Unveiling The Mughal Empire: A Cartographic Journey Through Time
Unveiling the Mughal Empire: A Cartographic Journey Through Time
Related Articles: Unveiling the Mughal Empire: A Cartographic Journey Through Time
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Mughal Empire: A Cartographic Journey Through Time. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Mughal Empire: A Cartographic Journey Through Time

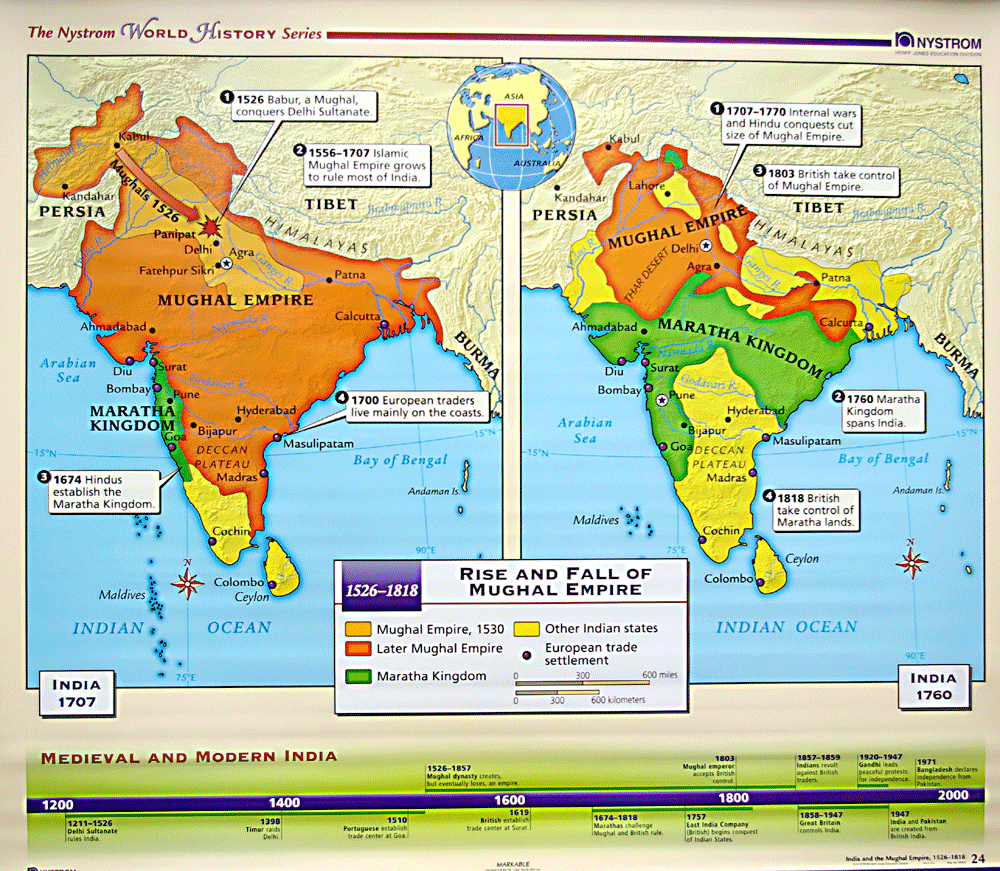
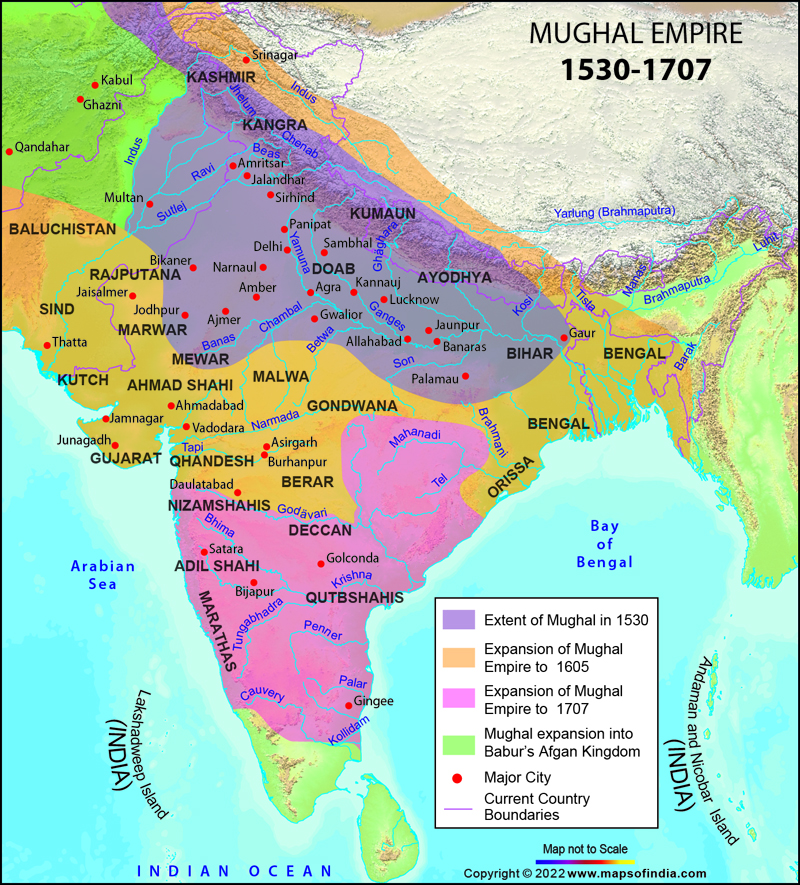
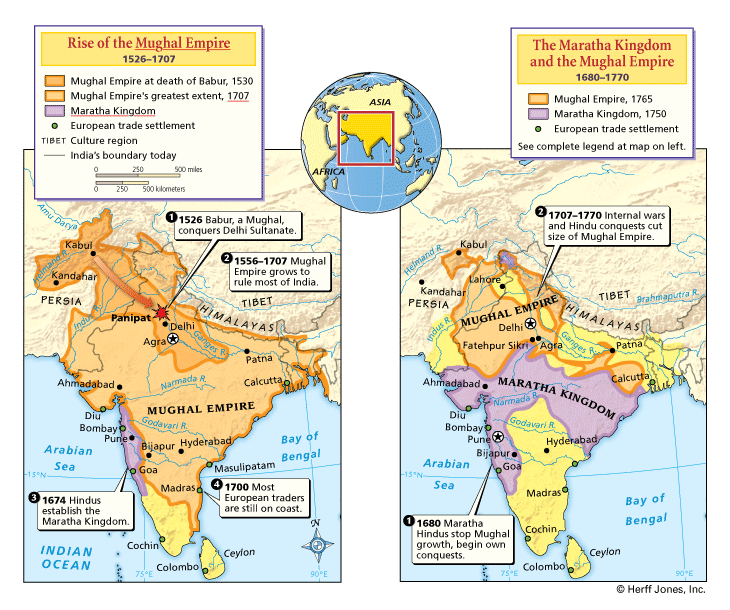
The Mughal Empire, a sprawling and vibrant dominion that dominated much of the Indian subcontinent for centuries, left behind a rich tapestry of art, architecture, and culture. Among its many legacies, cartography stands out as a crucial tool for understanding the empire’s vastness, administrative structure, and cultural nuances.
A Window into the Mughal World:
Mughal maps, crafted with meticulous detail and artistic flair, offer a unique glimpse into the empire’s multifaceted world. These maps, often commissioned by emperors and officials, served various purposes:
- Administrative Control: Maps provided a visual representation of the empire’s vast territories, aiding in efficient governance and resource management. They helped track revenue collection, military deployments, and the movement of goods.
- Strategic Planning: Military campaigns and conquests were meticulously planned using maps, highlighting key locations, terrain features, and potential routes of attack or defense.
- Cultural Significance: Maps were not merely utilitarian tools but also artistic expressions. Elaborate illustrations, decorative elements, and inscriptions reflected the cultural values and aesthetic sensibilities of the Mughal court.
Types of Mughal Maps:
Mughal cartography encompasses a diverse range of maps, each serving a specific purpose:
- Military Maps: These maps focused on strategic locations, fortifications, and routes of communication. They were essential for planning military campaigns and maintaining control over the empire’s vast borders.
- Revenue Maps: These maps detailed land ownership, agricultural productivity, and revenue collection, enabling efficient tax administration and resource allocation.
- City Plans: Detailed maps of major cities, like Delhi and Agra, provided insights into urban planning, infrastructure, and social organization.
- Regional Maps: Maps depicting specific regions, such as the Deccan or Punjab, highlighted local topography, important cities, and trade routes.
- World Maps: While less common, some Mughal maps attempted to depict the known world, incorporating elements of Islamic geography and European cartographic influences.
The Art of Mughal Cartography:
Mughal maps were not mere schematic representations but works of art in their own right. They incorporated intricate details, vibrant colors, and decorative elements that reflected the artistic traditions of the time.
- Artistic Conventions: Mughal mapmakers employed a unique blend of Persian, Indian, and European cartographic conventions. They often used a combination of geometric projections, compass directions, and symbolic representations to depict geographical features.
- Decorative Elements: Maps were adorned with intricate borders, floral motifs, and miniature paintings, reflecting the aesthetic sensibilities of the Mughal court.
- Inscriptions: Maps frequently included inscriptions in Persian, Arabic, or Sanskrit, providing information about the map’s purpose, creator, and date of creation.
Key Figures in Mughal Cartography:
Several prominent figures played a pivotal role in shaping the development of Mughal cartography:
- Emperor Akbar: Akbar, the third Mughal emperor, was a patron of the arts and sciences, including cartography. He commissioned the creation of numerous maps, including the renowned "Akbarnama," a historical chronicle that included detailed maps of the empire.
- Mirza Muhammad Haidar: A skilled cartographer and historian, Mirza Muhammad Haidar created a series of maps depicting the Mughal Empire and its surrounding regions. His maps are known for their accuracy and detailed representations of geographical features.
- The Portuguese: European cartographers, particularly the Portuguese, influenced Mughal cartography. They introduced new techniques and instruments, such as the astrolabe and compass, which improved the accuracy of mapmaking.
The Importance of Mughal Maps:
Mughal maps are invaluable historical documents that provide insights into the empire’s political, economic, and cultural landscape. They offer a unique perspective on:
- Territorial Expansion: Maps document the empire’s gradual expansion, highlighting its territorial boundaries and key conquests.
- Administrative Structure: They reveal the complex administrative structure of the empire, including the organization of provinces, districts, and revenue collection systems.
- Cultural Influences: The decorative elements and inscriptions on maps reflect the fusion of Persian, Indian, and European cultural influences in the Mughal court.
- Trade and Commerce: Maps highlight major trade routes, ports, and centers of commerce, providing insights into the economic activities of the empire.
- Urban Planning: City plans reveal the sophisticated urban planning of Mughal cities, including the layout of streets, public spaces, and architectural features.
FAQs about Mughal Maps:
Q: What materials were used to create Mughal maps?
A: Mughal mapmakers used a variety of materials, including paper, parchment, and cloth. They often used inks and pigments derived from natural sources to create their maps.
Q: How were Mughal maps used in military campaigns?
A: Military maps helped commanders plan campaigns, identify strategic locations, and assess the terrain. They also facilitated communication and coordination among different units.
Q: What is the significance of inscriptions on Mughal maps?
A: Inscriptions provide valuable information about the map’s purpose, creator, date of creation, and sometimes even historical events. They offer insights into the cultural context of the map.
Q: How did European cartography influence Mughal mapmaking?
A: European cartographers introduced new techniques, instruments, and concepts, such as the use of the astrolabe and compass, which improved the accuracy and detail of Mughal maps.
Q: Where can we find Mughal maps today?
A: Mughal maps are housed in museums, libraries, and private collections around the world. Some notable repositories include the British Library, the Victoria and Albert Museum, and the National Archives of India.
Tips for Studying Mughal Maps:
- Examine the details: Pay close attention to the geographical features, decorative elements, and inscriptions on the map.
- Consider the context: Understand the historical, political, and cultural context in which the map was created.
- Compare different maps: Compare maps from different periods to observe changes in cartographic techniques, artistic styles, and the empire’s territorial boundaries.
- Consult secondary sources: Refer to scholarly books, articles, and online resources to gain a deeper understanding of Mughal cartography.
Conclusion:
Mughal maps are not merely historical documents; they are windows into the empire’s multifaceted world. They offer a unique perspective on the empire’s vastness, administrative structure, cultural influences, and artistic sensibilities. By studying these maps, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and dynamism of the Mughal Empire and its enduring legacy.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Mughal Empire: A Cartographic Journey Through Time. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!