Unveiling The Global Tapestry Of Oil: A Comprehensive Guide To Oil Field Maps
Unveiling the Global Tapestry of Oil: A Comprehensive Guide to Oil Field Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Global Tapestry of Oil: A Comprehensive Guide to Oil Field Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Global Tapestry of Oil: A Comprehensive Guide to Oil Field Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Global Tapestry of Oil: A Comprehensive Guide to Oil Field Maps
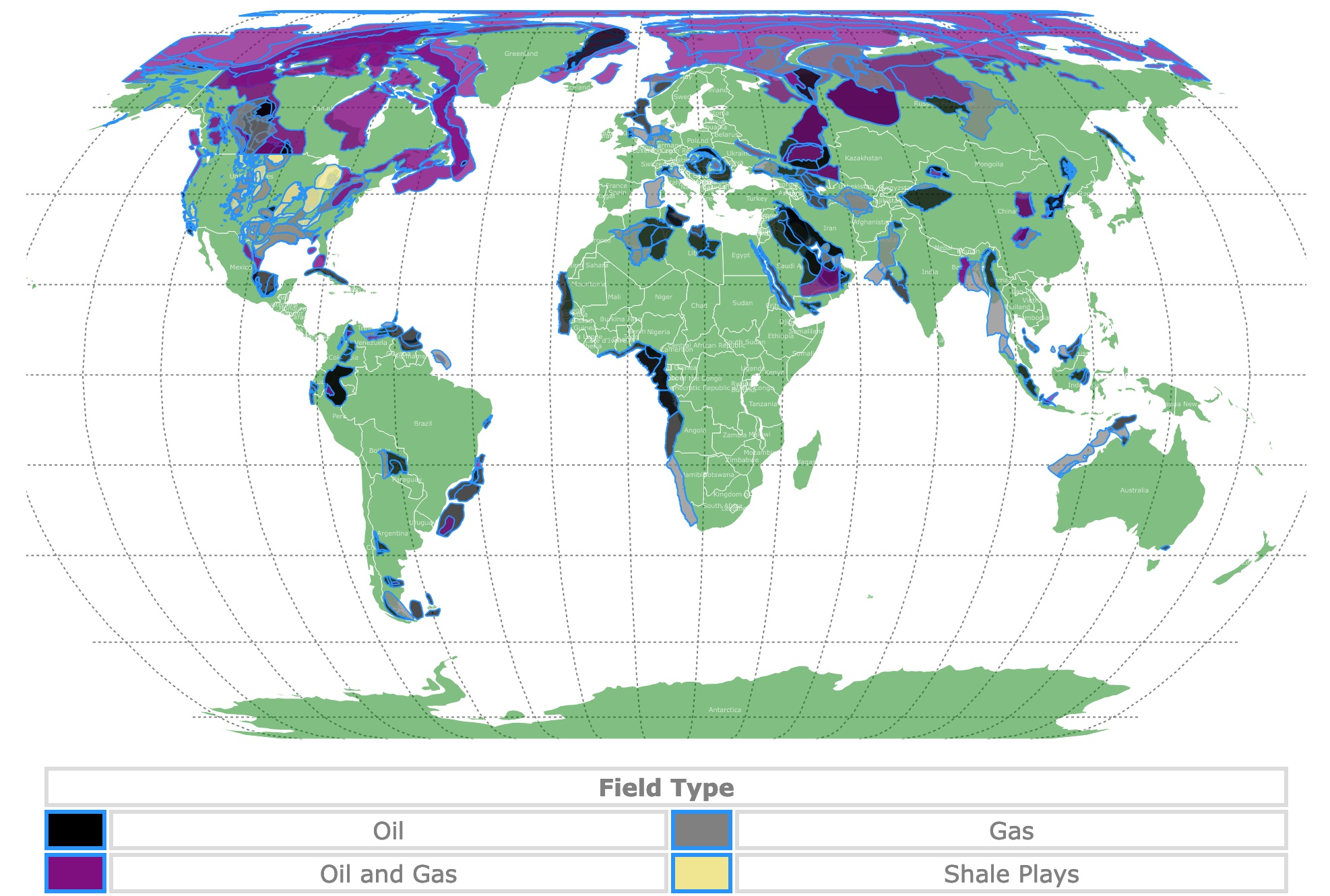
The world’s insatiable thirst for energy fuels a constant search for new resources, and oil remains a cornerstone of global energy supply. Understanding the distribution of oil reserves is crucial for policymakers, investors, and energy companies alike. This guide delves into the intricate world of oil field maps, exploring their significance, intricacies, and applications.
The Significance of Oil Field Maps
Oil field maps are not mere geographical representations; they are powerful tools that provide a visual blueprint of the world’s oil reserves. These maps serve several critical functions:
1. Exploration and Development: Oil exploration companies rely heavily on oil field maps to identify potential drilling sites. By analyzing geological formations, seismic data, and existing production data, these maps guide exploration efforts, minimizing risks and maximizing potential returns.
2. Resource Management: Maps offer a comprehensive overview of oil reserves, enabling governments and organizations to manage resources effectively. This includes estimating production capacity, planning infrastructure development, and ensuring sustainable resource utilization.
3. Investment Decisions: For investors, oil field maps provide valuable insights into the profitability and risk associated with oil exploration and production ventures. They help investors make informed decisions about where to allocate their capital, considering factors like production costs, geopolitical stability, and environmental regulations.
4. Policy Formulation: Government agencies use oil field maps to develop energy policies, including taxation strategies, environmental regulations, and strategic energy reserves. These maps inform decisions regarding energy security, international trade, and the development of alternative energy sources.
5. Educational and Research Purposes: Oil field maps are invaluable tools for academic research and education. They provide a visual representation of the global distribution of oil resources, facilitating research on energy economics, geopolitics, and environmental impact.
Types of Oil Field Maps
Oil field maps come in various forms, each serving a specific purpose:
1. Geological Maps: These maps depict the underlying geological formations, highlighting potential oil and gas reservoirs. They use colors, symbols, and contours to represent different rock types, geological structures, and potential oil traps.
2. Seismic Maps: Generated from seismic surveys, these maps show subsurface structures and potential oil and gas deposits. They use color gradients and contours to represent seismic reflections, indicating the presence of oil and gas reservoirs.
3. Production Maps: These maps showcase the location and production capacity of existing oil fields. They use symbols and colors to represent production volumes, well types, and infrastructure.
4. Exploration Maps: These maps focus on areas with potential for new oil discoveries. They depict geological structures, seismic data, and existing exploration activities, guiding future exploration efforts.
5. Regional Maps: These maps provide a comprehensive overview of oil fields within a specific geographic region. They highlight the distribution of oil reserves, production facilities, and infrastructure.
Key Features of Oil Field Maps
Oil field maps typically include the following essential features:
1. Geographic Coordinates: Latitude and longitude coordinates are crucial for pinpointing the exact location of oil fields and wells.
2. Geological Formations: Maps often highlight the presence of specific rock types, sedimentary basins, and geological structures relevant to oil and gas exploration.
3. Seismic Data: Seismic surveys provide valuable information about the subsurface structures, helping identify potential oil reservoirs.
4. Production Data: Information about oil production volumes, well types, and infrastructure is essential for understanding the economic viability of oil fields.
5. Exploration Activities: Maps may depict the location of exploration wells, seismic lines, and other activities undertaken to identify new oil deposits.
6. Legal and Regulatory Information: Maps may include information about land ownership, environmental regulations, and other legal frameworks relevant to oil exploration and production.
7. Infrastructure: Maps often showcase the location of pipelines, refineries, and other infrastructure essential for oil transportation and processing.
8. Environmental Data: Maps may include information about potential environmental impacts, such as habitat loss, water contamination, and greenhouse gas emissions.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their importance, oil field maps face certain challenges and limitations:
1. Data Availability: Obtaining accurate and comprehensive data for oil field maps can be difficult, particularly in remote or politically unstable regions.
2. Technological Limitations: Advances in technology are constantly refining our understanding of subsurface structures, leading to revisions and updates in oil field maps.
3. Environmental Considerations: The environmental impact of oil extraction is a complex issue that needs to be carefully considered when interpreting oil field maps.
4. Geopolitical Factors: Political instability, international sanctions, and territorial disputes can significantly impact the accessibility and development of oil fields.
5. Technological Advancements: The discovery of unconventional oil resources, such as shale oil and tar sands, has added complexity to oil field maps and resource assessments.
FAQs Regarding Oil Field Maps
1. What is the difference between a geological map and a seismic map?
Geological maps depict the surface geology, while seismic maps provide a visual representation of subsurface structures based on seismic data.
2. How are oil field maps used in exploration?
Oil exploration companies use oil field maps to identify potential drilling sites, analyze geological formations, and assess the risk associated with exploration ventures.
3. What are the main sources of data for oil field maps?
Data for oil field maps comes from geological surveys, seismic surveys, satellite imagery, well logs, and production data.
4. How can oil field maps be used to promote sustainable oil production?
Oil field maps can help identify areas with the least environmental impact, inform the development of responsible extraction practices, and guide the transition to cleaner energy sources.
5. What are the implications of technological advancements on oil field maps?
New technologies, such as 3D seismic imaging and artificial intelligence, are continuously improving the accuracy and detail of oil field maps, leading to more efficient exploration and production.
Tips for Understanding Oil Field Maps
1. Pay attention to the scale and projection of the map. Understanding the scale and projection helps interpret the map’s accuracy and geographic coverage.
2. Familiarize yourself with the symbols and colors used on the map. Each symbol and color represents specific geological features, production data, or infrastructure.
3. Consider the context of the map. Understanding the time period, data sources, and purpose of the map is essential for accurate interpretation.
4. Seek expert advice when interpreting complex maps. Consulting with geologists, geophysicists, or other experts can provide valuable insights into the information presented on oil field maps.
5. Stay informed about advancements in oil exploration and production technology. New technologies continuously refine our understanding of oil reserves and impact the interpretation of oil field maps.
Conclusion
Oil field maps serve as a vital tool for understanding the global distribution of oil reserves, guiding exploration efforts, informing investment decisions, and shaping energy policies. They provide a visual representation of the complexities of oil production, highlighting the challenges and opportunities associated with this critical energy resource. As technology advances and global energy demands evolve, oil field maps will continue to play a crucial role in navigating the complex landscape of oil exploration, production, and resource management.
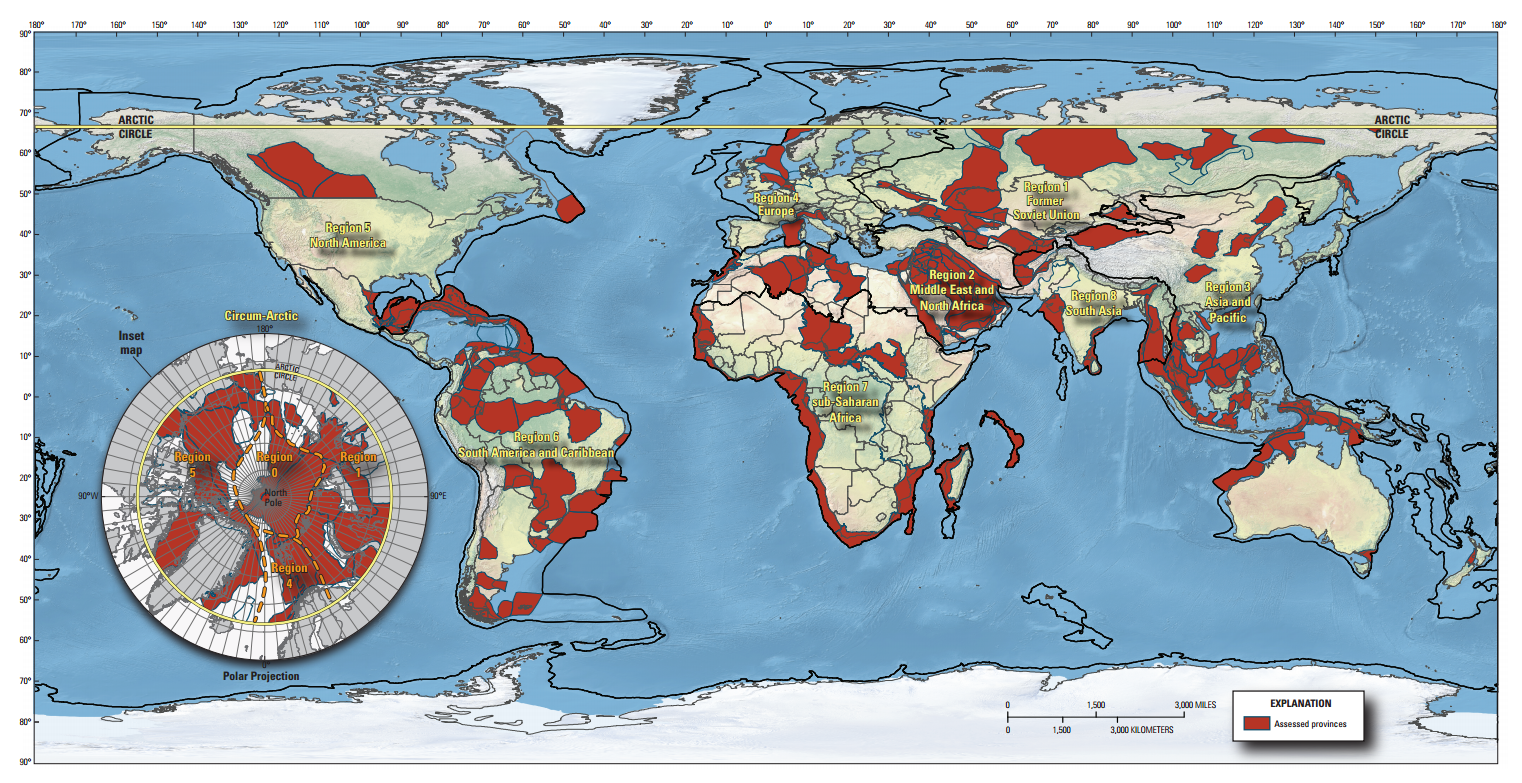
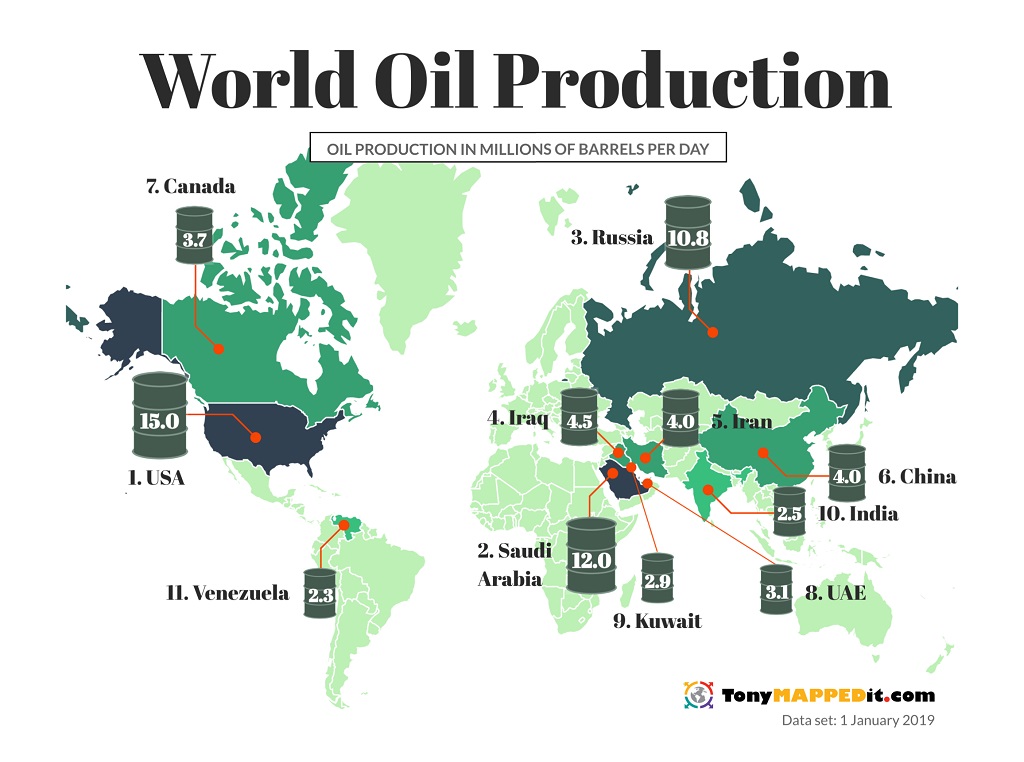
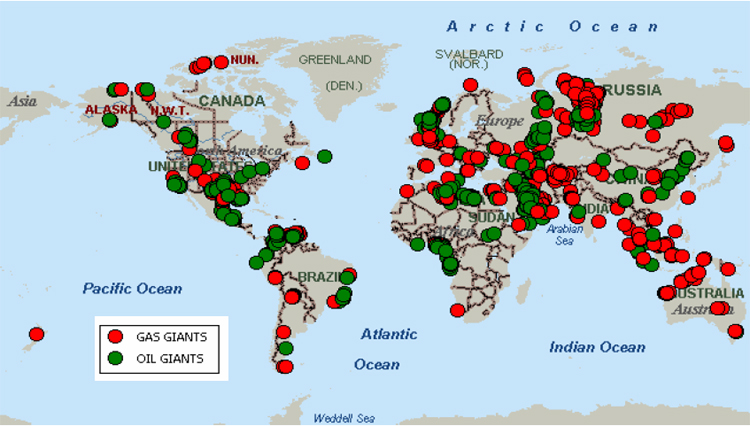

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Global Tapestry of Oil: A Comprehensive Guide to Oil Field Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!