Visualizing Data: Creating Maps with Zip Codes
Related Articles: Visualizing Data: Creating Maps with Zip Codes
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Visualizing Data: Creating Maps with Zip Codes. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Visualizing Data: Creating Maps with Zip Codes
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Visualizing Data: Creating Maps with Zip Codes
- 3.1 Understanding the Power of Zip Code Mapping
- 3.2 Tools and Techniques for Creating Zip Code Maps
- 3.3 Essential Considerations for Zip Code Mapping
- 3.4 FAQs about Creating Maps with Zip Codes
- 3.5 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Visualizing Data: Creating Maps with Zip Codes

In today’s data-driven world, the ability to visualize information effectively is paramount. Maps, particularly those incorporating zip code data, provide a powerful tool for understanding spatial relationships and trends. Whether you’re a business owner seeking to target specific demographics, a researcher analyzing geographic patterns, or a community leader planning infrastructure projects, creating maps with zip codes can unlock valuable insights.
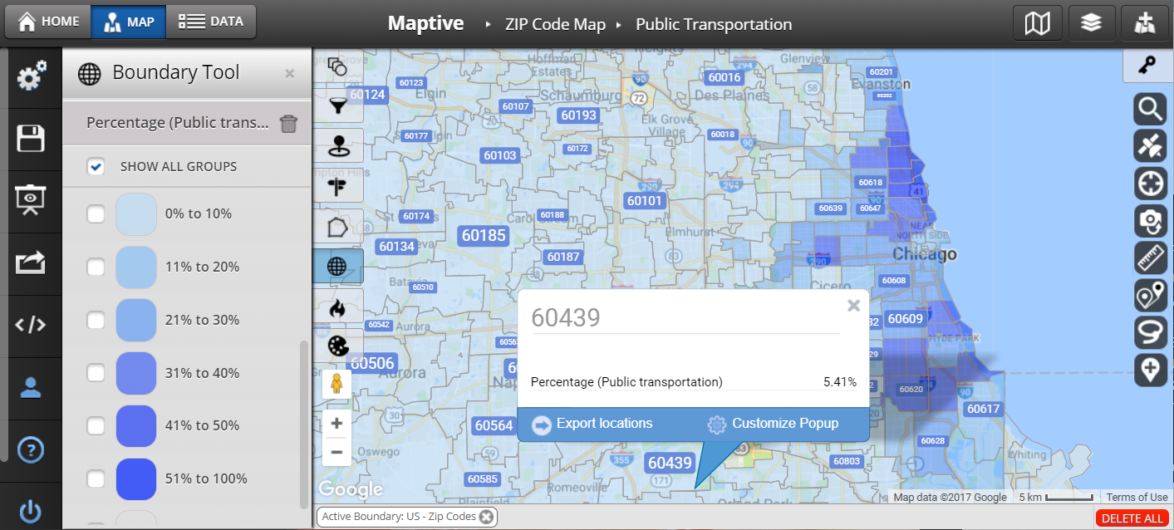
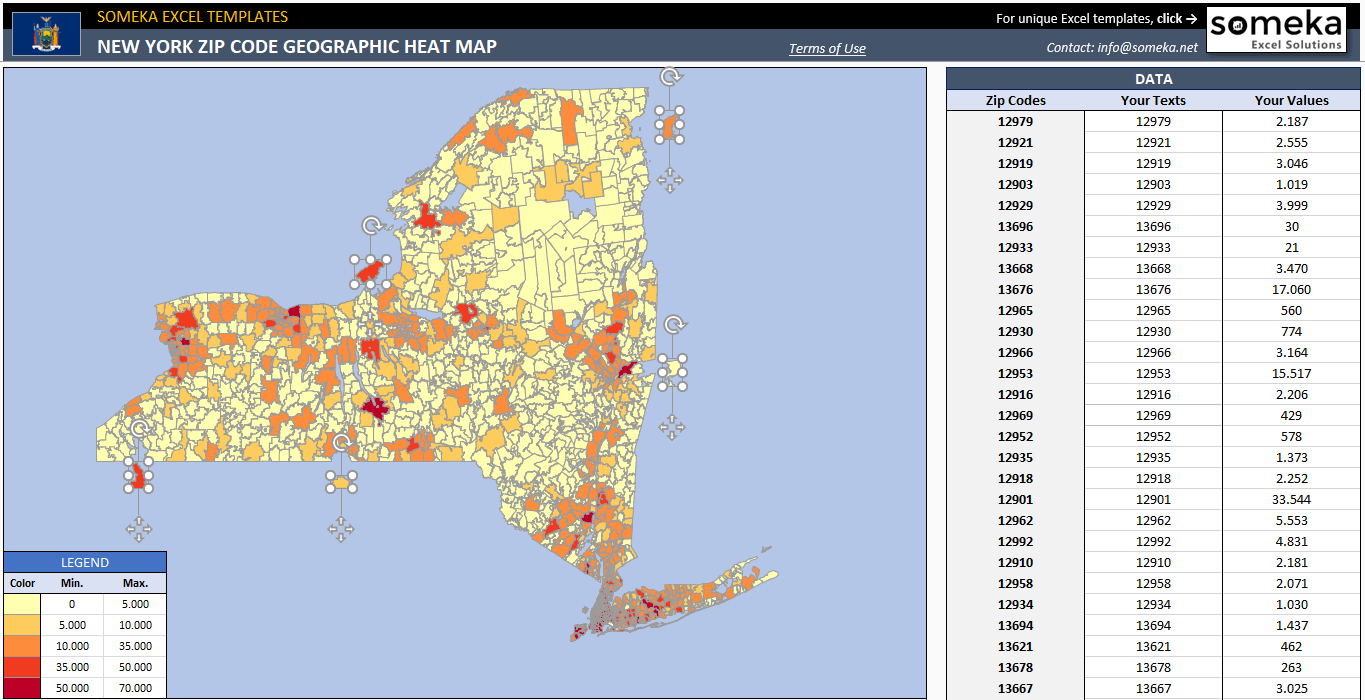
Understanding the Power of Zip Code Mapping
Zip codes, those five-digit numerical identifiers assigned to geographic areas, serve as valuable proxies for location-based data. They allow for the aggregation and analysis of information at a granular level, providing a detailed picture of population distribution, economic activity, and other factors.
Benefits of Creating Maps with Zip Codes:
- Targeted Marketing and Sales: Businesses can leverage zip code data to pinpoint specific customer segments, tailor marketing campaigns, and optimize delivery routes.
- Real Estate Analysis: Real estate professionals can analyze property values, market trends, and identify areas with high demand using zip code-based maps.
- Public Health and Epidemiology: Researchers can use zip codes to study disease prevalence, identify health disparities, and track the spread of infectious diseases.
- Urban Planning and Development: City planners can utilize zip code maps to assess population density, infrastructure needs, and transportation patterns.
- Community Engagement and Outreach: Nonprofit organizations and community groups can use zip code data to target outreach efforts and tailor programs to specific neighborhoods.
- Emergency Response and Disaster Management: First responders can use zip code maps to optimize resource allocation and ensure swift response during emergencies.
Tools and Techniques for Creating Zip Code Maps
Creating maps with zip codes involves a combination of data, software, and visualization techniques. Several popular tools and methods can be employed:
1. Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
GIS software is the gold standard for advanced spatial analysis. Programs like ArcGIS, QGIS, and MapInfo allow users to import zip code data, create maps, and perform complex analyses.
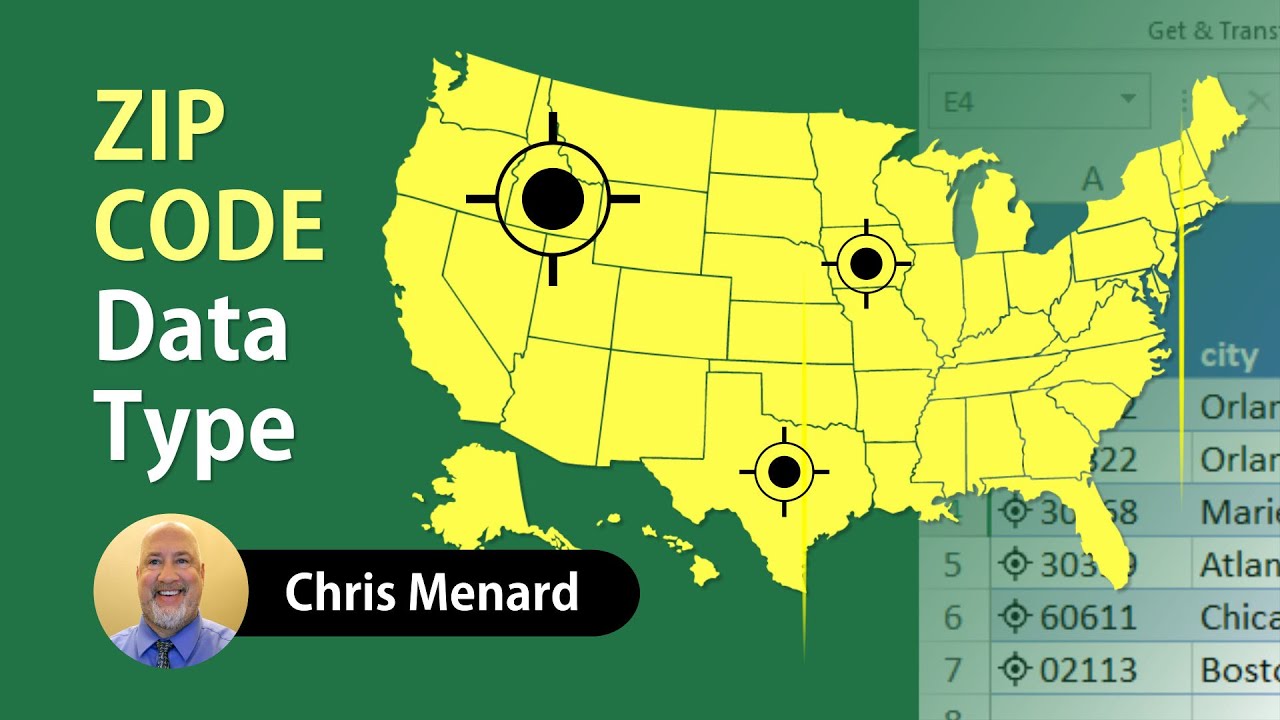
2. Spreadsheet Software with Mapping Features
Popular spreadsheet programs like Microsoft Excel and Google Sheets offer basic mapping capabilities. Users can import zip code data and create simple visualizations using built-in mapping features.
3. Online Mapping Platforms
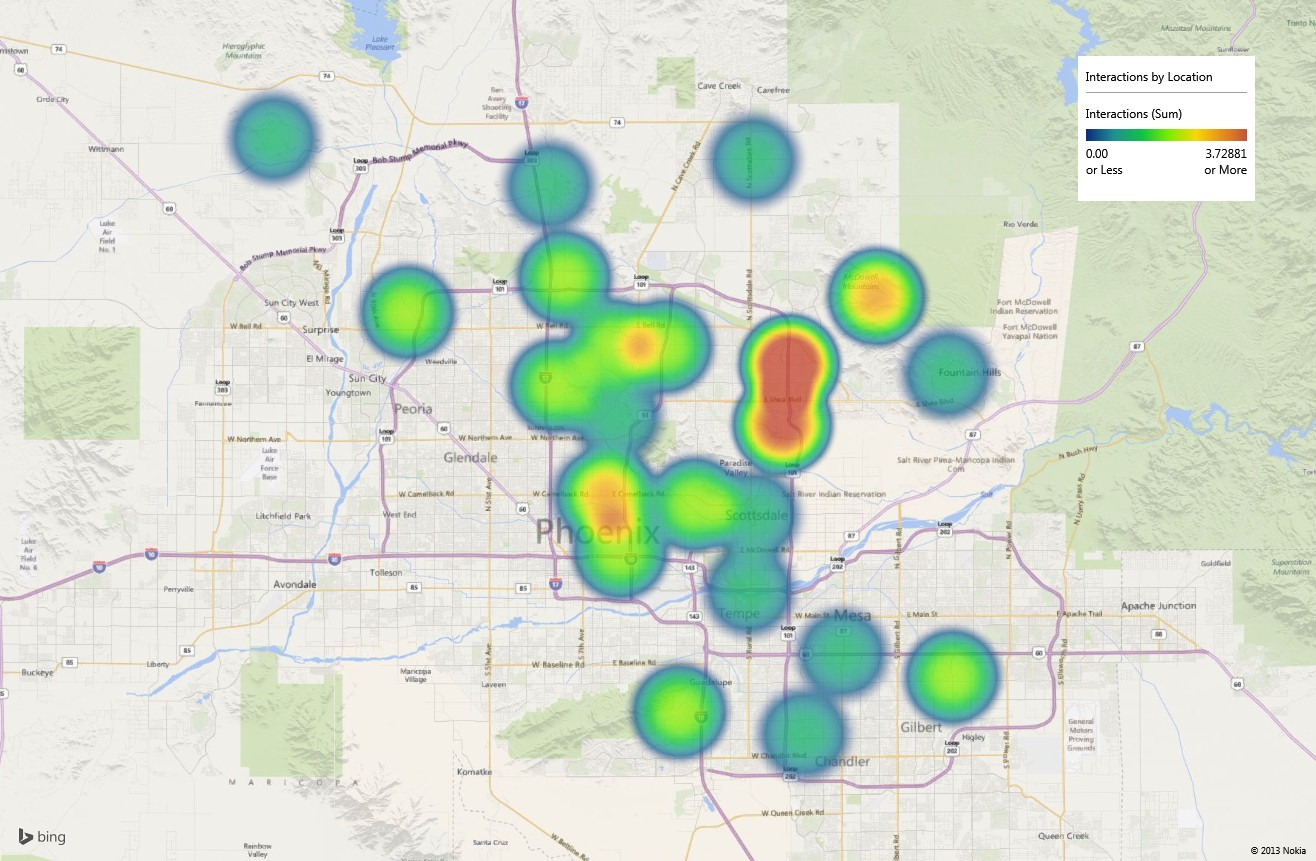
Numerous online platforms provide easy-to-use tools for creating maps with zip codes. Google Maps, Mapbox, and Leaflet are popular choices, offering a range of customization options and data integration capabilities.
4. Data Visualization Libraries
For developers and data scientists, Python libraries like Plotly, Matplotlib, and Folium offer extensive tools for creating interactive and customizable maps with zip code data.
Essential Considerations for Zip Code Mapping
Creating effective maps with zip codes requires careful planning and consideration of the following factors:
- Data Quality: Ensuring accurate and up-to-date zip code data is crucial for reliable analysis. Data sources should be validated and regularly updated.
- Map Projection: Choosing the appropriate map projection is important for accurate representation of geographic areas, especially when working with large datasets.
- Map Symbology: Using clear and consistent symbols, colors, and labels enhances map readability and helps convey information effectively.
- Data Aggregation and Visualization: Selecting the appropriate level of detail and aggregation for zip code data is essential for meaningful insights.
- Accessibility and Sharing: Maps should be accessible to diverse audiences, including those with visual impairments. Sharing options should be considered for wider dissemination.
FAQs about Creating Maps with Zip Codes
1. What are the best sources for zip code data?
Several reliable sources provide zip code data, including:
- United States Postal Service (USPS): The USPS maintains the official database of zip codes and boundaries.
- U.S. Census Bureau: The Census Bureau provides detailed demographic and socioeconomic data linked to zip codes.
- Esri: Esri, a leading GIS software provider, offers a variety of spatial data products, including zip code boundaries.
- OpenStreetMap: This open-source project provides a collaborative platform for collecting and sharing geographic data, including zip codes.
2. How do I ensure the accuracy of my zip code data?
- Verify data sources: Use reputable sources like those mentioned above.
- Check for updates: Ensure data is current, as zip code boundaries can change over time.
- Compare with other sources: Cross-reference data with multiple sources to confirm accuracy.
- Use data validation tools: GIS software and online platforms offer tools for data validation and cleaning.
3. What are some tips for creating effective zip code maps?
- Keep it simple: Use clear and concise map elements, avoiding clutter.
- Use appropriate symbology: Choose symbols and colors that are visually appealing and convey meaning effectively.
- Include a legend: Provide a clear explanation of map symbols and data categories.
- Add context: Include relevant background information, such as street names, landmarks, or geographic boundaries.
- Consider interactivity: Explore interactive features like tooltips, zoom capabilities, and data filtering.
4. What are some common applications of zip code maps?
- Business analysis: Identify customer demographics, market potential, and delivery areas.
- Public health research: Analyze disease prevalence, health disparities, and risk factors.
- Urban planning: Assess population density, infrastructure needs, and transportation patterns.
- Emergency response: Optimize resource allocation and communication during emergencies.
- Community outreach: Target specific neighborhoods with programs and services.
5. What are some challenges associated with using zip code data?
- Data granularity: Zip codes can be too broad for some analyses, particularly in densely populated areas.
- Data accuracy: Zip code boundaries can be outdated or inaccurate, leading to errors in analysis.
- Privacy concerns: Zip codes can be used to identify individuals, raising privacy concerns.
- Data accessibility: Obtaining comprehensive and reliable zip code data can be challenging.
Conclusion
Creating maps with zip codes offers a powerful way to visualize and analyze spatial data, providing valuable insights across various fields. By understanding the benefits, tools, and considerations involved, individuals and organizations can leverage this technique to gain a deeper understanding of geographic patterns, optimize resource allocation, and make informed decisions. As technology continues to evolve, the use of zip code mapping is expected to become even more prevalent, driving innovation and progress in data analysis and decision-making.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Visualizing Data: Creating Maps with Zip Codes. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!









.svg/revision/latest/scale-to-width-down/2000?cb=20150101005359)


.svg/revision/latest/scale-to-width-down/640?cb=20150101203436)