Unveiling The Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To Creating Perceptual Maps
Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating Perceptual Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating Perceptual Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating Perceptual Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating Perceptual Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating Perceptual Maps
- 3.1 Defining the Terrain: Understanding the Essence of Perceptual Maps
- 3.2 The Art of Creation: A Step-by-Step Guide to Constructing Perceptual Maps
- 3.3 Unveiling the Benefits: Why Perceptual Maps are Essential for Businesses
- 3.4 Navigating the FAQs: Addressing Common Questions About Perceptual Maps
- 3.5 Charting a Course: Tips for Effective Perceptual Map Creation
- 3.6 Conclusion: Unlocking the Power of Perceptual Maps for Strategic Success
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating Perceptual Maps
In the competitive landscape of today’s marketplace, understanding consumer perception is paramount for businesses seeking to thrive. A powerful tool for achieving this understanding is the perceptual map. This visual representation, akin to a strategic roadmap, allows businesses to analyze and visualize how consumers perceive their brand and its competitors within a specific market. By pinpointing key attributes and positioning, perceptual maps empower organizations to identify opportunities for differentiation, refine marketing strategies, and ultimately, gain a competitive edge.
Defining the Terrain: Understanding the Essence of Perceptual Maps
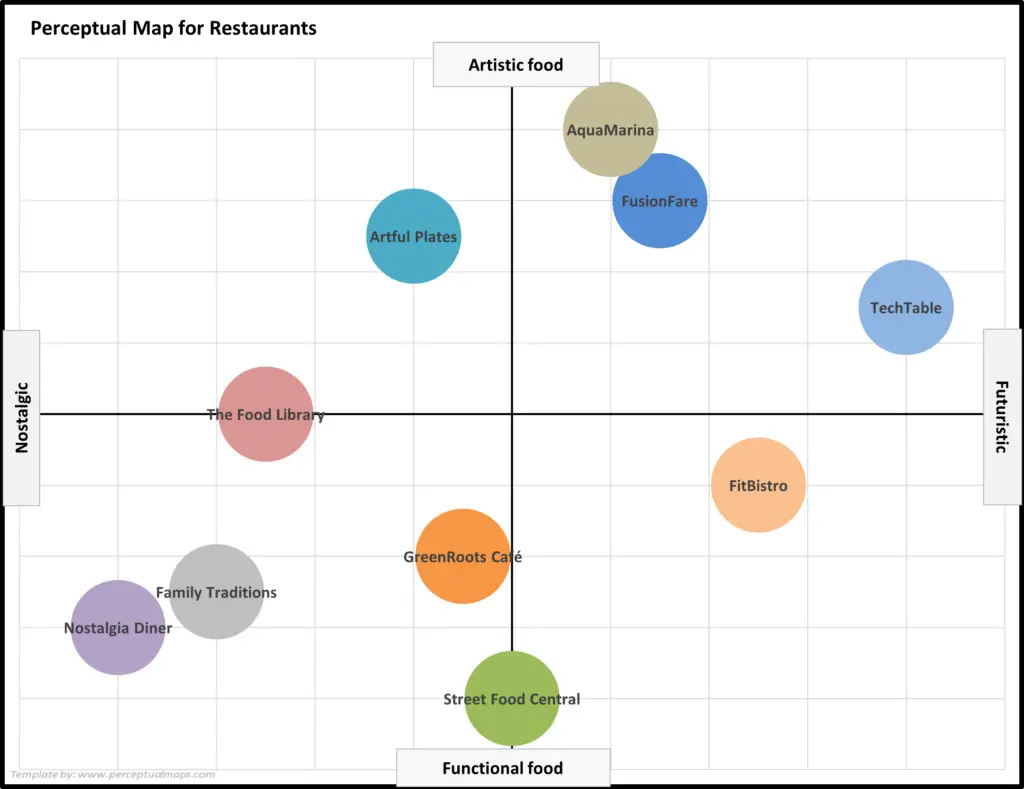
At its core, a perceptual map is a graphical depiction of consumer perceptions about competing products or brands within a given market. It employs a two-dimensional framework, typically using two key attributes, to plot various offerings based on how consumers perceive them. These attributes can be any relevant factors that influence purchase decisions, such as price, quality, features, brand image, or customer service.
For instance:
- A map for the smartphone market might use "Price" and "Camera Quality" as attributes.
- A map for the automobile industry could utilize "Fuel Efficiency" and "Luxury Features."
By positioning brands or products on this map, businesses gain valuable insights into:
- Consumer Preferences: Identifying the attributes that consumers prioritize when making purchase decisions.
- Competitive Landscape: Understanding how competitors are perceived and where they stand in relation to the brand.
- Market Gaps: Spotting potential opportunities for differentiation and offering unique value propositions.
The Art of Creation: A Step-by-Step Guide to Constructing Perceptual Maps
Crafting a meaningful and effective perceptual map requires a systematic approach. The process can be broken down into these key steps:
1. Defining the Target Market and Attributes:
- Identify the relevant market: Clearly define the specific product or service category and the target audience.
- Select key attributes: Choose two or three attributes that are most important to consumers within this market. These attributes should be distinct, measurable, and relevant to the purchase decision.
- Consider using quantitative data: Employ market research data, customer surveys, or focus group discussions to gather information about consumer perceptions.
2. Gathering Data and Generating Perceptions:
- Conduct surveys: Utilize structured questionnaires to collect data on consumer perceptions of brands or products along the chosen attributes.
- Utilize existing data: Leverage existing market research reports, customer reviews, or industry analysis to inform your understanding of consumer perceptions.
- Employ scaling techniques: Use rating scales, such as Likert scales, to quantify consumer responses and facilitate accurate plotting on the map.
3. Constructing the Map:
- Create a two-dimensional grid: Use a graph with the chosen attributes as the axes.
- Plot brands or products: Position each brand or product based on its perceived standing on each attribute.
- Use visual aids: Employ different symbols, colors, or sizes to represent brands or products on the map.
4. Analyzing the Map and Drawing Insights:
- Identify clusters: Observe groupings of brands based on their perceived similarities.
- Analyze brand positioning: Determine the relative positioning of each brand in relation to its competitors.
- Identify potential opportunities: Spot gaps in the market or areas where a brand can differentiate itself.
Unveiling the Benefits: Why Perceptual Maps are Essential for Businesses
Perceptual maps offer a multitude of advantages for organizations seeking to gain a competitive edge in the marketplace. They provide valuable insights that can inform strategic decision-making across various departments, including marketing, product development, and sales.
1. Competitive Analysis:
- Benchmarking: Perceptual maps allow businesses to compare their brand’s positioning against competitors, identifying strengths, weaknesses, and potential areas for improvement.
- Identifying market gaps: By analyzing the map, businesses can identify underserved segments or opportunities for differentiation, potentially leading to the development of new products or services.
2. Marketing Strategy Development:
- Targeting: Perceptual maps can help businesses understand which consumer segments are most receptive to their offerings and tailor marketing messages accordingly.
- Positioning: The map can be used to refine brand positioning and messaging, ensuring that it resonates with the target audience and differentiates the brand from competitors.
3. Product Development and Innovation:
- Product differentiation: Perceptual maps highlight areas where businesses can innovate and develop products or services that address unmet consumer needs or offer unique value propositions.
- New product development: By understanding consumer perceptions, businesses can identify potential gaps in the market and develop new products that align with consumer preferences.
4. Sales and Customer Relationship Management:
- Sales targeting: Perceptual maps can help sales teams focus their efforts on segments that are most likely to be receptive to their offerings.
- Customer service: By understanding customer perceptions, businesses can tailor their customer service approach to better meet customer expectations and build stronger relationships.
Navigating the FAQs: Addressing Common Questions About Perceptual Maps
1. What data sources can be used to create a perceptual map?
A variety of data sources can be utilized, including:
- Customer surveys: Structured questionnaires that gather direct feedback from consumers on their perceptions of brands or products.
- Market research reports: Industry reports and studies that provide insights into consumer preferences and market trends.
- Focus group discussions: Qualitative data gathering techniques that involve group discussions with consumers to understand their perceptions.
- Social media analytics: Analyzing social media data to gauge consumer sentiment and brand perception.
- Sales data: Examining sales figures to identify trends and patterns in consumer purchasing behavior.
2. How many attributes should be used in a perceptual map?
Generally, two or three attributes are sufficient to create a clear and informative map. Using too many attributes can make the map cluttered and difficult to interpret.
3. How can I ensure that the chosen attributes are truly relevant?
- Market research: Conduct thorough market research to identify the attributes that are most important to consumers within the target market.
- Customer feedback: Seek feedback from existing customers about the factors that influence their purchasing decisions.
- Industry analysis: Analyze industry trends and competitive offerings to identify the key attributes that drive consumer choice.
4. What are some common pitfalls to avoid when creating perceptual maps?
- Using too many attributes: Overcrowding the map can make it difficult to interpret.
- Ignoring qualitative data: While quantitative data is important, qualitative data can provide valuable insights into the nuances of consumer perceptions.
- Not updating the map regularly: Market dynamics are constantly changing, so it’s essential to update the map periodically to reflect evolving consumer preferences and competitor positioning.
5. How can I use a perceptual map to inform my marketing strategy?
- Target marketing: Identify the consumer segments that are most receptive to your offerings based on their perceived needs and preferences.
- Positioning: Develop a clear and compelling brand positioning that resonates with the target audience and differentiates your brand from competitors.
- Messaging: Tailor your marketing messages to address the key attributes that drive consumer decisions and highlight your brand’s unique value proposition.
Charting a Course: Tips for Effective Perceptual Map Creation
1. Clarity is Key:
- Simple and understandable: Keep the map clear and easy to understand, using straightforward language and visual aids.
- Focus on key attributes: Prioritize the most relevant attributes to avoid cluttering the map.
- Use consistent scaling: Employ a consistent scaling system for the attributes to ensure accurate positioning of brands.
2. Data-Driven Insights:
- Validate data sources: Ensure that the data used to create the map is reliable and representative of the target market.
- Consider both quantitative and qualitative data: Integrate both types of data to gain a comprehensive understanding of consumer perceptions.
- Utilize statistical analysis: Employ statistical techniques to identify significant patterns and trends in the data.
3. Visual Appeal and Interpretation:
- Use visually appealing graphics: Employ clear and concise visuals to enhance the map’s readability and impact.
- Highlight key findings: Use annotations, arrows, or color coding to draw attention to important insights and areas of opportunity.
- Encourage discussion and collaboration: Share the map with relevant stakeholders to foster discussion and generate strategic insights.
Conclusion: Unlocking the Power of Perceptual Maps for Strategic Success
Perceptual maps are a powerful tool for businesses seeking to understand consumer perceptions, analyze the competitive landscape, and inform strategic decision-making. By visually representing consumer perceptions, these maps provide valuable insights into market dynamics, consumer preferences, and brand positioning.
By following a systematic approach to map creation, businesses can effectively leverage this tool to:
- Identify opportunities for differentiation: Uncover areas where they can offer unique value propositions and stand out from competitors.
- Refine marketing strategies: Develop targeted marketing messages and campaigns that resonate with the target audience and address their key needs and preferences.
- Drive innovation: Identify potential product or service gaps in the market and develop new offerings that align with consumer expectations.
Ultimately, the success of a perceptual map lies in its ability to translate complex consumer perceptions into actionable insights that drive strategic decision-making and propel businesses towards sustainable growth and success.
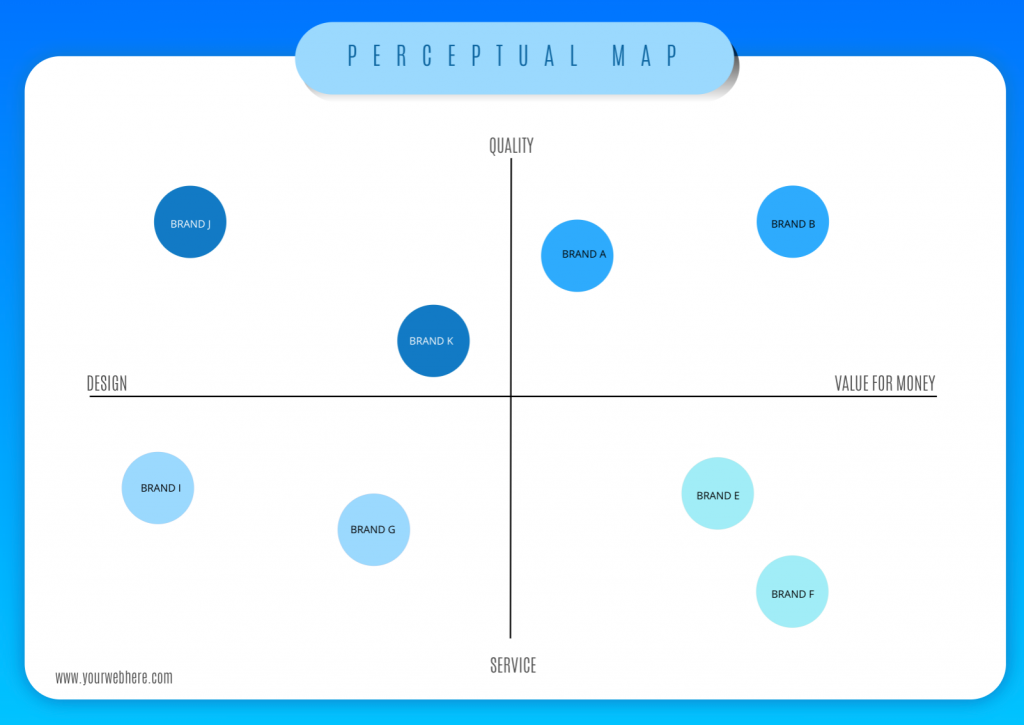
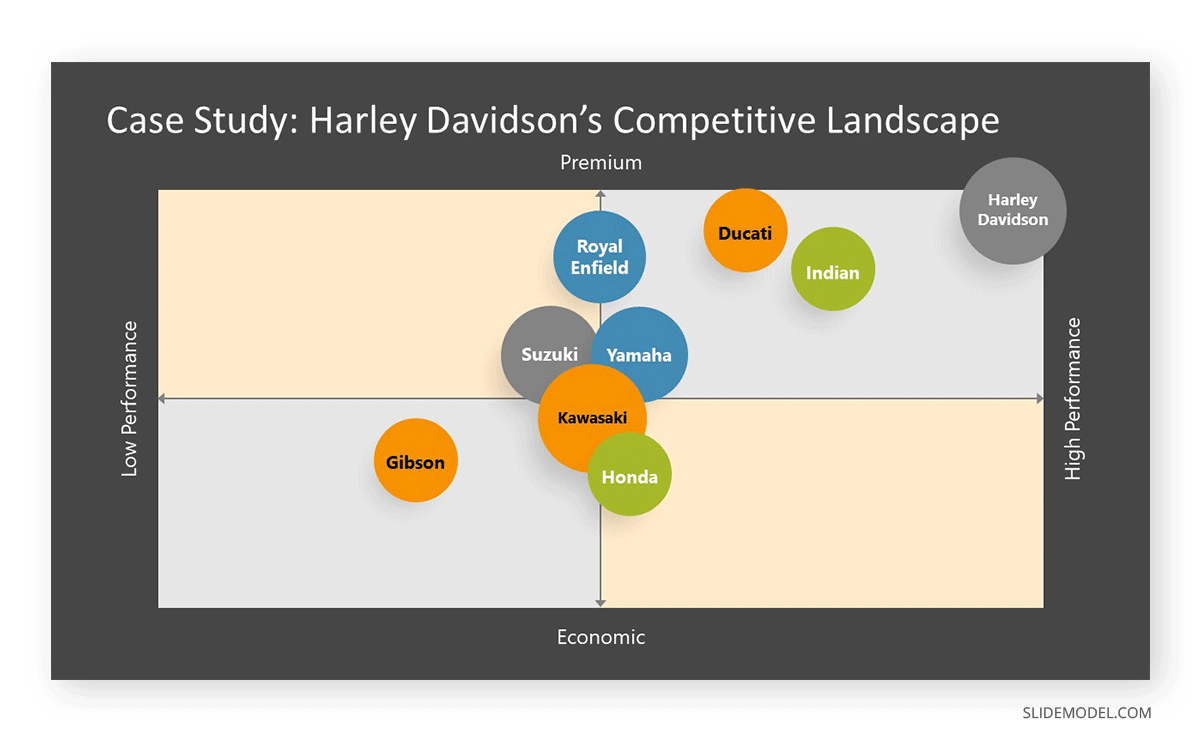
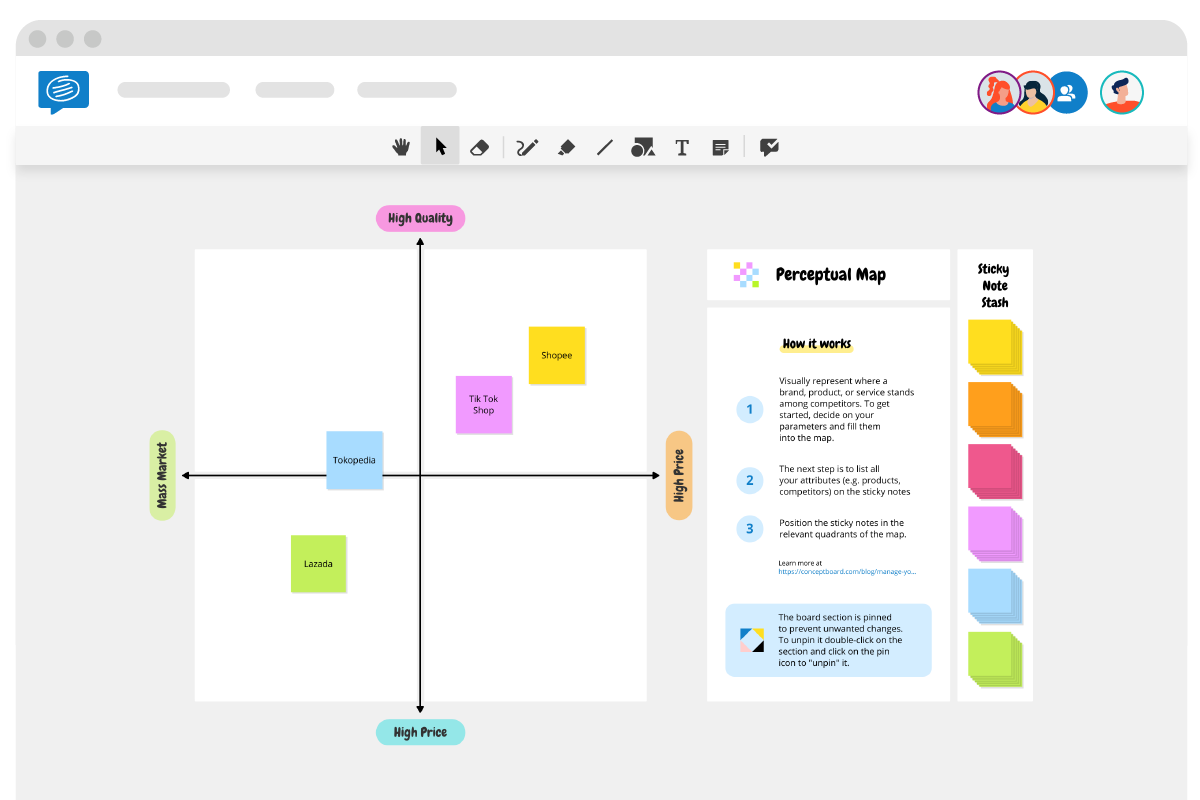


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating Perceptual Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!