Unveiling The Enchanting Tapestry Of Patagonia: A Comprehensive Guide To The Region’s Map
Unveiling the Enchanting Tapestry of Patagonia: A Comprehensive Guide to the Region’s Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the Enchanting Tapestry of Patagonia: A Comprehensive Guide to the Region’s Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Enchanting Tapestry of Patagonia: A Comprehensive Guide to the Region’s Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Enchanting Tapestry of Patagonia: A Comprehensive Guide to the Region’s Map
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Enchanting Tapestry of Patagonia: A Comprehensive Guide to the Region’s Map
- 3.1 A Geographical Tapestry: Decoding the Map of Patagonia
- 3.2 Climate Zones and Their Influence on the Map
- 3.3 Exploring the Sub-Regions of Patagonia: A Detailed Look at the Map
- 3.4 The Historical and Cultural Significance of the Patagonia Map
- 3.5 The Importance of the Patagonia Region Map for Conservation
- 3.6 FAQs: Exploring the Patagonia Region Map in Depth
- 3.7 Tips for Exploring the Patagonia Region Map
- 3.8 Conclusion: Embracing the Enchanting Tapestry of Patagonia
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Enchanting Tapestry of Patagonia: A Comprehensive Guide to the Region’s Map

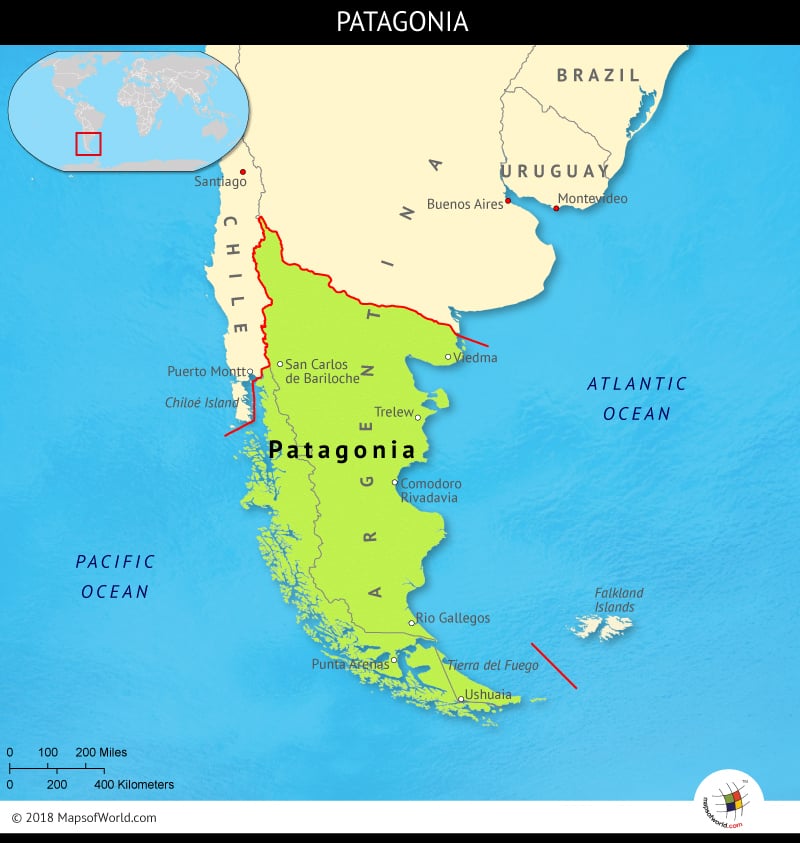
Patagonia, a land of stark beauty and untamed wilderness, stretches across the southernmost reaches of South America, encompassing parts of both Argentina and Chile. Its iconic landscapes, from towering peaks to vast glaciers, have captivated explorers and adventurers for centuries. Understanding the intricate geography of this remarkable region is crucial for appreciating its diverse ecosystems, rich cultural heritage, and unparalleled natural wonders.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the Patagonia region map, providing a detailed overview of its geographical features, climate zones, and distinct sub-regions. It further explores the historical and cultural significance of the map, highlighting its importance for navigation, exploration, and conservation efforts.
A Geographical Tapestry: Decoding the Map of Patagonia
The Patagonia region map is a visual representation of a land sculpted by time and shaped by geological forces. It encompasses a vast and diverse landscape, featuring:
- The Andes Mountains: A dominant presence throughout Patagonia, the Andes range forms a natural border between Argentina and Chile. Its snow-capped peaks, including the iconic Mount Fitz Roy and Cerro Torre, rise dramatically from the surrounding plains, creating a breathtaking spectacle.
- The Patagonian Steppe: A vast expanse of arid grasslands and scrubland, the Patagonian steppe stretches across the eastern side of the Andes, characterized by its unique flora and fauna.
- The Patagonian Ice Fields: The largest continental ice fields outside of Antarctica, the Patagonian ice fields are a mesmerizing sight, with massive glaciers carving their way through the landscape.
- The Chilean Fjords: A network of intricate waterways and islands, the Chilean fjords are a testament to the region’s dramatic coastline.
- The Strait of Magellan: A vital waterway connecting the Atlantic and Pacific oceans, the Strait of Magellan has played a significant role in exploration and trade throughout history.
Climate Zones and Their Influence on the Map
Patagonia’s climate is as diverse as its landscape. The region can be broadly divided into two distinct climate zones:
- The West Coast: Characterized by a temperate, maritime climate with heavy rainfall and frequent winds, the west coast of Patagonia experiences mild temperatures throughout the year.
- The East Coast: The east coast of Patagonia is significantly drier than the west coast, with a cold, semi-arid climate. Winters are harsh, with frequent snowfall and strong winds.
These climate variations are reflected in the vegetation patterns on the map. The west coast is home to dense rainforests and lush vegetation, while the east coast is dominated by grasslands and scrubland.
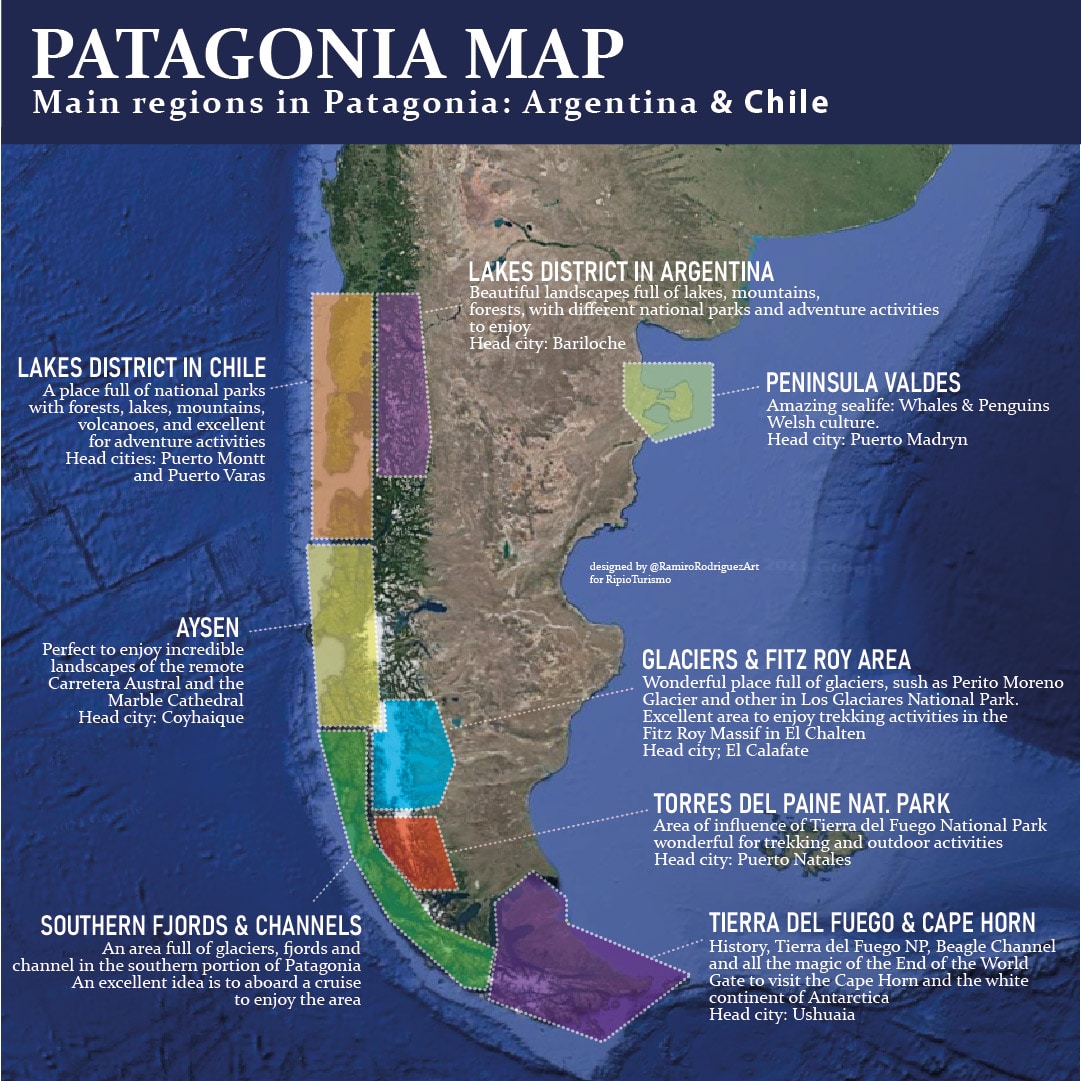
Exploring the Sub-Regions of Patagonia: A Detailed Look at the Map
The Patagonia region map is further divided into distinct sub-regions, each with its unique character and attractions:
- Northern Patagonia: This sub-region, encompassing the northern parts of Argentina and Chile, is characterized by a more temperate climate and diverse landscapes, including lakes, forests, and grasslands.
- Central Patagonia: This sub-region, stretching from the northernmost parts of the Patagonian ice fields to the Strait of Magellan, is known for its dramatic mountain scenery, glaciers, and vast grasslands.
- Southern Patagonia: This sub-region, encompassing the southernmost parts of Chile, is a land of rugged beauty, with towering mountains, glaciers, and a coastline dotted with islands and fjords.
Each sub-region offers unique opportunities for exploration and adventure, from hiking and trekking in the mountains to kayaking and sailing in the fjords.
The Historical and Cultural Significance of the Patagonia Map
The Patagonia region map has played a crucial role in the history of exploration and settlement in the region. Early explorers, including Ferdinand Magellan, used the map to navigate the treacherous waters of the Strait of Magellan, opening up new routes for trade and exploration.
The map also reflects the rich cultural heritage of the region. Indigenous tribes, including the Mapuche and Tehuelche, have inhabited Patagonia for centuries, leaving behind a legacy of traditions, languages, and stories that are woven into the fabric of the region.
The Importance of the Patagonia Region Map for Conservation
The Patagonia region map serves as a vital tool for conservation efforts, highlighting the delicate ecosystems and unique biodiversity of the region. The map helps to identify areas of ecological significance, such as the Patagonian ice fields and the Chilean fjords, which are crucial for the survival of numerous species.
Conservation organizations use the map to plan and implement strategies for protecting endangered species, managing resources, and mitigating the impact of climate change.
FAQs: Exploring the Patagonia Region Map in Depth
Q: What are the best ways to explore the Patagonia region map?
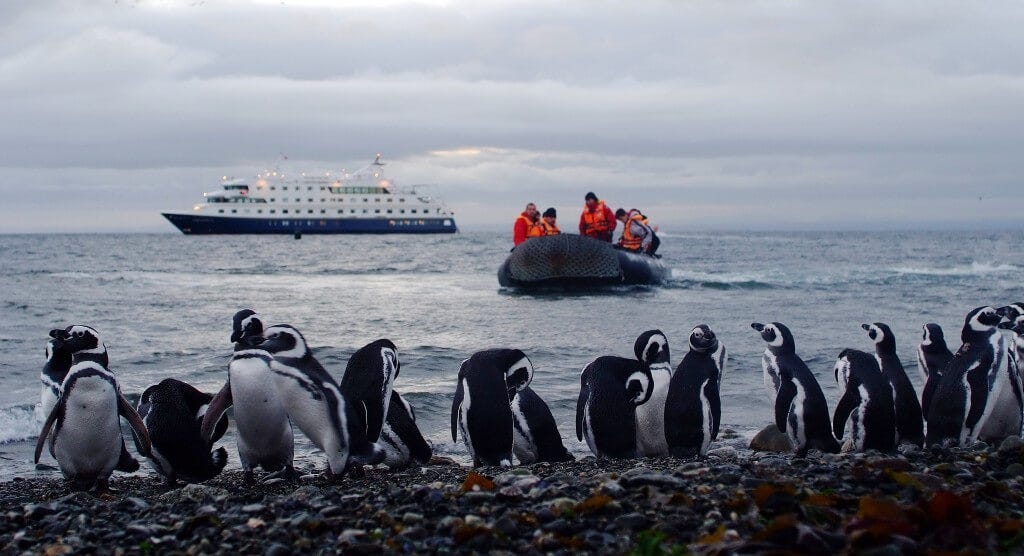
A: The best way to explore the Patagonia region map depends on your interests and preferences. For those seeking adventure, hiking and trekking are popular options, with numerous trails leading to stunning mountain peaks and glaciers. Kayaking and sailing offer a unique perspective on the region’s coastline, allowing visitors to explore the intricate fjords and islands. For those interested in wildlife, guided tours and wildlife safaris provide opportunities to observe the region’s diverse fauna, including penguins, guanacos, and condors.
Q: What are some of the key landmarks and attractions featured on the Patagonia region map?
A: The Patagonia region map is dotted with iconic landmarks and attractions, including:
- Mount Fitz Roy: A towering granite peak in the Los Glaciares National Park, Mount Fitz Roy is a popular destination for climbers and trekkers.
- Perito Moreno Glacier: A massive glacier in the Los Glaciares National Park, Perito Moreno Glacier is known for its spectacular ice calving events.
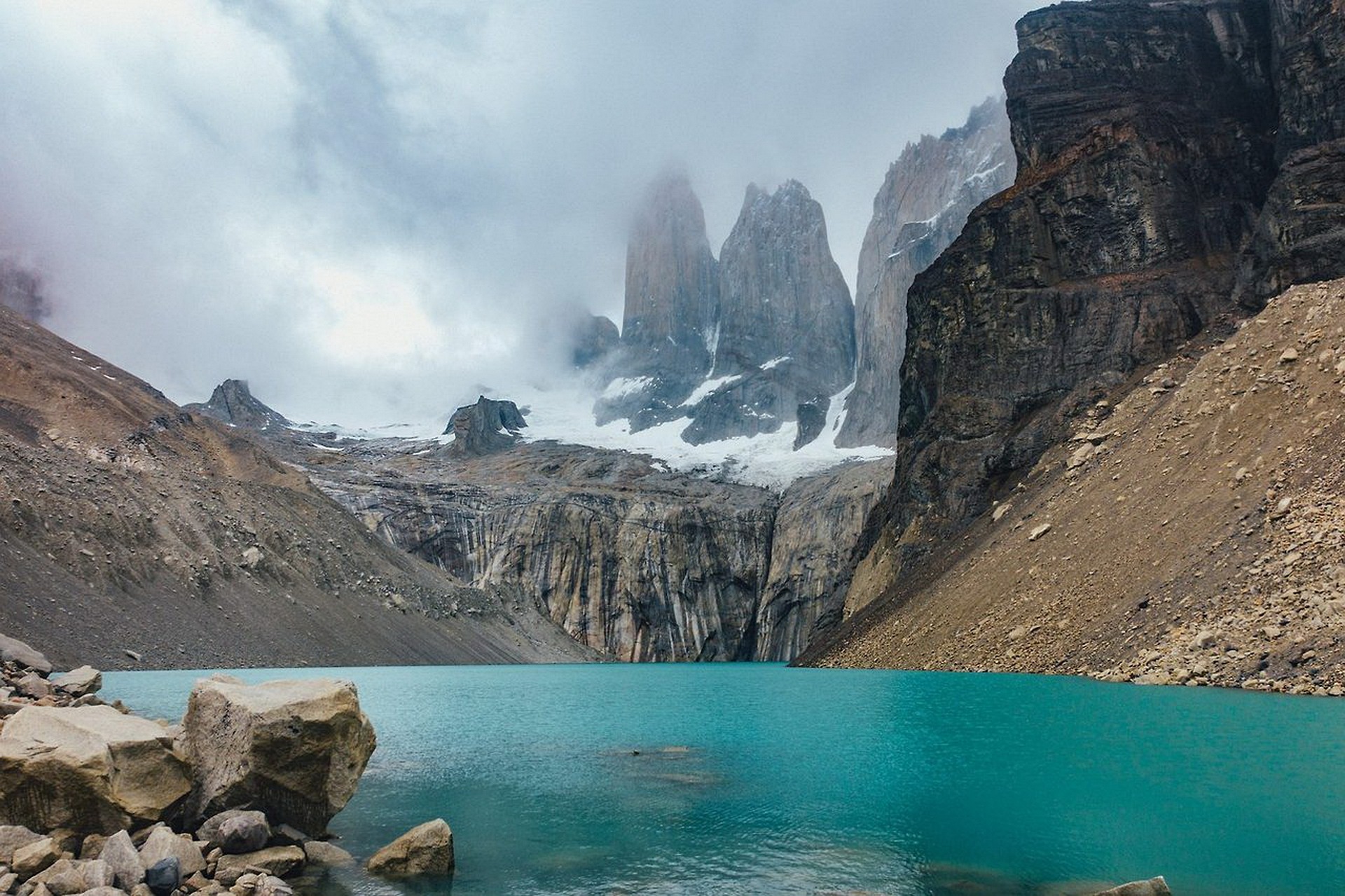
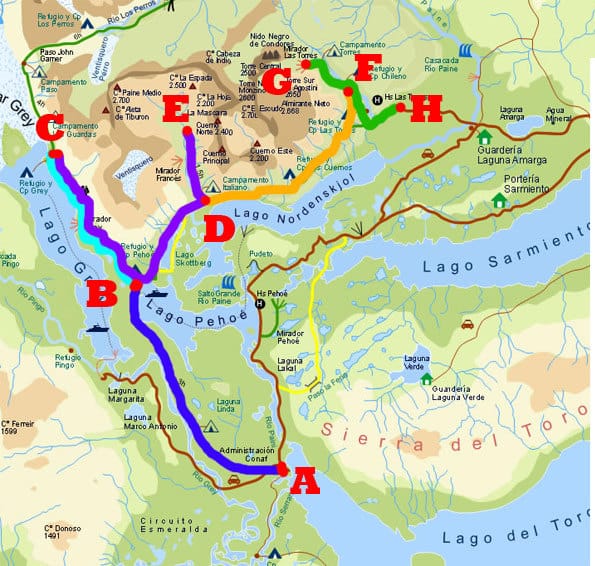
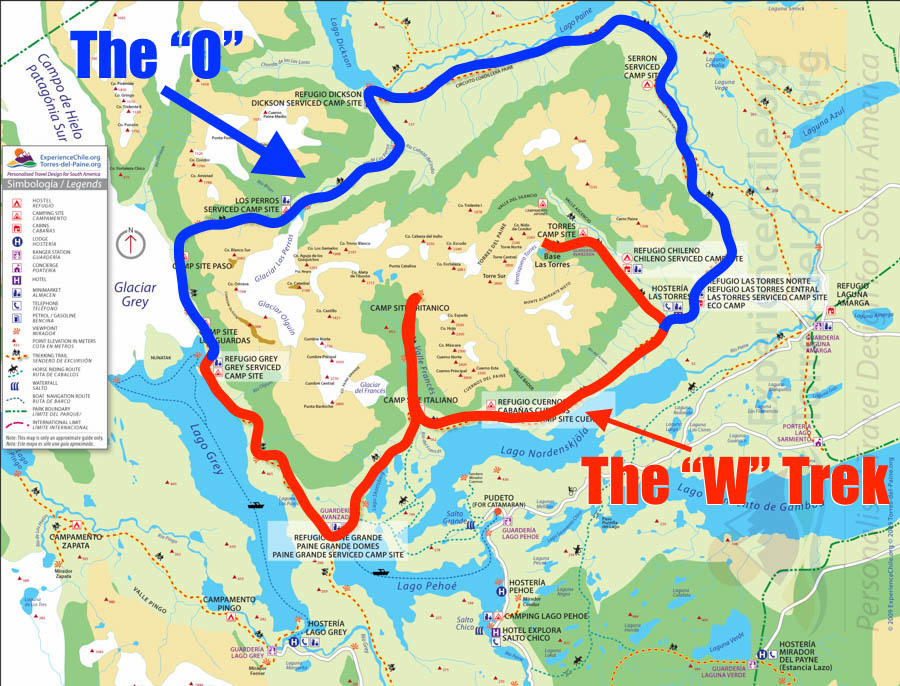
- Torres del Paine National Park: A UNESCO Biosphere Reserve, Torres del Paine National Park features towering granite peaks, glacial lakes, and diverse wildlife.
- The Strait of Magellan: A historic waterway connecting the Atlantic and Pacific oceans, the Strait of Magellan played a crucial role in exploration and trade.
- The Chilean Fjords: A network of intricate waterways and islands, the Chilean fjords offer stunning scenery and opportunities for kayaking and sailing.
Q: What are the best times to visit Patagonia?
A: The best time to visit Patagonia depends on your interests and preferences. For those seeking warmer weather and longer days, the summer months (December to February) are ideal. However, this is also the peak season, so expect larger crowds and higher prices. For those who enjoy winter activities, such as skiing and snowboarding, the winter months (June to August) offer the best conditions.
Q: What are some of the challenges of exploring Patagonia?
A: Exploring Patagonia presents unique challenges, including:
- Remote locations: Many areas of Patagonia are remote and difficult to access, requiring careful planning and preparation.
- Extreme weather: Patagonia is known for its unpredictable weather, with strong winds, heavy rainfall, and snowstorms.
- Limited infrastructure: Some areas of Patagonia have limited infrastructure, such as roads, accommodation, and communication services.
- High costs: Patagonia is a relatively expensive destination, with high costs for transportation, accommodation, and activities.
Q: What are some of the most important conservation efforts in Patagonia?
A: Conservation efforts in Patagonia focus on protecting the region’s unique ecosystems and biodiversity, including:
- Protecting the Patagonian ice fields: The Patagonian ice fields are a vital source of fresh water and play a crucial role in regulating the regional climate. Conservation efforts aim to mitigate the impact of climate change on the ice fields.
- Conserving endangered species: Patagonia is home to numerous endangered species, including the huemul deer, the Patagonian mara, and the Magellanic penguin. Conservation efforts focus on protecting their habitats and reducing threats such as poaching and habitat loss.
- Managing tourism: Tourism is a growing industry in Patagonia, but it also poses a threat to the region’s delicate ecosystems. Conservation efforts aim to manage tourism sustainably, minimizing its impact on the environment.
Tips for Exploring the Patagonia Region Map
- Plan ahead: Patagonia is a vast and diverse region, so it’s important to plan your trip carefully, considering your interests, time frame, and budget.
- Pack appropriately: Be prepared for all types of weather, including rain, wind, and snow. Pack layers of clothing, waterproof gear, and comfortable hiking boots.
- Respect the environment: Patagonia is a fragile ecosystem, so it’s important to respect the environment and minimize your impact. Leave no trace, stay on designated trails, and dispose of waste responsibly.
- Learn about the local culture: Patagonia has a rich cultural heritage, so take the time to learn about the local customs and traditions.
- Be aware of safety concerns: Patagonia is a remote and wild region, so be aware of potential safety concerns, such as wildlife encounters, weather hazards, and road conditions.
- Consider hiring a guide: For those seeking a more immersive experience, hiring a local guide can enhance your understanding of the region and provide valuable insights into its history, culture, and wildlife.
Conclusion: Embracing the Enchanting Tapestry of Patagonia
The Patagonia region map is a gateway to a land of unparalleled beauty and adventure. Its intricate geography, diverse ecosystems, and rich cultural heritage offer a unique and unforgettable experience for travelers. By understanding the map and its complexities, visitors can appreciate the region’s natural wonders and contribute to its conservation.
Whether exploring the towering peaks of the Andes, navigating the intricate fjords of the Chilean coast, or witnessing the grandeur of the Patagonian ice fields, Patagonia offers a journey of discovery and wonder. As you traverse the map, let the region’s raw beauty, untamed spirit, and enduring legacy leave an indelible mark on your soul.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Enchanting Tapestry of Patagonia: A Comprehensive Guide to the Region’s Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!