Unraveling Australia’s Diverse Landscapes: A Guide To The Biomes Of Australia Map
Unraveling Australia’s Diverse Landscapes: A Guide to the Biomes of Australia Map
Related Articles: Unraveling Australia’s Diverse Landscapes: A Guide to the Biomes of Australia Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling Australia’s Diverse Landscapes: A Guide to the Biomes of Australia Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling Australia’s Diverse Landscapes: A Guide to the Biomes of Australia Map
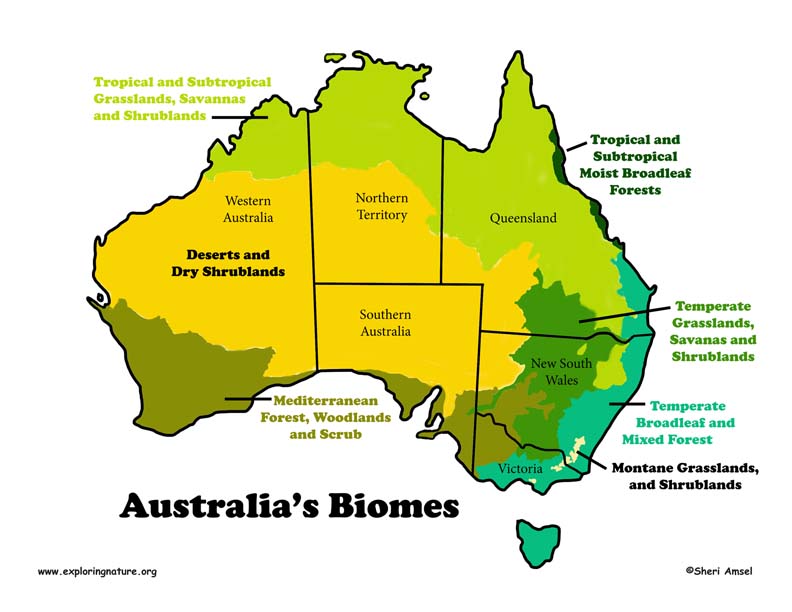
Australia, an island continent renowned for its vast and diverse landscapes, is home to a remarkable array of biomes, each characterized by unique climate, vegetation, and wildlife. Understanding the distribution of these biomes is crucial for comprehending Australia’s rich biodiversity, its ecological challenges, and the need for effective conservation strategies.
This comprehensive guide delves into the biomes of Australia, utilizing a detailed map to illustrate their spatial distribution. It aims to provide a clear understanding of the distinct characteristics of each biome, their importance for the Australian ecosystem, and the challenges they face.
A Visual Representation: The Biomes of Australia Map
The Biomes of Australia map serves as a visual tool, providing a comprehensive overview of the distribution of major biomes across the continent. Each biome is depicted with a distinct color, allowing for easy identification and comparison. This map is an invaluable resource for researchers, educators, and anyone interested in exploring the ecological diversity of Australia.
Exploring the Biomes:
1. Tropical Rainforest:
- Location: Primarily found in the northeastern part of Queensland, along the coast and extending inland.
- Climate: Characterized by high rainfall, humidity, and warm temperatures year-round.
- Vegetation: Dense, lush vegetation dominated by tall trees, including rainforest giants like the red cedar and the kauri pine.
- Wildlife: Home to an extraordinary array of endemic species, including the cassowary, the tree kangaroo, and various species of frogs, reptiles, and insects.
- Importance: These rainforests are biodiversity hotspots, playing a vital role in regulating the climate and providing essential ecosystem services.
- Challenges: Deforestation, habitat fragmentation, and invasive species pose significant threats to the survival of these unique ecosystems.
2. Temperate Forest:
- Location: Found in southeastern Australia, along the Great Dividing Range, and in Tasmania.
- Climate: Characterized by moderate rainfall, cool winters, and warm summers.
- Vegetation: Dominated by eucalyptus trees, with a diverse understory of shrubs and ferns.
- Wildlife: Home to iconic species like the koala, the grey kangaroo, and various bird species, including the lyrebird.
- Importance: These forests provide valuable timber resources, support diverse wildlife populations, and play a crucial role in carbon sequestration.
- Challenges: Logging, land clearing for agriculture, and bushfires pose significant threats to the integrity of these forests.
3. Grasslands:
- Location: Found across vast areas of inland Australia, including the plains of New South Wales, Victoria, and Queensland.
- Climate: Characterized by low rainfall, hot summers, and cool winters.
- Vegetation: Dominated by various grasses, with scattered trees and shrubs.
- Wildlife: Home to a diverse range of herbivores, including kangaroos, emus, and various rodents, as well as predators like the dingo.
- Importance: Grasslands play a crucial role in supporting livestock grazing and providing habitats for a wide range of wildlife.
- Challenges: Overgrazing, land clearing for agriculture, and invasive species threaten the health and resilience of these ecosystems.
4. Woodlands:
- Location: Found across Australia, often interspersed with grasslands and forests.
- Climate: Varies depending on location, but generally characterized by moderate rainfall and temperatures.
- Vegetation: Dominated by scattered trees, typically eucalyptus, with a diverse understory of shrubs and grasses.
- Wildlife: Home to a wide range of species, including kangaroos, wombats, and various bird species.
- Importance: Woodlands provide important habitats for wildlife, regulate water flow, and contribute to soil health.
- Challenges: Land clearing for agriculture, grazing pressure, and bushfires pose significant threats to the survival of these ecosystems.
5. Deserts:
- Location: Occupy a vast portion of central and western Australia, including the Great Victoria Desert and the Simpson Desert.
- Climate: Characterized by extremely low rainfall, high temperatures, and significant diurnal temperature variation.
- Vegetation: Sparse vegetation, adapted to harsh conditions, including spinifex grass, acacia trees, and saltbush.
- Wildlife: Home to specialized species adapted to arid conditions, including the red kangaroo, the thorny devil lizard, and various bird species.
- Importance: Deserts play a crucial role in regulating the climate, supporting unique biodiversity, and providing important cultural values for Indigenous Australians.
- Challenges: Climate change, overgrazing, and mining activities pose significant threats to the delicate balance of these ecosystems.
6. Alpine:
- Location: Found in the high-altitude regions of southeastern Australia, including the Australian Alps and Tasmania.
- Climate: Characterized by cold winters with heavy snowfall and cool, short summers.
- Vegetation: Dominated by alpine vegetation, including grasses, herbs, and shrubs, with stunted trees at lower elevations.
- Wildlife: Home to specialized alpine species, including the mountain pygmy possum, the snow gum, and various bird species.
- Importance: Alpine regions play a vital role in regulating water flow, providing habitats for unique wildlife, and offering recreational opportunities.
- Challenges: Climate change, invasive species, and recreational activities pose significant threats to the delicate balance of these ecosystems.
7. Wetlands:
- Location: Found throughout Australia, including coastal areas, inland lakes, and river systems.
- Climate: Varies depending on location, but generally characterized by high rainfall and humidity.
- Vegetation: Dominated by aquatic plants, including reeds, rushes, and water lilies.
- Wildlife: Home to a diverse range of aquatic species, including frogs, fish, birds, and reptiles.
- Importance: Wetlands play a crucial role in regulating water flow, filtering pollutants, and providing habitats for diverse wildlife.
- Challenges: Drainage, pollution, and invasive species pose significant threats to the health and integrity of these ecosystems.
8. Coastal:
- Location: Found along the extensive coastline of Australia, including beaches, dunes, and rocky shores.
- Climate: Varies depending on location, but generally characterized by moderate temperatures and high rainfall.
- Vegetation: Dominated by coastal vegetation, including dune grasses, saltbush, and mangroves.
- Wildlife: Home to a diverse range of coastal species, including seabirds, marine mammals, and reptiles.
- Importance: Coastal ecosystems provide important habitats for wildlife, protect coastlines from erosion, and offer recreational opportunities.
- Challenges: Coastal development, pollution, and climate change pose significant threats to the health and integrity of these ecosystems.
The Importance of Understanding Biomes:
The Biomes of Australia map is not merely a visual representation of geographical features; it serves as a crucial tool for understanding the complex interactions within the Australian ecosystem. By highlighting the distribution of different biomes, the map underscores the following:
- Biodiversity Conservation: The map helps identify biodiversity hotspots, allowing for targeted conservation efforts to protect unique species and their habitats.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Understanding the vulnerability of different biomes to climate change enables the development of adaptation strategies and mitigation measures.
- Sustainable Land Management: The map assists in identifying areas suitable for different land uses, promoting sustainable practices and minimizing environmental impacts.
- Ecological Restoration: By understanding the natural distribution of biomes, restoration efforts can be tailored to specific ecosystems, promoting their recovery and resilience.
FAQs about the Biomes of Australia Map:
Q: What is the largest biome in Australia?
A: The largest biome in Australia is the desert, covering a vast portion of central and western Australia.
Q: Which biome is most vulnerable to climate change?
A: The alpine biome is considered highly vulnerable to climate change, with rising temperatures and reduced snowfall threatening its unique ecosystems.
Q: How does the Biomes of Australia map help with conservation efforts?
A: The map identifies biodiversity hotspots, providing valuable information for conservation planning and targeted efforts to protect endangered species and their habitats.
Q: What are some of the key threats facing Australian biomes?
A: Major threats include habitat loss due to land clearing, invasive species, climate change, pollution, and unsustainable land management practices.
Tips for Using the Biomes of Australia Map:
- Explore the map: Use the map to identify the different biomes found in Australia and their distribution.
- Research specific biomes: Delve deeper into the characteristics, challenges, and importance of specific biomes that interest you.
- Connect with conservation organizations: Engage with organizations working to protect Australian biomes and contribute to their efforts.
- Promote awareness: Share information about the biomes of Australia and their significance with others, fostering a greater understanding and appreciation for Australia’s unique ecosystems.
Conclusion:
The Biomes of Australia map serves as a vital tool for understanding the intricate tapestry of Australia’s diverse landscapes. By highlighting the spatial distribution of these unique ecosystems, the map underscores the importance of conservation, sustainable land management, and climate change mitigation efforts. It is a reminder of the remarkable biodiversity that Australia harbors and the need for continued efforts to protect and preserve these invaluable ecosystems for future generations.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling Australia’s Diverse Landscapes: A Guide to the Biomes of Australia Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!