Unveiling The Topography Of India: A Comprehensive Look At The Elevation Map
Unveiling the Topography of India: A Comprehensive Look at the Elevation Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the Topography of India: A Comprehensive Look at the Elevation Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Topography of India: A Comprehensive Look at the Elevation Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Topography of India: A Comprehensive Look at the Elevation Map
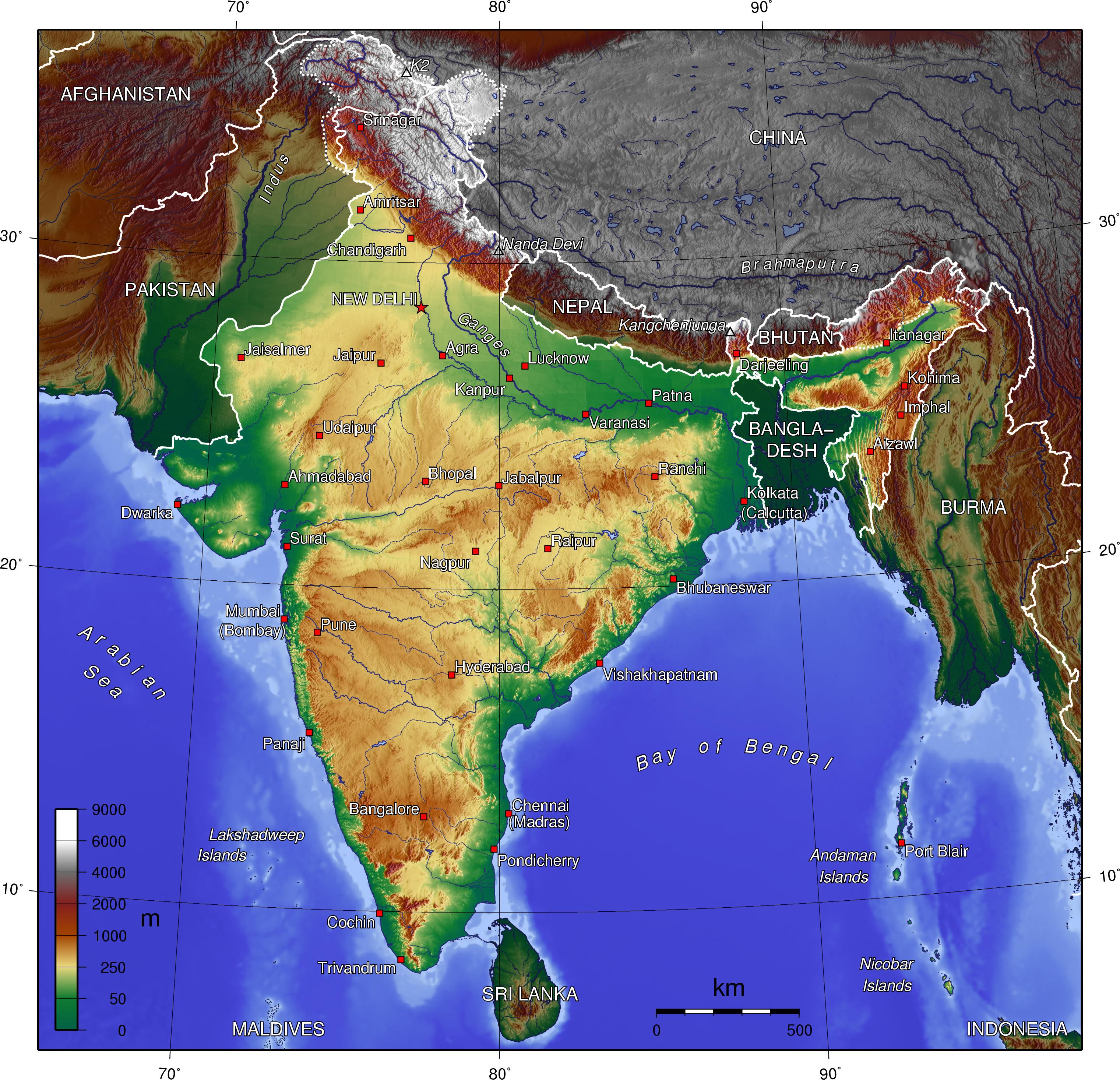
India, a land of diverse landscapes, harbors a fascinating tapestry of elevations, from the towering peaks of the Himalayas to the vast plains of the Ganges. Understanding the country’s topography through an elevation map is crucial for comprehending its geography, climate, and the distribution of its natural resources. This article delves into the intricacies of India’s elevation map, exploring its features, significance, and implications.
The Diverse Topography of India
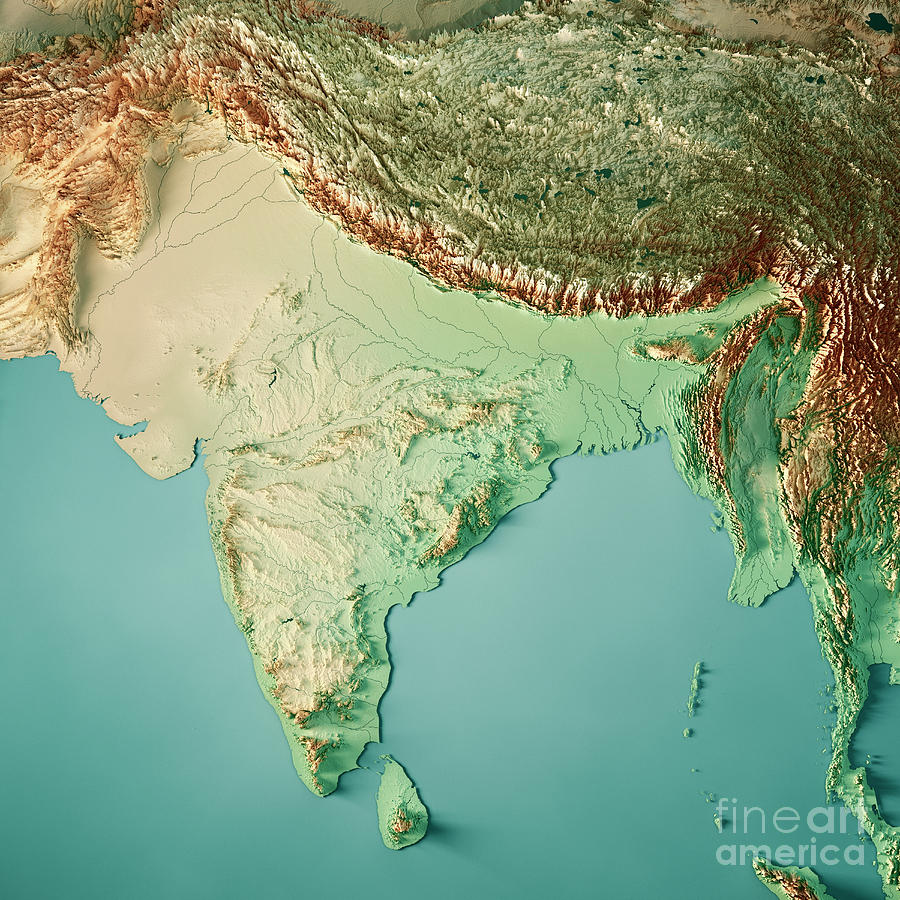
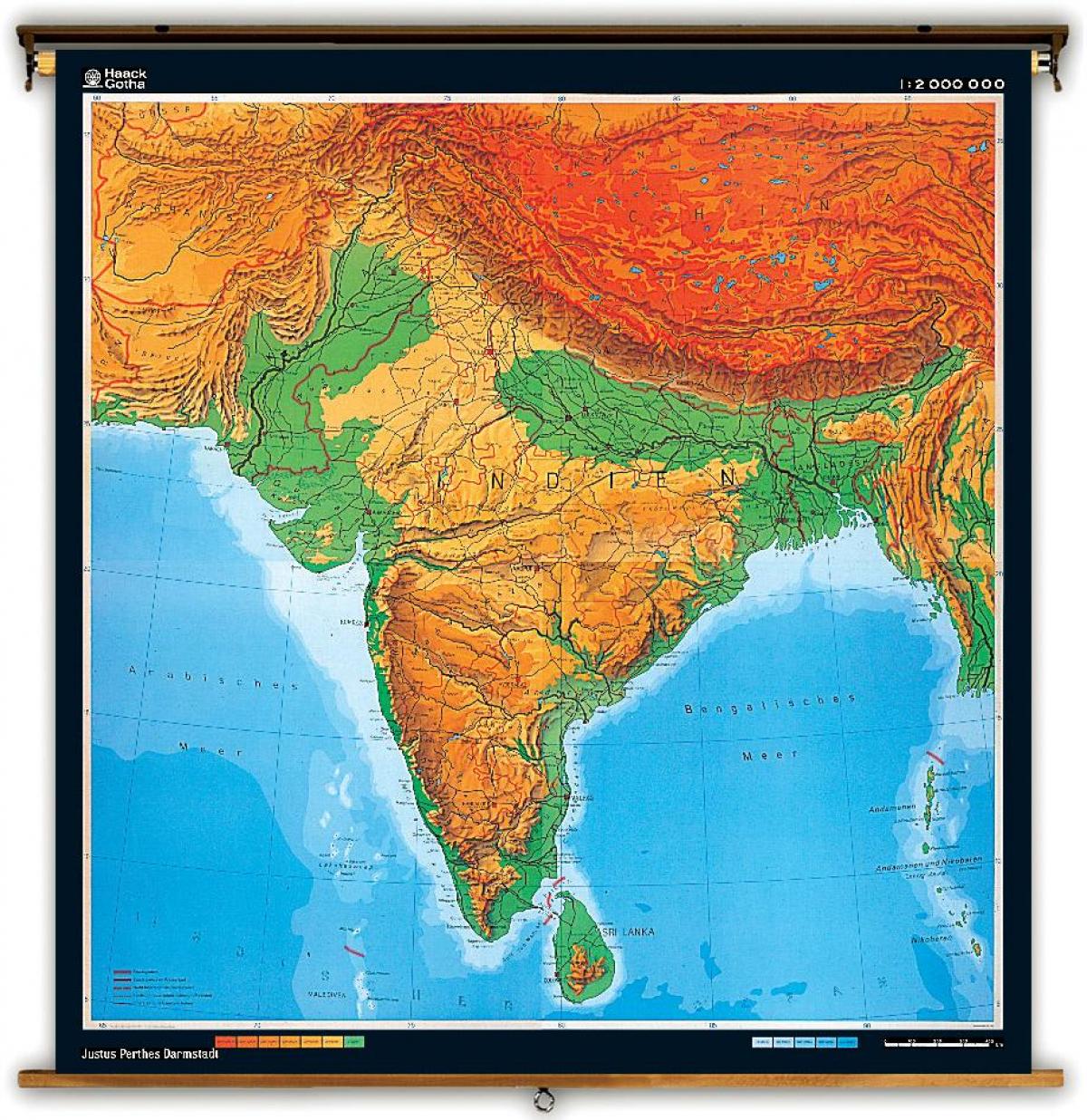
The elevation map of India showcases a remarkable range of landforms, shaped by the forces of tectonic activity, erosion, and deposition over millennia.
-
The Himalayan Range: Dominating the northern frontier, the Himalayas are a formidable mountain range that includes the world’s highest peaks, including Mount Everest. This region exhibits the highest elevations in India, with altitudes exceeding 8,000 meters (26,247 feet).
-
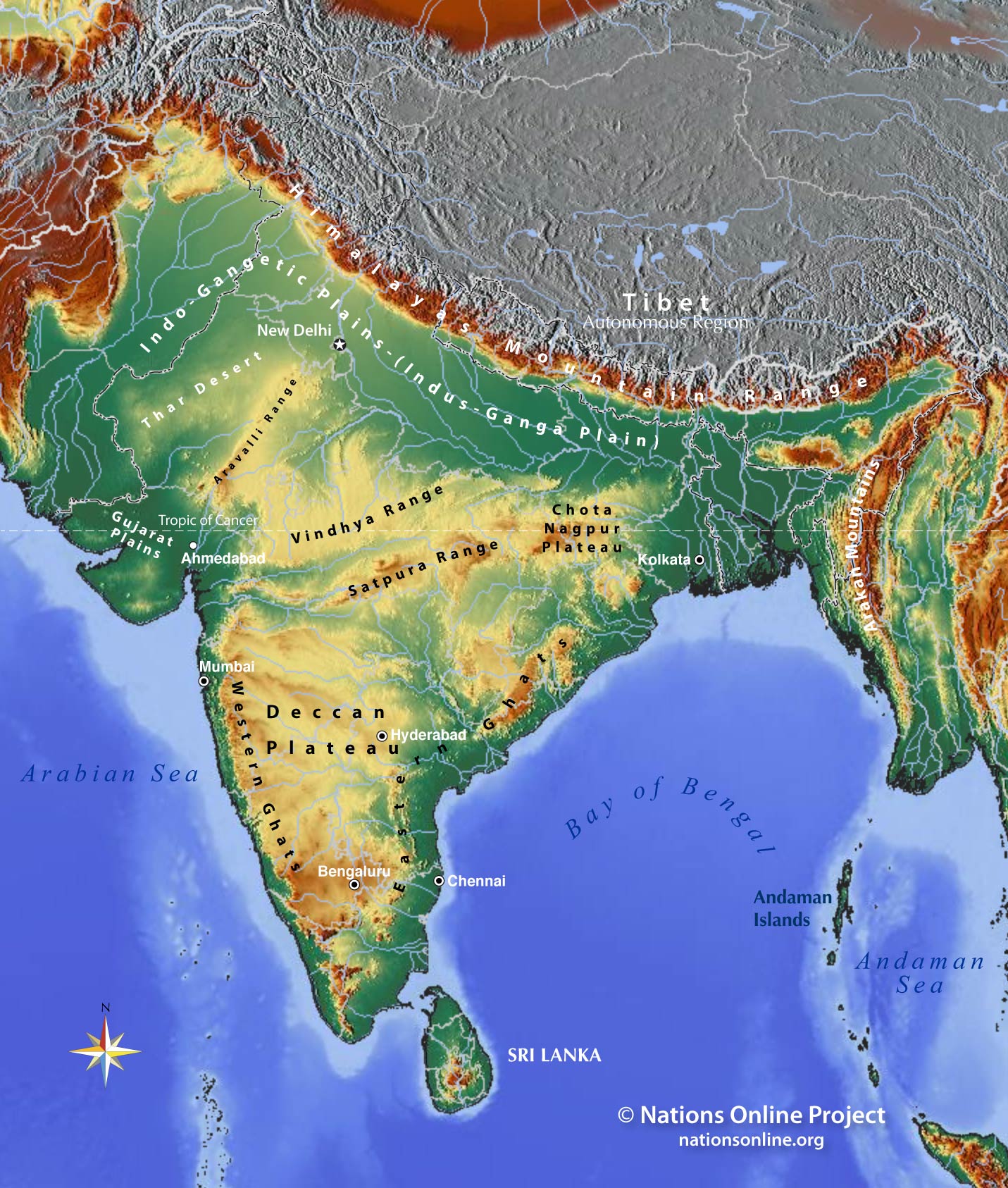
The Northern Plains: Stretching south of the Himalayas, the vast Indo-Gangetic Plain is a fertile and densely populated region. This plain is characterized by low elevations, typically ranging from 100 to 300 meters (328 to 984 feet) above sea level.
-
The Deccan Plateau: Occupying the central and southern parts of India, the Deccan Plateau is a vast, elevated plateau with an average elevation of around 600 meters (1,969 feet). It is characterized by rolling hills, rocky outcrops, and river valleys.
-
The Coastal Plains: Along the eastern and western coasts of India, narrow coastal plains extend outwards, characterized by relatively low elevations. These plains are home to major cities, ports, and agricultural land.
-
The Islands: India also includes several islands in the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea, each with its unique elevation profile. The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are characterized by volcanic peaks, while the Lakshadweep Islands are low-lying coral atolls.
The Importance of Understanding India’s Elevation Map
The elevation map of India plays a crucial role in various aspects of life and development:
-
Climate and Weather Patterns: Elevation significantly influences temperature, precipitation, and wind patterns. The Himalayas act as a barrier, blocking cold air from Central Asia and creating distinct microclimates in the northern plains.
-
Water Resources: Elevation dictates the flow of rivers and the distribution of groundwater resources. The Himalayan glaciers feed major rivers like the Ganga and Brahmaputra, providing water for irrigation and drinking.
-
Agriculture and Forestry: Different elevations support diverse agricultural practices and forest ecosystems. The northern plains are ideal for cultivating wheat and rice, while the Deccan Plateau is known for its dryland agriculture and deciduous forests.
-
Infrastructure Development: Understanding the elevation map is essential for planning infrastructure projects, such as roads, railways, and dams. It helps engineers assess the feasibility of construction and mitigate potential risks.
-
Biodiversity Conservation: Different elevations harbor unique biodiversity, ranging from alpine meadows in the Himalayas to tropical rainforests in the Western Ghats. The elevation map helps identify and protect these diverse ecosystems.
-
Tourism and Recreation: India’s varied elevations attract tourists from around the world. The Himalayas offer breathtaking views and challenging trekking trails, while the coastal plains provide opportunities for beach vacations and water sports.
Exploring the Elevation Map: A Closer Look
To gain a deeper understanding of India’s elevation map, it’s helpful to analyze specific features and their implications:
-
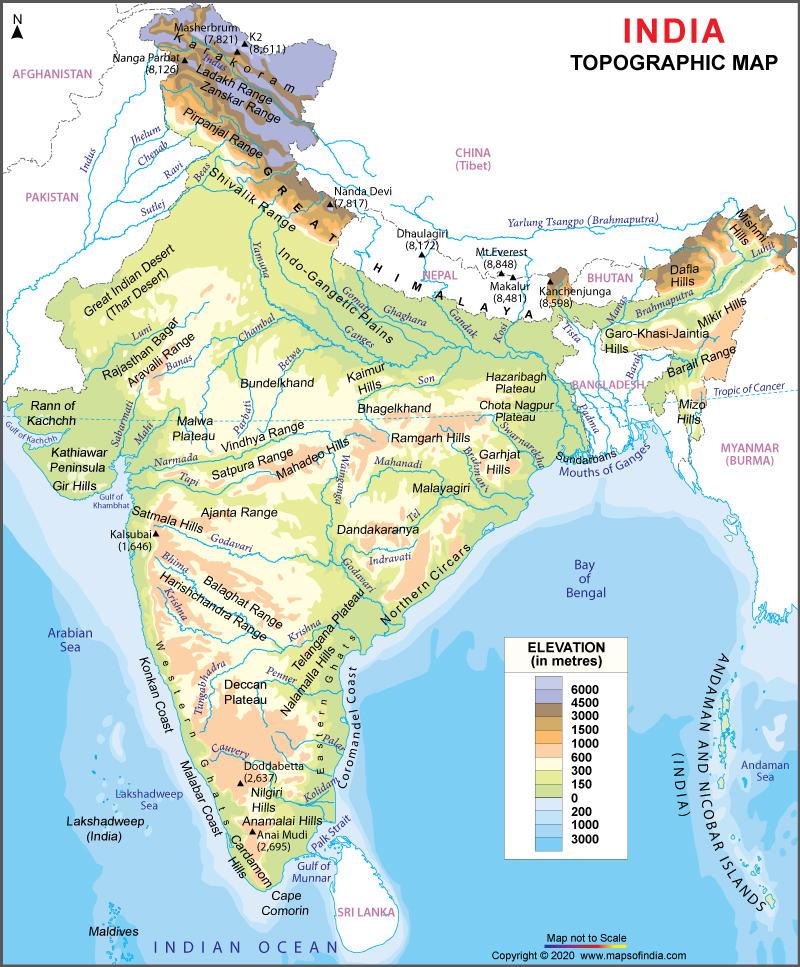
The Great Dividing Range: The Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats form a significant dividing range that separates the Deccan Plateau from the coastal plains. These ranges play a crucial role in influencing rainfall patterns and creating unique ecosystems.
-
The Indus River Basin: The Indus River, originating in the Himalayas, flows through the northern plains, creating a fertile valley that has supported civilizations for millennia. The elevation map reveals the gradual descent of the river from the mountains to the plains.
-
The Ganges River Basin: The Ganga River, also originating in the Himalayas, flows through the northern plains, supporting a vast agricultural belt and densely populated cities. The elevation map highlights the meandering course of the river and its tributaries.
-
The Thar Desert: Located in western India, the Thar Desert is characterized by low elevations and arid conditions. The elevation map reveals the gradual transition from the plains to the desert, influenced by the monsoon winds.
FAQs on India’s Elevation Map
Q: What is the highest point in India?
A: The highest point in India is Mount Kangchenjunga, located in the state of Sikkim, with an elevation of 8,586 meters (28,169 feet).
Q: What is the lowest point in India?
A: The lowest point in India is the Kuttanad region in Kerala, which lies below sea level.
Q: How does elevation affect rainfall in India?
A: Higher elevations receive more rainfall due to the orographic effect, where moist air is forced to rise and condense, leading to precipitation. This is evident in the Himalayas and the Western Ghats.
Q: How does elevation affect temperature in India?
A: Temperature decreases with increasing altitude. The Himalayas experience cold temperatures due to their high elevation, while the coastal plains are generally warmer.
Q: How is the elevation map used in planning infrastructure projects?
A: The elevation map helps engineers determine the feasibility of constructing roads, railways, and dams. It reveals potential challenges such as steep slopes, river crossings, and seismic zones.
Tips for Understanding India’s Elevation Map
-
Use online tools: Interactive maps and elevation data are available online, allowing users to explore the country’s topography in detail.
-
Consult atlases and textbooks: Geography textbooks and atlases often include detailed elevation maps of India, providing valuable insights into the country’s landforms.
-
Explore the terrain: Visiting different parts of India and experiencing the varied elevations firsthand provides a deeper understanding of the country’s topography.
Conclusion
The elevation map of India is a powerful tool for understanding the country’s diverse landscape, its influence on climate, resources, and human activities. By analyzing the map, we gain insights into the unique characteristics of each region, enabling informed decisions in areas such as infrastructure development, resource management, and environmental conservation. The elevation map serves as a vital guide to appreciating the intricate tapestry of India’s topography and its profound impact on the lives of its people.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Topography of India: A Comprehensive Look at the Elevation Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!