in motion radar maps can detect various forms of precipitation, including rain, snow, hail, and even sleet. However, they are less effective in detecting light precipitation or very low-lying clouds.
2. How accurate are weather in motion radar maps?
Radar maps provide a relatively accurate depiction of precipitation patterns. However, their accuracy can be influenced by factors such as terrain, atmospheric conditions, and the limitations of radar technology.
3. How often are radar maps updated?
Radar maps are typically updated every few minutes, offering a continuous stream of real-time data. The frequency of updates can vary depending on the radar system and the specific weather conditions.
4. Can radar maps predict future weather events?
Radar maps primarily show the current state of weather conditions. While they can provide insights into the movement of storms, they are not designed to predict future weather events with absolute certainty.
5. Are there any limitations to radar maps?
Radar maps have limitations, including:
- Signal Attenuation: Heavy rain or dense clouds can attenuate radar signals, making it difficult to detect precipitation behind these barriers.
- Ground Clutter: Reflections from buildings, trees, and other objects can interfere with radar signals, potentially obscuring actual precipitation.
- Limited Coverage: The coverage area of radar maps is determined by the location and range of radar stations.
Tips for Interpreting Weather in Motion Radar Maps:
- Focus on the Color Scale: Pay attention to the color-coded overlays to understand the intensity of precipitation.
- Observe the Motion Arrows: The direction and speed of motion arrows indicate the movement of precipitation, helping you anticipate storm arrival.
- Consider Time Lapses: Use time lapse features to observe the progression of weather events and understand potential impacts.
- Consult Multiple Sources: Combine radar data with other sources of weather information, such as satellite imagery and weather forecasts, for a comprehensive understanding.
- Stay Informed: Regularly check radar maps, especially during periods of severe weather, to stay informed and make informed decisions.
Conclusion:
Weather in motion radar maps play a crucial role in modern weather forecasting and public safety. By providing real-time insights into precipitation patterns, these maps empower individuals and institutions to make informed decisions, prepare for potential hazards, and ensure the safety of communities. As technology continues to evolve, weather in motion radar maps are likely to become even more sophisticated, offering even greater accuracy and insights into the intricacies of our ever-changing atmosphere.

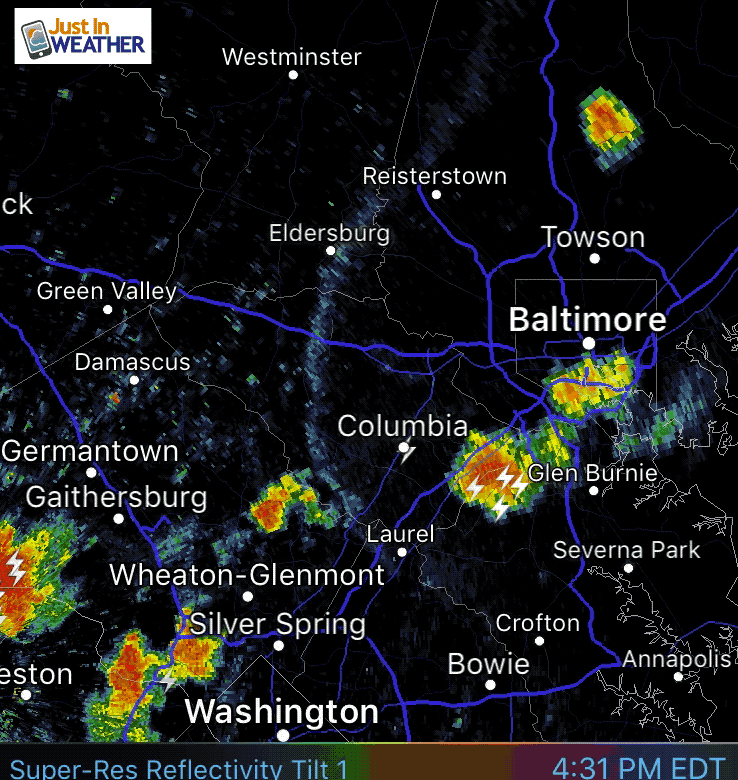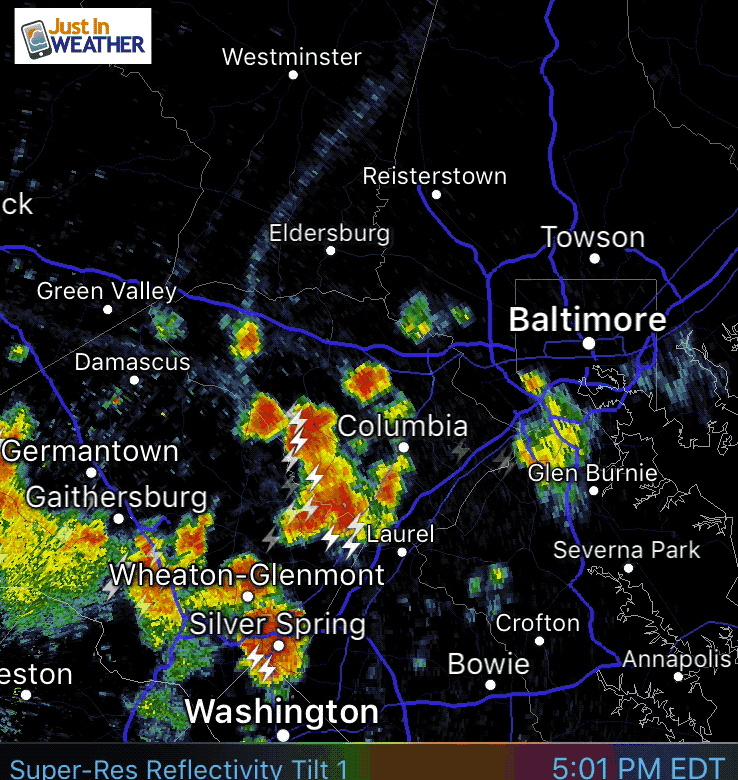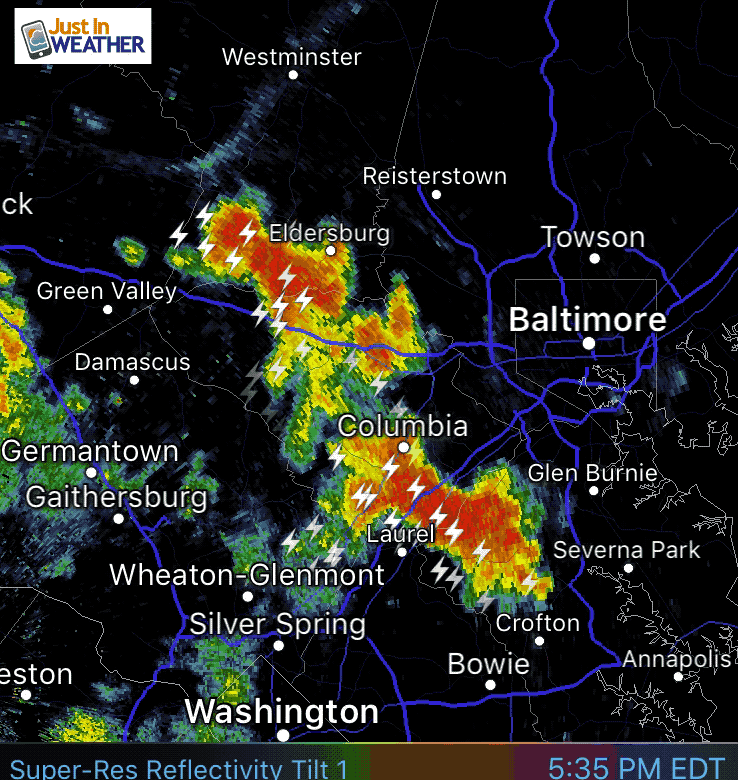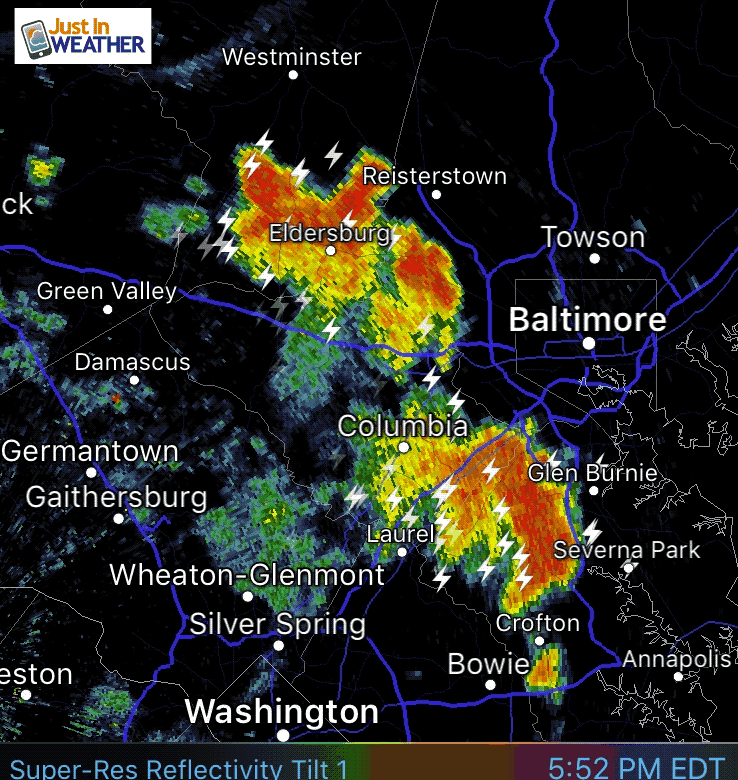

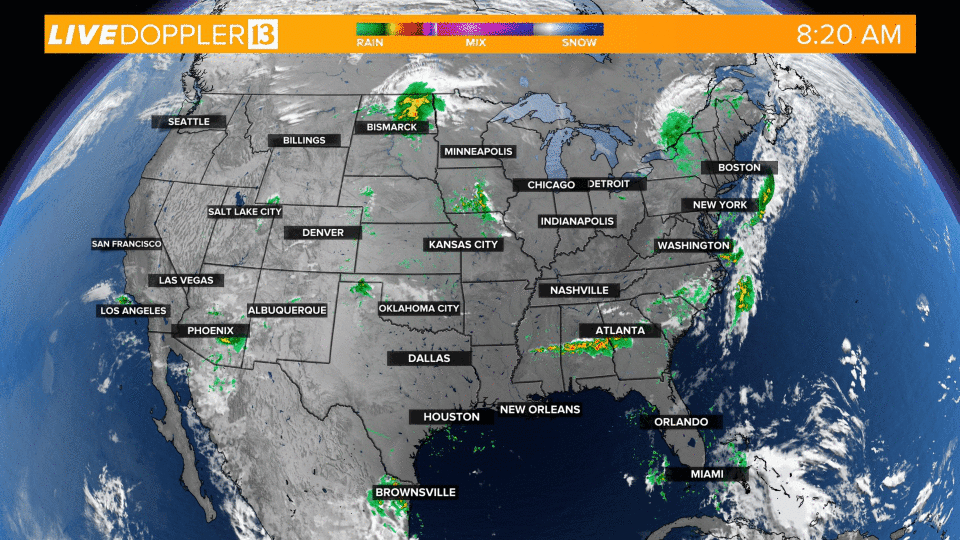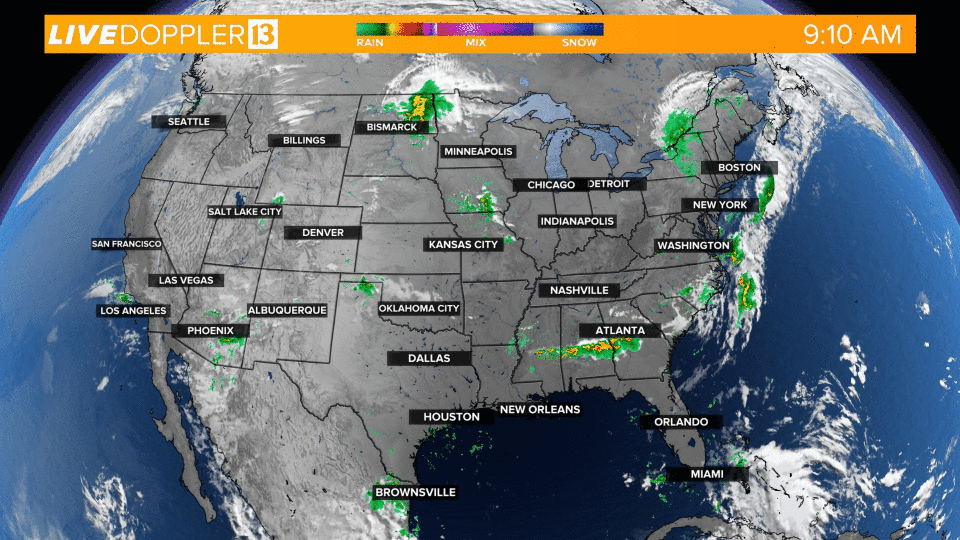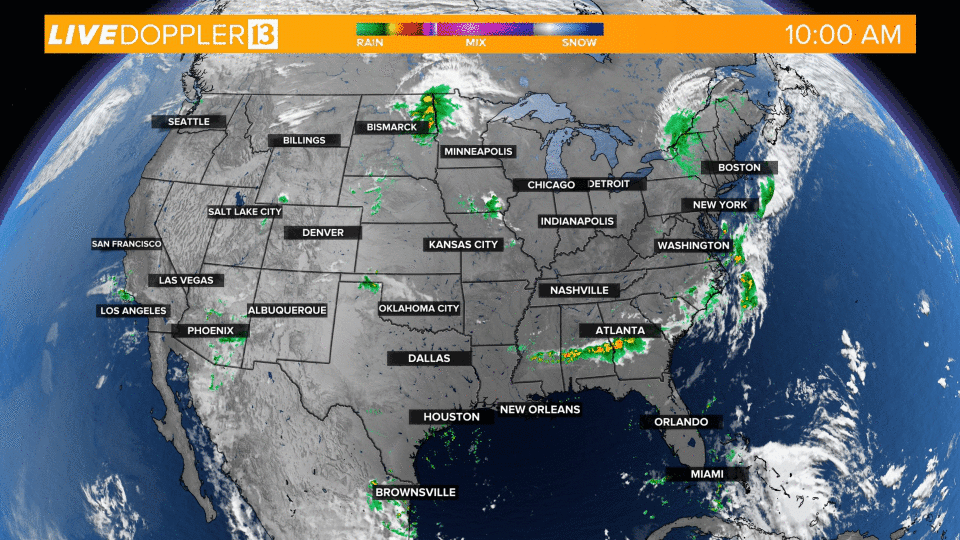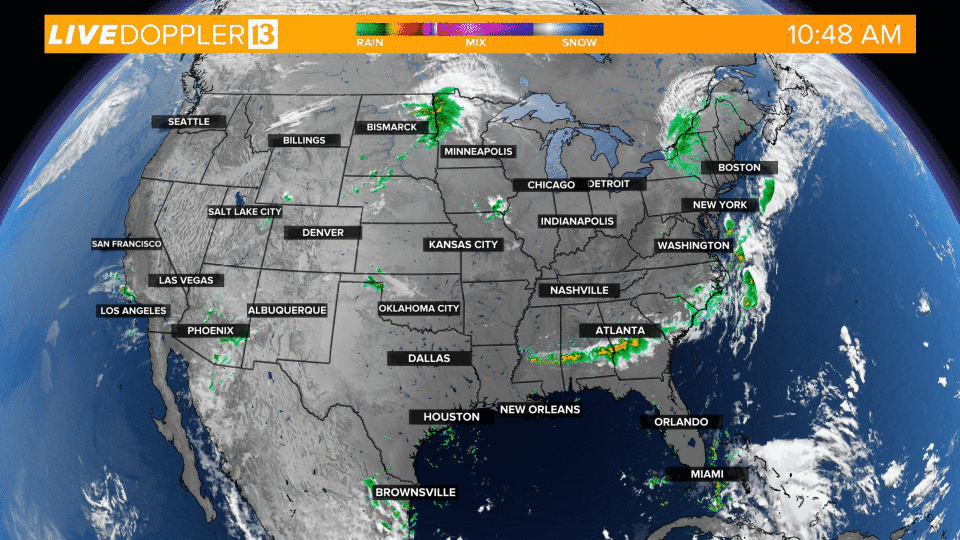

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Power of Weather in Motion Radar Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!